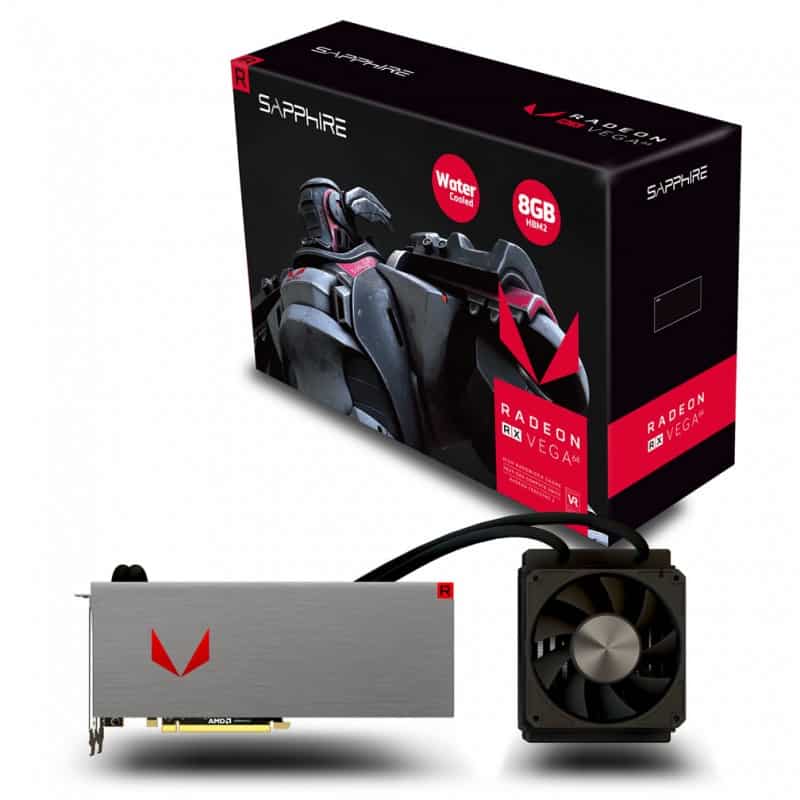
AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 Liquid Cooled Mining: Review| Hashrate| Benchmark| – AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 Liquid Cooled video card review: an unexpected alternative. The release of the GeForce RTX 2070 and RTX 2060 has hurt the Vega family of video cards, and soon the Radeon VII will be on sale on the next generation AMD chip.
It’s time to take a closer look at the liquid-cooled Radeon RX Vega 64 – and this is not a joke at all NVIDIA is releasing accelerators of the GeForce 20 family one after another, real-time ray tracing has taken possession of the minds of gamers, and many have a reasonable question: what does AMD have? Luckily for fans of the Radeon brand and critics of NVIDIA, the red team is poised to make its return to the big leagues. Soon we will get our hands on the latest graphics card from AMD, which is based on the first discrete GPU, made at the rate of 7 nm. The seventh of February is the day when we will be able to publish the results of testing Radeon VII.

We, of course, mean the GeForce RTX 2060. The first video cards based on Turing chips did not threaten the position of the Radeon RX Vega, because the GeForce RTX 2080 and RTX 2080 Ti belong to a completely different class – both in terms of speed and even more so in terms of price. The GeForce RTX 2070 in games without ray tracing turned out to be just an accelerated analogue of the GeForce GTX 1080, and this is already a big problem for Vega 64. But the GeForce RTX 2060 became the really terrible enemy of both Vega models: at prices starting at $ 349, the younger Turing easily bypassed Radeon in gaming tests The RX Vega 56, which cost at least $ 499 in early January, is too close to the Vega 64 in performance to continue to be bought for $ 599.
The only thing AMD could do in such a situation was to cut prices. As a result, various modifications of the Radeon RX Vega 64 now occupy the same price range as the GeForce RTX 2070, and the Vega 56 has approached the GeForce RTX 2060. And here’s how it relates to the topic of the review: the reduction in the price of the entire Vega family did not bypass the Radeon RX Vega 64 Liquid Cooled. Moreover, among all the varieties of Vega 64, the option with built-in LSS has unexpectedly become one of the most attractive. Let’s see why he is so good.
Specifications, prices
Since discrete GPU manufacturers have mastered 14/16 nm technology, AMD has not developed many new chips for video cards and is trying to use each in several models of gaming accelerators. Apart from the Radeon RX Vega 64 Limited Edition, which differs from the black reference Vega 64 only in a shiny metal case, the company has released five devices based on the Vega 10 GPU: the familiar Radeon RX Vega 56, Vega 64, two Vega Frontier Edition modifications ( boards equipped with 16 GB of RAM) – with an air cooler or CBO – and, finally, Vega 64 Liquid Cooled.
In its large family, the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC has the highest clock speeds: the Boost Clock of the GPU is 1677 MHz, while the reference air-cooled Vega 64 samples are content with a frequency of 1546 MHz. It should be noted once again that the parameters specified in the specifications of any Radeon RX Vega models have little resemblance to the real GPU frequencies. Although AMD and NVIDIA use the same terminology, Boost Clock in GeForce video cards means the average frequency in typical tasks, while in Vega it is the maximum frequency (also in typical tasks). And yet, no other Vega 64 modification, including the products of the famous factory overclocking champions – PowerColor and SAPPHIRE, makes an application for such frequencies as the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC.
But we certainly believe in the tabular value of the board’s power, which is 345 W for the flagship Vega. It remains only to find out what magic allows the small heatsink of the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC to dissipate a colossal flow of heat.
| Manufacturer | AMD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Radeon RX Vega 56 | Radeon RX Vega 64 | Radeon RX Vega 64 Liquid Cooled | Radeon RX Vega Frontier Edition | Radeon RX Vega Frontier Edition Liquid Cooled |
| GPU | |||||
| Name | Vega 10 XL | Vega 10 XT | Vega 10 XTX | Vega 10 XT | Vega 10 XTX |
| Microarchitecture | GCN 1.4 | GCN 1.4 | GCN 1.4 | GCN 1.4 | GCN 1.4 |
| Process technology, nm | 14 нм FinFET | 14 нм FinFET | 14 нм FinFET | 14 нм FinFET | 14 нм FinFET |
| Number of transistors, million | 12 500 | 12 500 | 12 500 | 12 500 | 12 500 |
| Clock frequency, MHz: Base Clock / Boost Clock | 1156/1471 | 1247/1546 | 1406/1677 | 1382/1600 | 1382/1600 |
| Number of shader ALUs | 3584 | 4096 | 4096 | 4096 | 4096 |
| Number of texture mapping units | 224 | 256 | 256 | 256 | 256 |
| ROP number | 64 | 64 | 64 | 64 | 64 |
| RAM | |||||
| Bus width, bit | 2048 | 2048 | 2048 | 2048 | 2048 |
| Chip type | HBM2 | HBM2 | HBM2 | HBM2 | HBM2 |
| Clock frequency, MHz (bandwidth per contact, Mbps) | 800 (1600) | 945 (1890) | 945 (1890) | 945 (1890) | 945 (1890) |
| Volume, MB | 8096 | 8096 | 8096 | 16192 | 16192 |
| I / O bus | PCI Express 3.0 x16 | PCI Express 3.0 x16 | PCI Express 3.0 x16 | PCI Express 3.0 x16 | PCI Express 3.0 x16 |
| Performance | |||||
| Peak performance FP32, GFLOPS (based on maximum specified frequency) | 10544 | 12665 | 13738 | 13107 | 13107 |
| FP32 / FP64 performance | 1/16 | 1/16 | 1/16 | 1/16 | 1/16 |
| RAM bandwidth, GB / s | 410 | 484 | 484 | 484 | 484 |
| Image output | |||||
| Image output interfaces | HDMI 2.0, DisplayPort 1.4 | HDMI 2.0, DisplayPort 1.4 | HDMI 2.0, DisplayPort 1.4 | HDMI 2.0, DisplayPort 1.4 | HDMI 2.0, DisplayPort 1.4 |
| TDP, Tue. | 210 | 295 | 345 | <300 | 350 |
| Retail price (USA, excluding tax), $ | From 339 (newegg.com) | From 399 (newegg.com) | From 599 (amazon.com) | 999 (recommended at the time of release) | 1499 (recommended at the time of release) |
| Retail price (Russia), rub. | From 26 563 (market.yandex.ru) | From 35 940 (market.yandex.ru) | From 39 229 (market.yandex.ru) | ND | ND |
Initially, AMD viewed the water-cooled Radeon RX Vega 64 as an offer for enthusiasts willing to sacrifice large sums of money for higher clock speeds: the base Vega 64 went on sale at a suggested price of $ 499, and the Vega 64 LC was priced at a good $ 200 more. But today’s high-performance graphics card market looks very different.
The lower limit of the price corridor of the Radeon RX Vega 64 now lies in the region of $ 399, while the GeForce RTX 2070 costs at least $ 499. The last wave of discounts has not yet reached the Russian market, but in rubles the Vega 64 at least has ceased to be more expensive than the RTX 2070. Depending on the specific modification, both devices are sold for an amount of 35-49 thousand rubles. But most importantly, Vega 64 LC (39-48 thousand) is now in this range – the only video card with a pre-installed liquid cooling system that can be bought for such money.
Construction
Until now, a large part of all Radeon RX Vega 64 graphics cards that are on sale represent the reference model that is produced by SAPPHIRE. AMD was ready for the fact that partners would not soon start producing devices of the original design, and decided not to skimp on the design of reference samples. As a result, the Radeon RX Vega 56 and Vega 64 received a printed circuit board with an appropriately powerful voltage regulator and a fairly efficient cooler consisting of a radiator with a vapor chamber and a radial-type fan.
The Radeon Vega 64 LC has a lot in common with the usual reference Vega 64 card, but in terms of appearance and workmanship, it is noticeable that this is a product of a higher level. The printed circuit board and cooling system components are enclosed in an all-metal box, with the entire front of the case made of a single thick sheet of aluminum. AMD adopted its love of metal from NVIDIA, but unlike the Founders Edition graphics cards, the design of the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC is dominated by right angles and the surface has a rough texture. The few elements of the case, made of plastic, are the Radeon inscription and a transparent red corner: when the board receives power, they glow brightly.
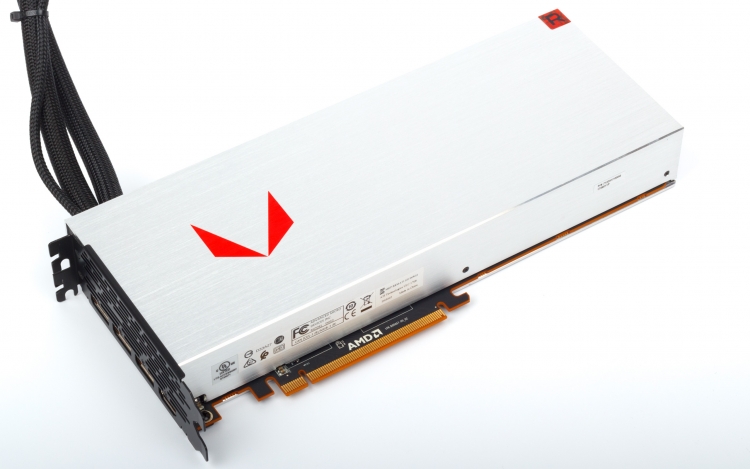
Changing the air cooler to LSS had almost no effect on the dimensions of the device, although the case was made a couple of millimeters longer and wider than the standard reference model in order to hide the edge of the PCB at the junction of the metal plates.
But of course, the most interesting thing about the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC is the design of the liquid cooling system. It is not the first time that water has found application in “red” video cards: after the Radeon R9 295X2, the Radeon R9 Fury X, and then the Radeon Pro Duo based on two Fiji chips, AMD gained enough experience to design a truly high-quality and durable solution. Indeed, the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC is very well thought out.

LSS components are custom-made by CoolerMaster – they do not sell anything like that in retail. The system works as follows. The liquid from the external radiator first enters the pump with an integrated water block – the copper base of this part is pressed against the GPU chips and HBM2 memory assemblies. But the metal frame, under which almost the entire area of the PCB is hidden, except for the GPU substrate and power connectors, is also part of the cooling circuit: from the outside, it has an u-shaped cover, under which liquid heated by the GPU flows from the pump.
This is how the water cooling circuit of such a powerful video card as the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC should look like, because the VRM components here also need enhanced heat dissipation. But field-effect transistors, drivers, capacitors and chokes are capable of operating at a higher temperature than GPUs and HBM2 chips, so the latter have received priority.
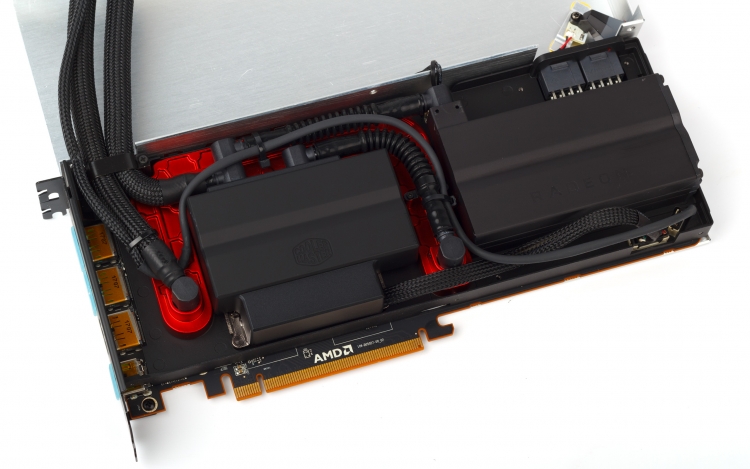
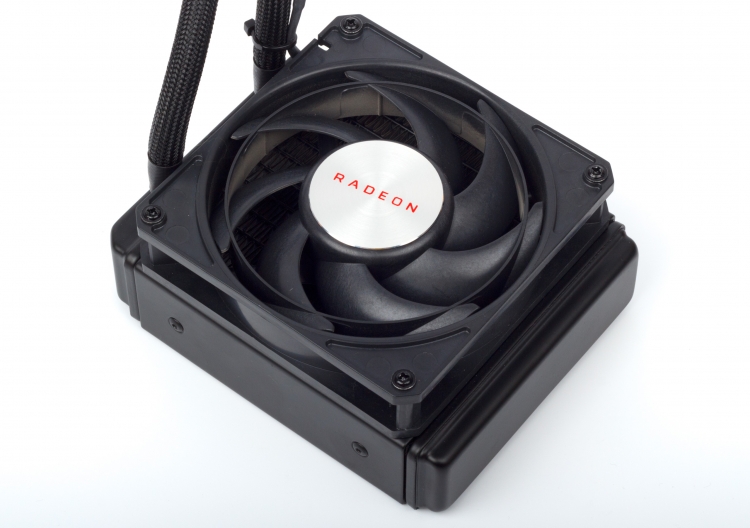
A typical Closed Loop Liquid Cooler (CLLC) found in central processing units is designed to last about five years. Due to the fact that the coolant gradually escapes from the circuit through the pores of the connecting hoses and is replaced by air, the internal lubricant dries up in the pump – and the mechanics wear out quickly. To prevent this problem, AMD and CoolerMaster use teflon-coated hoses (be careful with bends!), And most importantly, they integrated a reservoir with a liquid reserve into the LSS – this is a plastic box that occupies the right side of the space under the casing. The reservoir is connected with a single tube to the pump inlet, and on the other side it has an air valve – thus making up for the slow loss of coolant from the main circuit.
The cooling ring is closed by a compact radiator with a single 120 mm fan. Although the Vega 64 LC has a very serious heat dissipation, AMD did not make the radiator thicker than in the Radeon R9 Fury X (38 mm). In addition, he got rid of the expansion cavity, which sometimes complicates installation in the seats for case fans, because there is already a separate reservoir under the casing of the video card. The fan, however, is the same Nidec Servo product that is well known under the Scythe Gentle Typhoon brand. The variant for the Fury X and Vega 64 LC (D1225C12B7ZP) has a ring connecting the blades and can accelerate to 3000 rpm. But at a speed of rotation within 1200 rpm, which the Vega 64 LC suffices even with an intense load, it is practically inaudible.

Printed circuit board
All reference versions of Vega accelerators, be it Vega 56, Vega 64 or Vega 64 LC, are based on the same printed circuit board. With the Vega 10 GPU and two HBM2 memory stacks bonded together by a silicon substrate, there is a lot of free space on the face of the PCB. The manufacturer could shorten the PCB, as is done in the Radeon R9 Fury X, so that the Vega 64 LC becomes the same compact device, but then it would have to abandon the coolant reservoir, and in the standard Vega versions, the dimensions are still determined by the air cooling system.
The lion’s share of the PCB area is occupied by VRM. The voltage regulator consists of thirteen phases – a dozen for the GPU and one for the HBM2 chips. To simplify the control logic in the GPU power circuit and get by with an eight-phase PWM controller (International Rectifier IR35217), AMD uses dual FET drivers – one chip per pair of MOSFETs.
In most Vega 64s, the gaps between the GPU and HBM2 chips are filled with epoxy.
Additional power is supplied to the board through two eight-pin connectors. Together with the power lines of the PCI Express slot, they provide the board with a nominal power of 375 W. This number usually says nothing about real power consumption, but not in the case of the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC, which we will soon see. The LEDs next to the power connectors form a red indicator bar that indicates GPU utilization. Using a DIP switch, for which a hole is made in the shield on the back of the PCB, you can turn off the LEDs or change their color to blue.
No high-performance graphics card based on AMD chips is complete without a backup UEFI chip, but for Vega this is not just insurance in case of unsuccessful flashing: the second copy of the firmware limits the power, and therefore frequencies, and heating of the GPU.
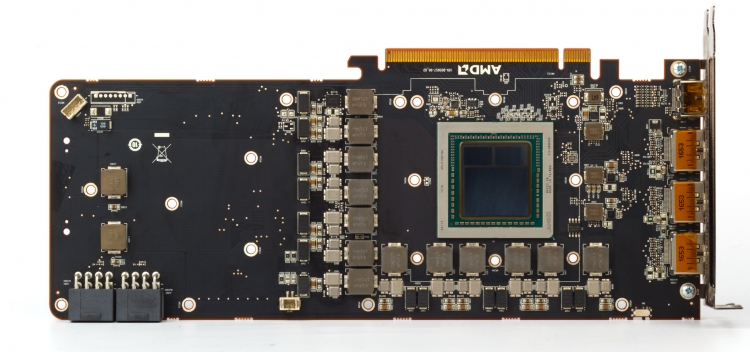
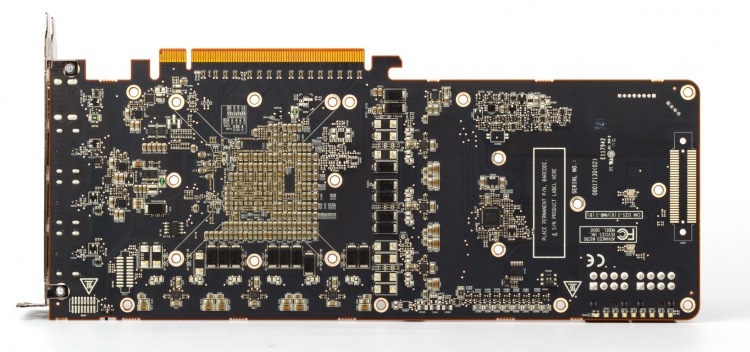
This is a printed circuit board of the standard version of the Radeon RX Vega 64 – we did not disassemble the valuable Vega 64 LC to the ground
Test stand, testing methodology
| Test bench configuration | |
|---|---|
| CPU | Intel Core i7-5960X @ 4 GHz (100 MHz × 40) Constant |
| Motherboard | ASUS RAMPAGE V EXTREME |
| RAM | Corsair Vengeance LPX 2133 MHz 4GB x 4GB |
| PZU | Intel SSD 760p, 1024 GB |
| Power Supply | Corsair AX1200i, 1200 Вт |
| CPU cooling system | Thermalright Archon |
| Frame | CoolerMaster Test Bench V1.0 |
| Monitor | NEC EA244UHD |
| Operating system | Windows 10 Pro x64 |
| AMD GPU software | |
| All graphics cards | AMD Radeon Software Adrenalin 2019 Edition 19.1.1 (Tesselation: Use application settings) |
| NVIDIA GPU software | |
| All graphics cards | NVIDIA GeForce Game Ready Driver 417.71 |
| Synthetic tests of 3D graphics | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Test | API | Permission | Full screen anti-aliasing |
| 3DMark Fire Strike 1.1 | DirectX 11 (feature level 11_0) | 1920 × 1080 | Off |
| 3DMark Fire Strike 1.1 Extreme | 2560 × 1440 | ||
| 3DMark Fire Strike 1.1 Ultra | 3840 × 2160 | ||
| 3DMark Time Spy 1.1 | DirectX 12 (feature level 11_0) | 2560 × 1440 | |
| 3DMark Time Spy Extreme 1.1 | 3840 × 2160 |
| Game tests | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Game (in order of release date) | API | Settings, test method | Full screen anti-aliasing | |
| 1920 × 1080 / 2560 × 1440 | 3840 × 2160 | |||
| GTA V | DirectX 11 | Max. quality. Built-in benchmark | MSAA 4x + FXAA + Reflection MSAA 4x | Off |
| The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt | DirectX 11 | Max. quality. OCAT, location Caer Morhen | TAA + HairWorks AA 4x | |
| Tom Clancy’s The Division | DirectX 12 | Max. quality, HFTS off. Built-in benchmark | SMAA 1x Ultra + TAA: Supersampling | TAA: Stabilization |
| DOOM | volcano | Max. quality. OCAT, Mission Foundry | TSSAA 8TX | Off |
| Deus Ex: Mankind Divided | DirectX 12 | Max. quality. Built-in benchmark | MSAA 4x | |
| Battlefield 1 | DirectX 12 | Max. quality. OCAT, the start of the Over the Top mission | TAA | |
| Ashes of the Singularity: Escalation | volcano | Max. quality. Built-in benchmark | MSAA 4x + TAA 4x | |
| Total War: WARHAMMER II, built-in benchmark | DirectX 12 | Max. quality. Built-in benchmark (Battle Benchmark) | MSAA 4x | |
| Far Cry 5 | DirectX 11 | Max. quality. Built-in benchmark | TAA | |
| F1 2018 | DirectX 11 | Max. quality. Built-in benchmark | TAA | |
| Shadow of the Tomb Raider | DirectX 12 | Max. quality. Built-in benchmark | SMAA 4x |
| General Purpose Computing, Video Encoding / Decoding | ||
|---|---|---|
| Program | Settings | |
| AMD | NVIDIA | |
| CompuBench 2.0 | Ocean Surface Simulation | — |
| N-Body Simulation 1024K | — | |
| LuxMark 3.1 | Hotel Lobby (Complex Benchmark) | — |
| SiSoftware Sandra Titanium (2018) 2018.8.28.26 | GPGPU Scientific Analysis | OpenCL, FP16/FP32 |
We measure the power of video cards separately from the CPU and other PC components. For this, a rigid PCI Express x16 riser is used, in which the +12 V and ground lines coming from the motherboard are broken and brought to a separate six-pin power connector. The Corsair AX1200i power supply using the Corsair LINK 4 utility allows you to register the total current passing through the additional power connectors of the video card and the riser with a period of 1 s, and the power is calculated by multiplying the current value by the voltage value of 12 V at each moment in time.
The test load is FurMark with the most aggressive settings (3840 × 2160, MSAA 8x) and Crysis 3 (maximum graphics quality, 3840 × 2160, MSAA 4x). Power measurements are taken after the video card has warmed up, when the GPU temperature and clock speeds stabilize. Also, during the test using MSI Afterburner software, we register a number of other variables: clock frequency, voltage and temperature of the GPU, rotation speed of the cooling fans.
Test participants
The following video cards took part in performance testing:
Clock frequencies, power consumption, temperature, overclocking
The maximum frequency for which the graphics processor Radeon RX Vega 64 Liquid Cooled is designed is 1750 MHz. In real computing tasks, the GPU video card does not even come close to such values, however, the extended thermal package of Vega 10 under the LSS allows you to keep the frequencies at 1606 MHz under prolonged load. This is, whatever one may say, 124 MHz more than the frequencies of the reference Vega 64 samples equipped with a “turbine” cooler, and partner video cards with open cooling systems in the standard mode are not capable of such auto-overclocking.
At such high frequencies, the Vega 10 GPU is operating well beyond the best power efficiency range, and for each additional megahertz it has to pay a significant increase in power. According to the results of measurements in the FurMark test, the power consumption limit of the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC lies in the region of 382W, which roughly corresponds to the combined rating of two eight-pin power connectors and a PCI Express slot. Even in gaming, the device’s appetite is 95W more than the standard Vega 64.
As experiments with overclocking Vega 56 and Vega 64 “in the air” have shown more than once, only a massive 2.5- or three-slot cooler with high-speed fans copes well with such a monstrous load, but LSS is incomparably more effective. Thanks to the water cooling, the GPU temperature on the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC is 15-17 ° C lower than the standard version of the Vega 64, and the fan does not spin above 1200 rpm.
| Video adapter | Settings | GPU clock frequency, MHz | GPU supply voltage, V | Fan speed, rpm (% of max.) | Fan speed 2, rpm (% of max.) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Max. | Limit | Average | Max. | Limit | Average | Average | ||
| AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 (1630/1890 MHz, 8 GB) | WattMan: Balanced | 1482 | 1482 | 1630 | 1,037 | 1,037 | 1,250 | 2405 (50%) | ND |
| AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 LC (1750/1890 MHz, 8 GB), -200 mV vCore | -200 мВ vCore | 1589 | 1589 | 1750 | 1,056 | 1,056 | 1,250 | 938 (29%) | ND |
| AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 LC (1750/1890 MHz, 8 GB) | WattMan: Balanced | 1606 | 1615 | 1750 | 1,105 | 1,218 | 1,250 | 1119 (34%) | ND |
| AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 LC (1750/2250 MHz, 8 GB), + 50% TDP | + 50% TDP, 100% RPM | 1699 | 1699 | 1750 | 1,193 | 1,193 | 1,250 | 2909 (89%) | ND |
| NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 FE (1607/10008 MHz, 8 GB) | 1697 | 1785 | 1911 | 0,920 | 0,993 | 1,243 | 2194 (55%) | ND | |
| NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 Ti FE (1480/11010 MHz, 11 GB) | 1329 | 1329 | 1911 | 1,000 | 1,000 | 1,243 | 2021 (42%) | ND | |
| NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2060 FE (1365/14000 MHz, 6 GB) | 1845 | 1845 | 1995 | 1,006 | 1,006 | 1,243 | 1849 (50%) | 1847 (50%) | |
| ASUS ROG Strix GeForce RTX 2070 OC (1410/14000 MHz, 8 GB) | 1950 | 1950 | 2040 | 1,037 | 1,037 | 1,243 | 1697 (51%) | 1695 (51%) | |
| NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 FE (1515/14000 MHz, 8 GB) | 1879 | 1890 | 1995 | 1,010 | 1,018 | 1,243 | 1765 (48%) | 1765 (48%) |
Note: All parameters are measured in Crysis 3 (maximum graphics quality, 3840 × 2160, MSAA 4x) after the GPU has warmed up.
In the normal mode, the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC supplies a fairly high voltage to the graphics core – up to 1.218 V with a maximum allowable 1.25 V. Based on this data, you can go in two ways: either overclock the video card by increasing the available GPU power, or moderate it power consumption due to undervolting, keeping operating frequencies, if possible. First, let’s explore the second option.
It turned out that our Vega 64 LC runs stably even when the GPU voltage corresponding to the top three clock positions is reduced by 0.2 V (although in reality it only drops by 0.049 V). In modern video cards, the clock frequencies and the voltage of the GPU are closely related, they can be adjusted separately only within narrow limits, so that as a result of undervolting, the GPU frequency under load dropped by 17 MHz, but the power was also reduced by 39 W. This practically does not affect the temperature, since the AMD PowerTune automation is still guided by the target value of 65 ° C, but the rotation speed of the LSS fan has dropped to 938 rpm.
– Hats off to CoolerMaster engineers. The cables and connectors for the additional power supply will have a hard time, and the VRM of the video card raises concerns: field-effect transistors in the GPU harness are always taken with a current margin, and here they are cooled with liquid, but passive components and tracks on the PCB may turn out to be a weak link. Unlike Vega 56 and accelerators on Polaris chips, whose frequency potential is often limited by VRM power, overclocking of the flagship Vega is not combined with undervolting. An attempt to at least slightly reduce the GPU voltage in our example of Radeon RX Vega 64 LC not only does not help overclocking, but also leads to a loss of stability at higher frequencies. field-effect transistors in the GPU harness are always taken with a current margin, and here they are cooled with liquid, but passive components and tracks on the PCB can be a weak link. Unlike Vega 56 and accelerators on Polaris chips, whose frequency potential is often limited by VRM power, overclocking of the flagship Vega is not combined with undervolting. An attempt to at least slightly reduce the GPU voltage in our example of Radeon RX Vega 64 LC not only does not help overclocking, but also leads to a loss of stability at higher frequencies. field-effect transistors in the GPU harness are always taken with a current margin, and here they are cooled with liquid, but passive components and tracks on the PCB can be a weak link. Unlike Vega 56 and accelerators on Polaris chips, whose frequency potential is often limited by VRM power, overclocking of the flagship Vega is not combined with undervolting. An attempt to at least slightly reduce the GPU voltage in our example of Radeon RX Vega 64 LC not only does not help overclocking, but also leads to a loss of stability at higher frequencies.
A good compromise between speed and power of a video card would be undervolting the GPU while overclocking the RAM. Most Vega 64 models can significantly speed up RAM due to the fact that they mainly use Samsung HBM2 chips. On the contrary, in most assemblies of the Vega 56, Hynix memory is used, which cannot cope with the same high frequencies. However, HBM2 requires intensive cooling even in normal mode, so here the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC is out of competition: we managed to increase the effective RAM frequency from 1890 to 2250 MHz, which means an almost 20 percent increase in bandwidth.
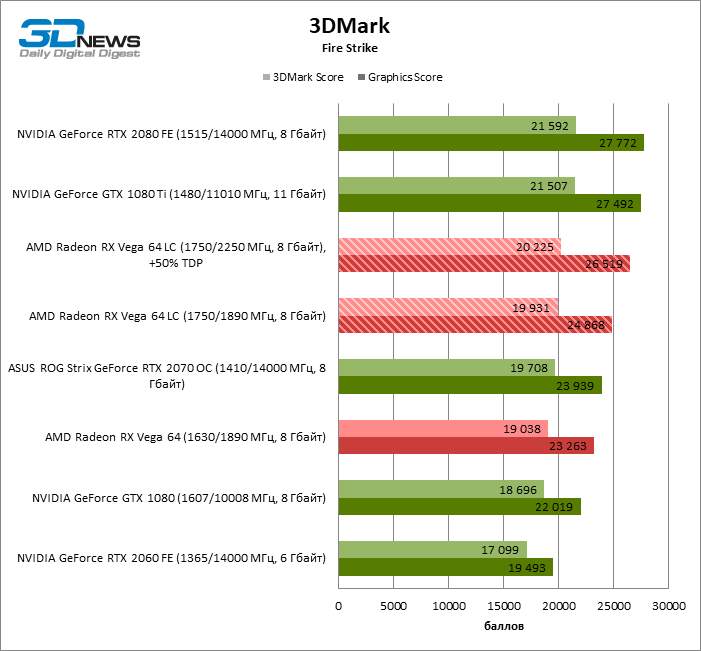
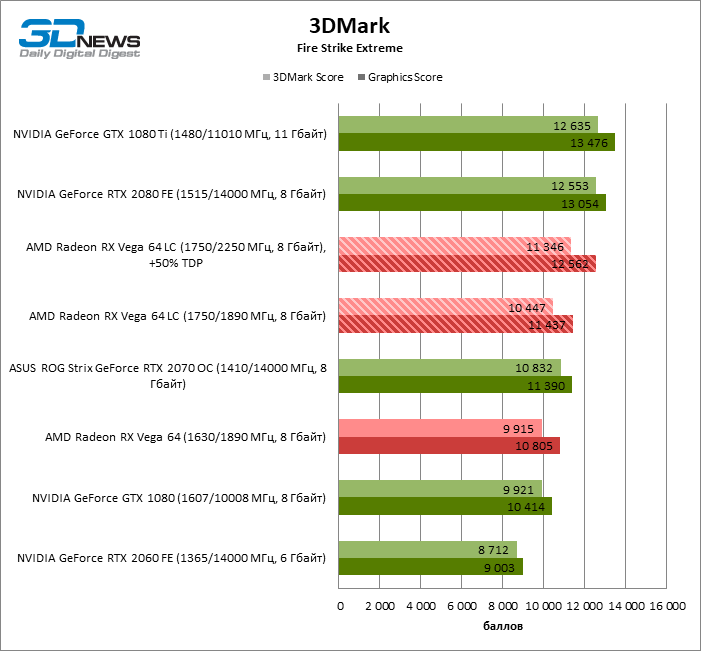
The 3DMark tests are very sensitive to the clock frequencies of video cards and fit perfectly with the Graphics Core Next architecture. Here, the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC scored 6% more points compared to the “air” model Vega 64. As for NVIDIA video cards of a similar level of performance, in order to beat the GeForce GTX 1080 in “synthetics”, AMD does not need an LSS. Radeon RX Vega 64 LC only consolidated previous achievements with a 10% lead over the competitor.
At the same time, the collision with the senior accelerator of the Pascal family and NVIDIA novelties based on Turing chips ended not in favor of the top Vega, even in synthetic tests. Until the Radeon VII appeared on sale, the GeForce GTX 1080 Ti, as well as the GeForce RTX 2080 comparable in speed, was too tough for AMD devices – these video cards went 16 and 24% ahead in 3DMark points. Even the GeForce RTX 2070 outperforms the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC by 7%.
Only overclocking, which is given to Vega video cards at the cost of a catastrophic increase in power, can save the situation. The increased GPU and RAM frequencies provided the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC with an additional 9% points and a coveted draw with the GeForce RTX 2070.
Game tests ( 1920 × 1080, 2560 × 1440)
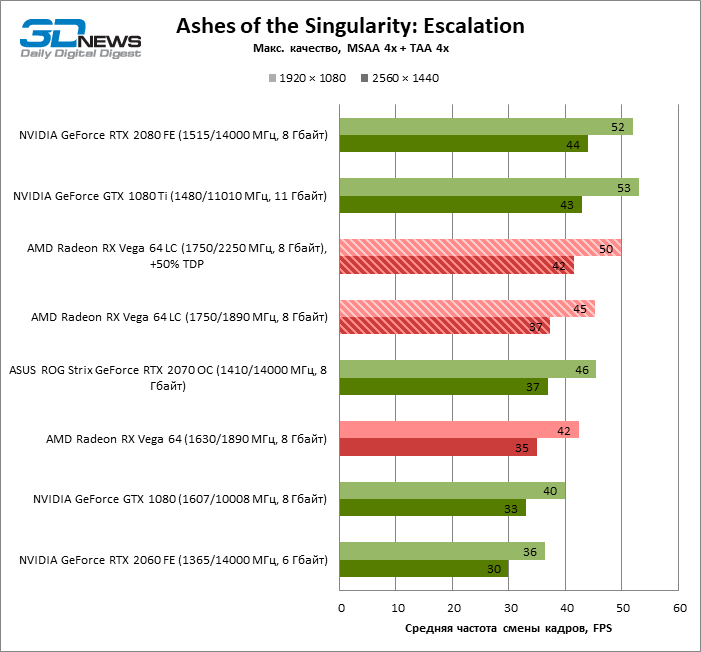
Gaming benchmarks react differently not only to the architectural features of NVIDIA and AMD chips, but also to the characteristics of individual models within the same graphics card family. So, the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC on average is only 6-8% higher than the standard Vega 64 in terms of frame rate, but in Shadow of the Tomb Raider – oddly enough, one of the most inconvenient games for the GCN architecture in our test method – the difference is reaches 11-14%.
In opposition to the standard version of the Radeon RX Vega 64 and GeForce GTX 1080, most games prefer AMD, but the results of GTA V, Shadow of the Tomb Raider and The Witcher 3 are so strongly shifted in favor of NVIDIA that the GeForce GTX is still ahead of the average score. 1080. But thanks to the factory overclocking of the Vega 10 chip under LSS, the advantage is again on the side of the “red”: Radeon RX Vega 64 LC is ahead of GeForce GTX 1080 by 4-6%.
The GeForce RTX 2070 separates from the GeForce GTX 1080, and therefore the standard Vega 64, a significant distance that the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC cannot overcome: the RTX 2070 is 7–8% faster. But in this case, again, we need to make an allowance for individual games in which NVIDIA’s victory is a foregone conclusion. If you do not take into account GTA V, Shadow of the Tomb Raider and The Witcher 3, then we can state a draw between the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC and GeForce RTX 2070 in 1080p mode, and at 1440p the distance between them is only 3% in terms of average refresh rate. frames.
GeForce GTX 1080 Ti and GeForce RTX 2080 are out of reach for the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC: the results of the first are 16-21, and the second is 19-26% higher. Whatever one may say, in gaming tests AMD has nothing to oppose to senior NVIDIA accelerators.
Overclocking the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC at a screen resolution of less than 4K increases FPS by an average of 7% – in this case, the AMD accelerator is practically not inferior to the GeForce RTX 2070.
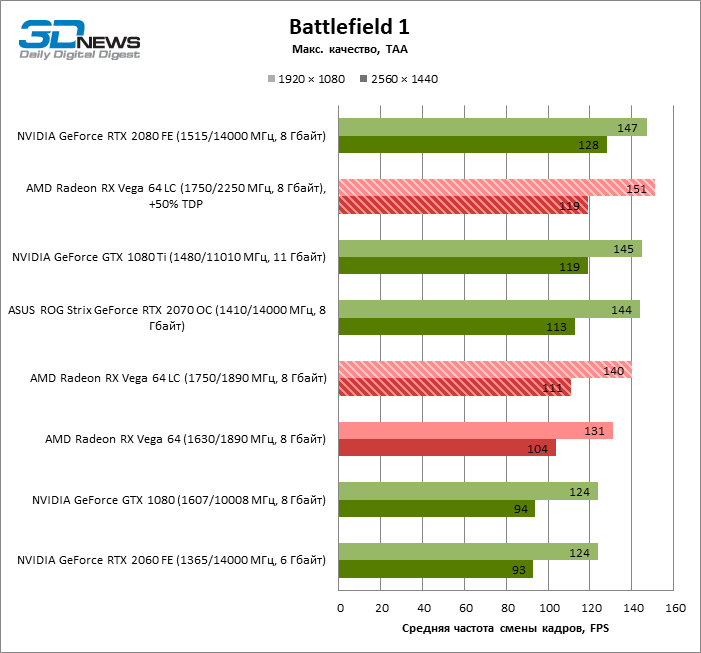
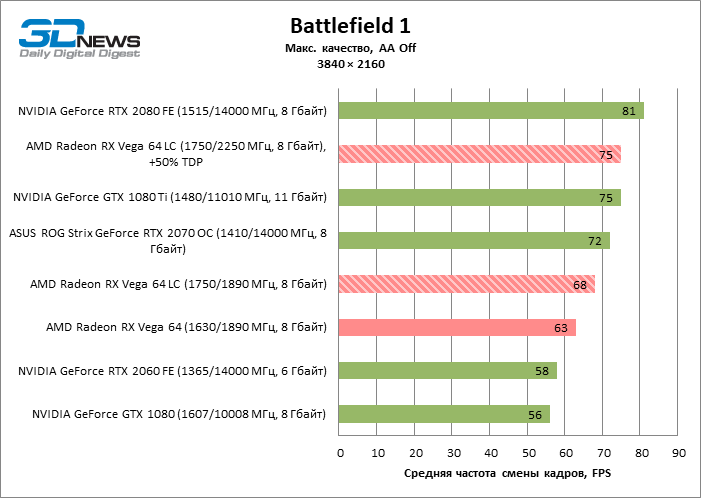
Game tests ( 3840 × 2160)
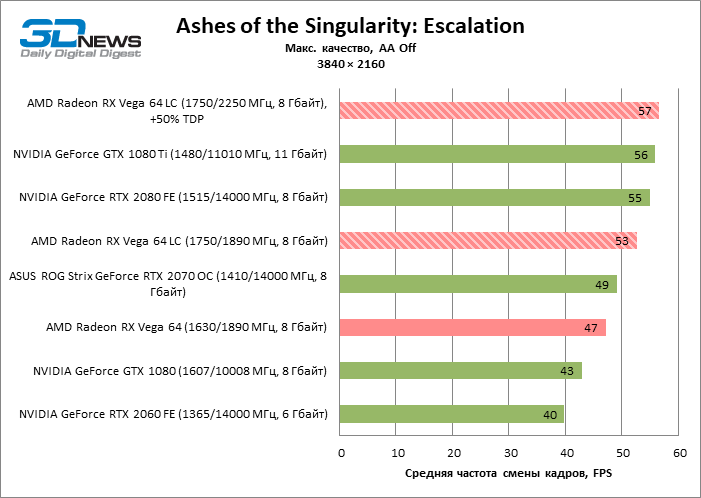
In 2160p mode, Vega 10-class GPUs are protected from the proverbial processor dependency, and performance scales well with clock speeds. Changing the Radeon RX Vega 64 air cooling system to LSS increased the average frame rate by 8%, but those games that were especially sensitive to the factory overclocking of the AMD card at lower resolutions win even more in 4K. So, in Shadow of the Tomb Raider, the difference between the standard Vega 64 and Vega 64 LC is no less than 19%.
The GeForce GTX 1080 at this screen resolution is pulled to the bottom by a relatively narrow, 256-bit memory bus. Even taking into account the results in games that are problematic for the GCN architecture, Radeon RX Vega 64 LC is faster by 10%, and without them – by all 15%.
The GeForce RTX 2070, on the other hand, is no worse equipped for 4K tests than the Vega 64. As a result, the power balance between this model and the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC has remained virtually unchanged: the NVIDIA video card leads by 7%, but if not take into account GTA V, Shadow of the Tomb Raider and The Witcher 3, then we can talk about an average difference of only 4%.
GeForce GTX 1080 Ti and GeForce RTX 2080 still dominate over AMD accelerators: the advantage of these video cards over the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC is 21 and 24% in terms of frame rates in the aggregate of gaming tests, not to mention the notorious trinity of GTA V, Shadow of the Tomb Raider and The Witcher 3.
In 2160p mode, overclocking the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC has the biggest impact on performance: on average, the frame rate has increased by 10% – already enough to defeat the GeForce RTX 2070. But in some games (Deus Ex: Mankind Divided and DOOM), there is an increase at 13-14% FPS.
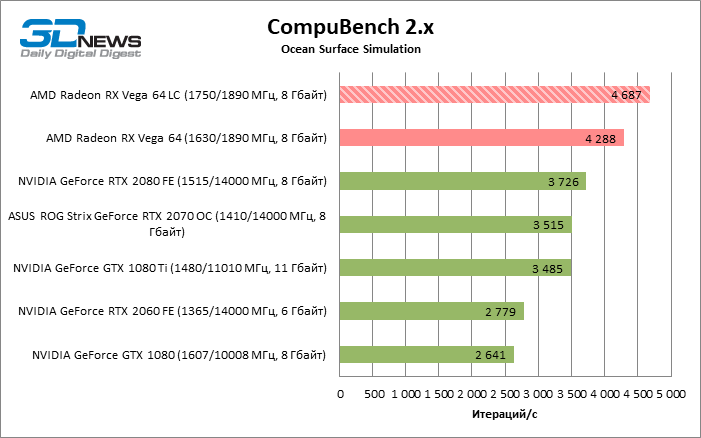
General Purpose Computing
When it comes to the accelerators of the Radeon RX Vega family, computational tasks not related to gaming 3D graphics cannot be ignored. In tests of general-purpose calculations, everything is extremely simple – the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC (and the regular version of Vega 64) had no competitors equal in performance for the same money. Among all AMD’s rivals, only the GeForce RTX 2080 coped with the flagship Vega, and even then only in the only test – LuxMark. The Turing architecture is unmatched for ray-traced rendering, even when the application is not using the RT-cores of the GPU.
Results of all graphic tests
| 3DMark (Graphics Score) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permission | AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 (1630/1890 MHz, 8 GB) | AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 LC (1750/1890 MHz, 8 GB) | AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 LC (1750/2250 MHz, 8 GB), + 50% TDP | NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 (1607/10008 MHz, 8 GB) | NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 Ti (1480/11010 MHz, 11 GB) | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2060 FE (1365/14000 MHz, 6 GB) | ASUS ROG Strix GeForce RTX 2070 OC (1410/14000 MHz, 8 GB) | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 FE (151 5/14000 MHz, 8 GB) | |
| Fire Strike | 1920 × 1080 | 23 263 | 24 868 | 26 519 | 22 019 | 27 492 | 19 493 | 23 939 | 27 772 |
| Fire Strike Extreme | 2560 × 1440 | 10 805 | 11 437 | 12 562 | 10 414 | 13 476 | 9 003 | 11 390 | 13 054 |
| Fire Strike Ultra | 3840 × 2160 | 5 473 | 5 816 | 6 400 | 5 079 | 6 643 | 4 168 | 5 573 | 6 472 |
| Time Spy | 2560 × 1440 | 7 225 | 7 677 | 8 201 | 7 193 | 9 165 | 7 466 | 9 395 | 10 870 |
| Time Spy Extreme | 3840 × 2160 | 3 450 | 3 653 | 3 987 | 3 304 | 4 330 | 3 400 | 4 380 | 5 020 |
| Max. | +7% | +17% | −0% | +27% | +3% | +30% | +50% | ||
| Average | +6% | +15% | −4% | +23% | −11% | +13% | +31% | ||
| Min. | +6% | +14% | −7% | +18% | −24% | +2% | +18% |
| 1920 × 1080 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full screen anti-aliasing | AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 (1630/1890 MHz, 8 GB) | AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 LC (1750/1890 MHz, 8 GB) | AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 LC (1750/2250 MHz, 8 GB), + 50% TDP | NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 (1607/10008 MHz, 8 GB) | NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 Ti (1480/11010 MHz, 11 GB) | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2060 FE (1365/14000 MHz, 6 GB) | ASUS ROG Strix GeForce RTX 2070 OC (1410/14000 MHz, 8 GB) | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 FE (1515/14000 MHz, 8 GB) | |
| Ashes of the Singularity: Escalation | MSAA 4x + TAA 4x | 42 | 45 | 50 | 40 | 53 | 36 | 46 | 52 |
| Battlefield 1 | TAA | 131 | 140 | 151 | 124 | 145 | 124 | 144 | 147 |
| Deus Ex: Mankind Divided | MSAA 4x | 41 | 43 | 48 | 40 | 52 | 36 | 46 | 52 |
| DOOM | TSSAA 8TX | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| F1 2018 | TAA | 123 | 129 | 137 | 115 | 148 | 113 | 139 | 158 |
| Far Cry 5 | TAA | 100 | 101 | 103 | 103 | 109 | 98 | 106 | 110 |
| GTA V | MSAA 4x + FXAA + Reflection MSAA 4x | 69 | 73 | 78 | 84 | 94 | 77 | 85 | 93 |
| Shadow of the Tomb Raider | SMAA 4x | 55 | 61 | 64 | 64 | 74 | 56 | 69 | 82 |
| Tom Clancy’s The Division | SMAA 1x Ultra + TAA: Supersampling | 86 | 94 | 101 | 82 | 108 | 71 | 90 | 107 |
| Total War: WARHAMMER II | MSAA 4x | 39 | 41 | 44 | 36 | 47 | 33 | 41 | 46 |
| The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt | TAA + HairWorks AA 4x | 80 | 87 | 93 | 93 | 120 | 87 | 105 | 128 |
| Max. | +11% | +17% | +21% | +50% | +10% | +31% | +60% | ||
| Average | +6% | +13% | +2% | +23% | −5% | +13% | +26% | ||
| Min. | +0% | +0% | −8% | +0% | −17% | +0% | +0% |
| 2560 × 1440 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full screen anti-aliasing | AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 (1630/1890 MHz, 8 GB) | AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 LC (1750/1890 MHz, 8 GB) | AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 LC (1750/2250 MHz, 8 GB), + 50% TDP | NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 (1607/10008 MHz, 8 GB) | NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 Ti (1480/11010 MHz, 11 GB) | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2060 FE (1365/14000 MHz, 6 GB) | ASUS ROG Strix GeForce RTX 2070 OC (1410/14000 MHz, 8 GB) | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 FE (1515/14000 MHz, 8 GB) | |
| Ashes of the Singularity: Escalation | MSAA 4x + TAA 4x | 35 | 37 | 42 | 33 | 43 | 30 | 37 | 44 |
| Battlefield 1 | TAA | 104 | 111 | 119 | 94 | 119 | 93 | 113 | 128 |
| Deus Ex: Mankind Divided | MSAA 4x | 25 | 28 | 31 | 26 | 34 | 23 | 30 | 35 |
| DOOM | TSSAA 8TX | 154 | 155 | 155 | 152 | 196 | 147 | 187 | 196 |
| F1 2018 | TAA | 91 | 97 | 105 | 88 | 116 | 84 | 105 | 122 |
| Far Cry 5 | TAA | 85 | 87 | 93 | 79 | 96 | 72 | 88 | 99 |
| GTA V | MSAA 4x + FXAA + Reflection MSAA 4x | 51 | 55 | 59 | 66 | 79 | 57 | 69 | 80 |
| Shadow of the Tomb Raider | SMAA 4x | 36 | 41 | 44 | 41 | 49 | 37 | 47 | 57 |
| Tom Clancy’s The Division | SMAA 1x Ultra + TAA: Supersampling | 61 | 67 | 72 | 59 | 77 | 51 | 62 | 76 |
| Total War: WARHAMMER II | MSAA 4x | 26 | 28 | 30 | 25 | 33 | 23 | 29 | 33 |
| The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt | TAA + HairWorks AA 4x | 62 | 67 | 71 | 68 | 90 | 65 | 80 | 96 |
| Max. | +14% | +24% | +30% | +56% | +13% | +36% | +58% | ||
| Average | +8% | +15% | +2% | +30% | −6% | +17% | +35% | ||
| Min. | +1% | +1% | −10% | +13% | −16% | +2% | +16% |
| 3840 × 2160 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full screen anti-aliasing | AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 (1630/1890 MHz, 8 GB) | AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 LC (1750/1890 MHz, 8 GB) | AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 LC (1750/2250 MHz, 8 GB), + 50% TDP | NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 (1607/10008 MHz, 8 GB) | NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 Ti (1480/11010 MHz, 11 GB) | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2060 FE (1365/14000 MHz, 6 GB) | ASUS ROG Strix GeForce RTX 2070 OC (1410/14000 MHz, 8 GB) | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 FE (1515/14000 MHz, 8 GB) | |
| Ashes of the Singularity: Escalation | Off | 47 | 53 | 57 | 43 | 56 | 40 | 49 | 55 |
| Battlefield 1 | 63 | 68 | 75 | 56 | 75 | 58 | 72 | 81 | |
| Deus Ex: Mankind Divided | 29 | 32 | 36 | 28 | 37 | 25 | 32 | 38 | |
| DOOM | 81 | 80 | 91 | 84 | 108 | 79 | 105 | 112 | |
| F1 2018 | 57 | 61 | 67 | 54 | 74 | 53 | 67 | 79 | |
| Far Cry 5 | 48 | 50 | 56 | 44 | 57 | 40 | 51 | 58 | |
| GTA V | 48 | 50 | 54 | 54 | 71 | 47 | 58 | 69 | |
| Shadow of the Tomb Raider | 32 | 38 | 42 | 32 | 43 | 28 | 39 | 47 | |
| Tom Clancy’s The Division | TAA: Stabilization | 35 | 39 | 43 | 34 | 44 | 29 | 37 | 46 |
| Total War: WARHAMMER II | Off | 23 | 24 | 26 | 21 | 28 | 20 | 24 | 28 |
| The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt | 40 | 43 | 46 | 46 | 62 | 43 | 54 | 63 | |
| Max. | +19% | +31% | +15% | +55% | +8% | +35% | +58% | ||
| Average | +8% | +19% | −2% | +30% | −9% | +15% | +34% | ||
| Min. | −1% | +12% | −11% | +19% | −17% | +4% | +17% |
Conclusions
Whatever one may say, the accelerators of the Radeon RX Vega family failed to return AMD to its former confidence in the fight against NVIDIA in the market of high-performance graphics cards. Until the second generation of the second-gen Vega silicon-based Radeon VII comes on sale, Vega 64 Liquid Cooled is the best that Radeon Technologies Group engineers have to offer gamers, and at the same time the clearest example of why the GCN architecture in its current form did not meet the expectations of fans of the red teams.
From the point of view of performance, there are no complaints about the Radeon RX Vega 64 Liquid Cooled. Thanks to water cooling, the far from modest potential of the Vega 10 chip is fully unleashed. When the GPU is clocked at over 1600 MHz, the performance in games increases by 7-8% compared to the standard version of the Vega 64 – enough to beat the GeForce GTX 1080 went to Vega 64 LC without the slightest difficulty. It is possible, albeit with reservations, to recognize it as an equal rival for the GeForce RTX 2070.
The weakness of the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC, as you might guess, is in power consumption. To operate at these frequencies, the Vega 10 GPU requires a high supply voltage and develops a monstrous power – at the level of 380 watts under heavy load. It’s hard to say why the energy efficiency of AMD chips has suffered so much over the years. Either the Ryzen team pulled the best minds of the company involved in processor circuitry, or the Graphics Core Next architecture itself already repeats the ridiculous story of Bulldozer in central processors and needs a complete replacement, but it is from the power consumption problems that the “red” GPUs of the current generation suffer the most. …
However, we didn’t think about the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC ahead of the release of the Radeon VII in order to step on AMD once again. After all, there is good news: under pressure from the GeForce RTX 2060 and RTX 2070, prices for all Vega accelerators have collapsed, including the liquid-cooled model. Now, the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC costs no more than the high-quality GeForce GTX 1080 and RTX 2070 variants equipped with air coolers.
Of course, among these names, the future belongs to the RTX 2070, but until ray tracing and DLSS have received massive support from game makers, hardware buyers for $ 600 have other requests, including aesthetics, reliability and cooling of the device are not the last places. It’s hard to find a counterpart to the system that AMD and CoolerMaster have built among out-of-the-box liquid cooling kits – at least for the price difference between the stock Vega 64 and the LC – it’s amazingly efficient, quiet, and built to last. The build quality and design of the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC are also top notch.
It is worth recalling another advantage of the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC. Vega 10 is still one of the best general purpose computing processors. In many tasks of this kind, the Radeon RX Vega 64, even without LSS, surpasses the GeForce GTX 1080 Ti and at least is not inferior to the GeForce RTX 2080. So it turns out that the best situation for buying a flagship video card of the Vega family is right now, when the Radeon brand is going through hard times … However, we advise you to wait a little longer – the release of Radeon VII may provoke another round of discounts.














