AMD gives a blow today, presenting its new family of Ryzen 4000 processors for portable computers, based on the Zen 2 architecture at 7nm, with specific improvements that will make this new layer of CPUs, a more than interesting alternative at the time of choosing a team.
All this is given thanks to the existence of Zen in the year 2017, with this and what has been learned in the area of the APUs, AMD decided to hit this opportunity, and bring to the market the world’s first 786 mobile x86 SoC .
At the time, AMD’s leadership in the mobile area was generally graphical, but since the appearance of Ryzen, things started to get more interesting, increasing multithreaded performance almost exponentially, being the heel of You long track single-core performance.
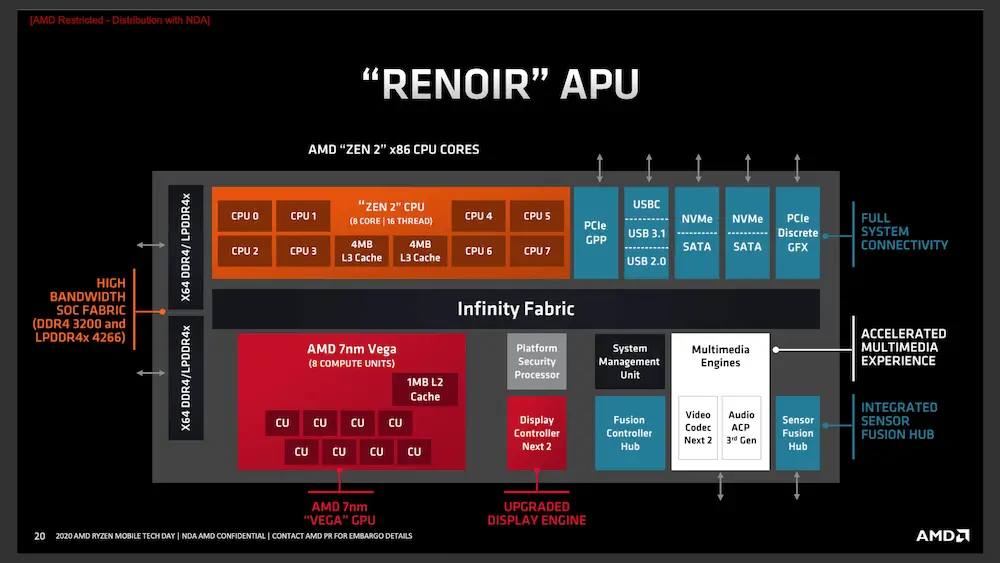
That is so far thanks to Zen 2, where AMD increased the IPC of its processors, and can offer better performance in that regard, thus promising a single-core performance close to the competition.
Another change is that they integrated a dual memory controller, capable of supporting DDR4 @ 3200Mhz chips, or LPDDR4x @ 4266MHz. With one you gain bandwidth (LPDDR4x), and with the other density (DDR4).
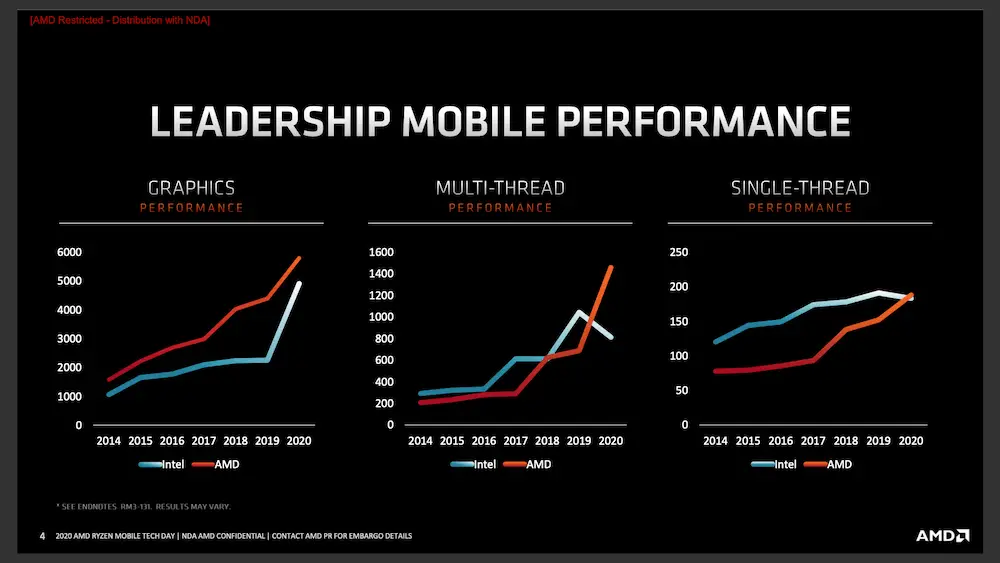
Among the improvements that this new CPU design has, is that these new Ryzen 4000 have an improvement in consumption and energy efficiency, with which another of AMD’s weaknesses in this space is better covered.
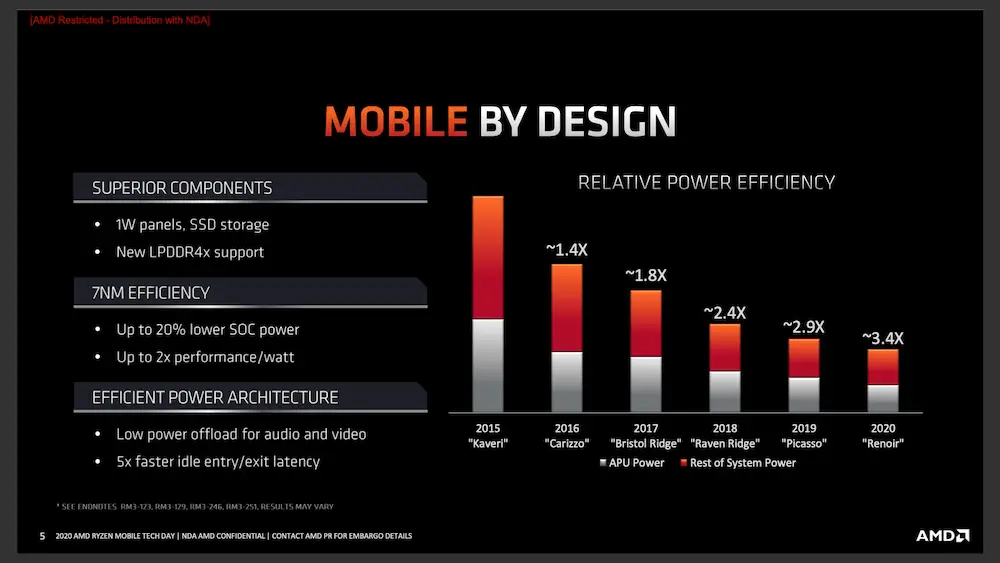
Finally the 3 pillars on which these new processors are: the optimization of IPC, with an increase in the final working frequencies. Go to a 7nm manufacturing process that implies intrinsic improvements in the design and optimization in the density of the transistors, and finally improvements in energy efficiency, increasing the performance per Watt to double, decreasing the final consumption of the packaging.

All this is reflected in the fact that for the first time you have an 8-core processor for ultra-thin equipment, high-level single / multi-core performance, industry-leading graphics performance, and all without compromising the final experience. of the users.

The families
Like any new product, AMD has specific products for each market segment, be these ultra-portable (U-Series), uncompromising performance (H-Series), and finally those oriented in corporate environments (Pro-Series) .

The list of SKUs by product line is:
The Series H, It is for teams that require maximum performance for both content creation work as well as Gamers.
| Model | Freq Base / Boost | Cores / Threads | Cache | GPU Cores | GPU Freq | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryzen 9 4900H | 3.3 GHz / 4.4 GHz | 8/16 | 12 MB | 8 | 1750 MHz | 45W |
| Ryzen 7 4800H | 2.9 GHz / 4.2 GHz | 8/16 | 12 MB | 7 | 1600 MHz | 45W |
| Ryzen 5 4600H | 3.0 GHz / 4.0 GHz | 6/12 | 11 MB | 6 | 1500 MHz | 45W |
U series, These are geared for ultra-portable computers, where their focus is on battery life, with performance that doesn’t wane.
| Model | Freq Base / Boost | Cores / Threads | Cache | GPU Cores | GPU Freq | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryzen 7 4800U | 1.8 GHz / 4.2 GHz | 8/16 | 12 MB | 8 | 1750 MHz | 15W |
| Ryzen 7 4700U | 2.0 GHz / 4.1 GHz | 8/8 | 12 MB | 7 | 1600 MHz | 15W |
| Ryzen 5 4600U | 2.1 GHz / 4.0 GHz | 6/12 | 11 MB | 6 | 1500 MHz | 15W |
| Ryzen 5 4500U | 2.3 GHz / 4.0 GHz | 6/6 | 11 MB | 6 | 1500 MHz | 15W |
| Ryzen 3 4300U | 2.7 GHz / 3.7 GHz | 4/4 | 6 MB | 5 | 1400 MHz | 15W |
Finally you have the Pro series, focused on corporate environments, which focus on security and reliability. These SKUs are the best silicon (wafer center), and with improvements in terms of security and error correction control. The detail of the SKUs does not yet exist, but we believe that they should be very similar to the existing ones.
performance
What many hope to know is how these new processors will perform, because AMD presents us with its traditional performance graphics of a referential team, versus a commercial team with the processors of the competition.
U-series
The performance of these new processors is very promising, considering that they are oriented to a segment that opts for portability and work without so much commitment. This new U series would represent a substantial improvement over the previous generation of AMD Ryzen processors, and they put a fight to the Intel counterpart in this segment.
H-series
This is the expected performance that can be obtained with these processors, on a computer that incorporates a dedicated NVIDIA GPU (RTX 2060).
In another article we will delve a little into the new applied technologies, and how AMD achieved what we are showing you today in a preliminary way.

In order to make all these improvements, the AMD people set 3 fundamental pillars of work. More telemetry, deeper control of the environment, and the entire system working together for energy management.

Regarding telemetry, AMD moved to the second version of its Temperature Tracking System (STT v2). In simple words, added another temperature measurement point, now in the chassis of the equipment, that way you can have a more complete measurement of the CPU environment, in order to better determine the Boost Clock reached, and based on this, this Boost can be maintained for a longer period of time.

As it can be seen in the graph, having as the control variable the chassis temperature, the Boost clock is maintained for a longer period, and then gradually decays to the defined limit. This staggered drop goes hand in hand with the chassis temperature increase curve, so something that was once a peak boost clock is now somewhat more sustained over time, gaining more performance in the process.

The second point is a Deeper Control, for this AMD developed what they call SmartShift. In simple words, it is about taking advantage of the TDP limit for which the equipment is designed and manufactured, and above this value, performing the movement of clocks between CPU and dGPU as necessary.
For example, if for a task more power is required in the CPU, the clocks of the dGPU are lowered and it goes into a state of saving consumption, and all that “surplus” TDP goes to give more “space” to the CPU. to raise its frequency, gaining performance thanks to that extra “headroom” it has.

This is done through Infinity Fabric, and makes the dGPU look as if it were an integrated one, that way, all the packaging is controlled as one. The focus of this development is to be able to offer discrete cards of the “Navi 10” range in conjunction with Ryzen 4000 processors.

The final pillar is that both technologies operate together, this is STT v2 + SmartShift. With this, by having more temperature sensors, such as in the dGPU, thanks to STTv2, longer Boost clocks can be achieved, both in the CPU and the GPU, and with Smartshift you can make the change between one and the other, quickly and based on the needs of the task being performed.
Obviously we will have a team for review, with which we will test all these assertions, and it will be seen in reality if all this is fulfilled, and as far as.