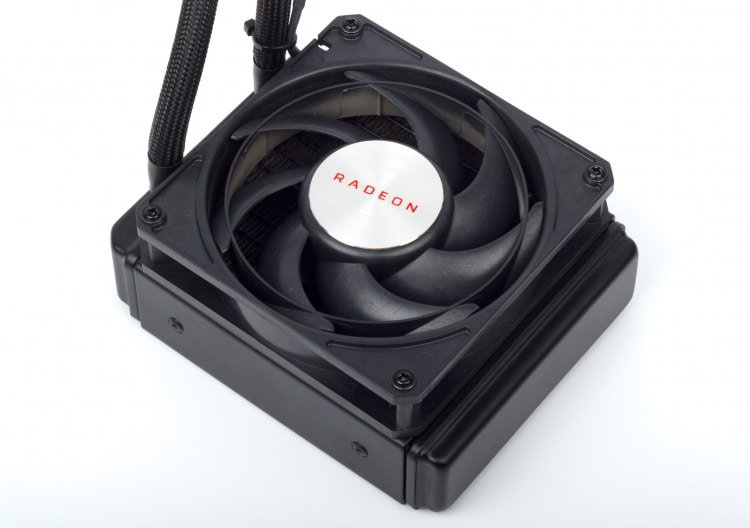
AMD Radeon RX Vega 64 Liquid Cooled video card – The output of the GeForce RTX 2070 and RTX 2060 hit the Vega family video cards, and soon Radeon VII on the next-generation AMD chip will appear on sale. It’s time to take a closer look at the liquid-cooled Radeon RX Vega 64 – and this is not a joke.
NVIDIA launches the GeForce 20 family of accelerators one by one, real-time ray tracing has taken hold of gamers’ minds, and many have a reasonable question: what about AMD? Fortunately for fans of the Radeon brand and critics of NVIDIA, the red team is ready to return to the big leagues. Soon we will fall into our hands with the latest AMD graphics card, which is based on the first discrete GPU, made at the norm of 7 nm. The seventh of February is the day we can publish our Radeon VII test results.
However, the Seven is only a signal that AMD is not giving up, but the company is not yet ready to give NVIDIA a fight on all fronts. Radeon VII will go on sale at a recommended price of $ 699 and will compete with the GeForce RTX 2080. But the prospects for more affordable gaming cards with Vega 20 chips of a “lightweight” configuration (more precisely, truncated even more than Radeon VII, because it itself is not equipped with fully functional GPU) is still in doubt. The production of Radeon VII components – both the GPU and the HBM2 memory assemblies – is expensive, AMD will not receive large revenues from the sale of the flagship and is unlikely to agree to lose money in order to quickly replace the Radeon RX Vega 56 and Vega 64. This means that the accelerators on the first-generation Vega chips will remain in service even after the release of Radeon VII, and AMD has no timely response to the latest NVIDIA move.

Of course, we mean the GeForce RTX 2060. The first video cards based on Turing chips did not threaten the positions of Radeon RX Vega, because the GeForce RTX 2080 and RTX 2080 Ti belong to a completely different class – both in terms of speed, and even more so in terms of price. The GeForce RTX 2070 in games without ray tracing turned out to be only an accelerated analog of the GeForce GTX 1080, and this is already a big problem for Vega 64. But the GeForce RTX 2060 was really a terrible enemy of both Vega models : at prices from $ 349, the younger Turing easily outperformed Radeon gaming tests The RX Vega 56, which cost at least $ 499 in early January, is too close in performance to the Vega 64 to still be bought for $ 599.
The only thing AMD had to do in this situation was to go down in prices. As a result, various modifications of the Radeon RX Vega 64 now occupy the same price range as the GeForce RTX 2070, and the Vega 56 is closer to the GeForce RTX 2060. And here’s how it relates to the review topic: the cheaper Vega family did not bypass the Radeon RX Vega 64 Liquid Cooled. Moreover, among all varieties of Vega 64, the option with an integrated LLS suddenly became one of the most attractive. Let’s see why he is so good.
Specifications, prices
Since manufacturers of discrete GPUs have mastered 14/16 nm technology, AMD has developed not so many new chips for video cards and is trying to use each in several models of game accelerators. Apart from the Radeon RX Vega 64 Limited Edition, which differs from the black reference Vega 64 only in a shiny metal case, the company released five devices based on the Vega 10 GPU: the familiar Radeon RX Vega 56, Vega 64, two modifications of the Vega Frontier Edition ( boards equipped with 16 GB of RAM) – with an air cooler or CBO – and, finally, Vega 64 Liquid Cooled.
In its large family, the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC has the highest clock speeds: the Boost Clock of the GPU is 1677 MHz, while the air-cooled Vega 64 reference samples are content with a frequency of 1546 MHz. It is worth noting once again that the parameters indicated in the specifications of any Radeon RX Vega models are not very similar to the real GPU frequencies. Although AMD and NVIDIA use common terminology, the Boost Clock in GeForce video cards means the average frequency in typical tasks, and in Vega – the maximum frequency (also in typical tasks). And yet, no other Vega 64 modification, including the products of well-known factory overclocking champions – PowerColor and SAPPHIRE, makes an application for such frequencies as the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC.
But the tabular value of the power of the board, which is the flagship “Vega” is 345 watts, we certainly believe. It remains only to find out what magic allows a small heatsink Radeon RX Vega 64 LC to dissipate a tremendous stream of heat.
| Manufacturer | AMD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Radeon RX Vega 56 | Radeon RX Vega 64 | Radeon RX Vega 64 Liquid Cooled | Radeon RX Vega Frontier Edition | Radeon RX Vega Frontier Edition Liquid Cooled |
| GPU | |||||
| Title | Vega 10 XL | Vega 10 XT | Vega 10 XTX | Vega 10 XT | Vega 10 XTX |
| Microarchitecture | Gcn 1.4 | Gcn 1.4 | Gcn 1.4 | Gcn 1.4 | Gcn 1.4 |
| Process technology, nm | 14 nm FinFET | 14 nm FinFET | 14 nm FinFET | 14 nm FinFET | 14 nm FinFET |
| The number of transistors, million | 12 500 | 12 500 | 12 500 | 12 500 | 12 500 |
| Clock, MHz: Base Clock / Boost Clock | 1156/1471 | 1247/1546 | 1406/1677 | 1382/1600 | 1382/1600 |
| Number of Shader ALUs | 3584 | 4096 | 4096 | 4096 | 4096 |
| Number of texture mapping blocks | 224 | 256 | 256 | 256 | 256 |
| ROP Number | 64 | 64 | 64 | 64 | 64 |
| RAM | |||||
| Bit depth, bit | 2048 | 2048 | 2048 | 2048 | 2048 |
| Chip type | HBM2 | HBM2 | HBM2 | HBM2 | HBM2 |
| Clock frequency, MHz (bandwidth per contact, Mbps) | 800 (1600) | 945 (1890) | 945 (1890) | 945 (1890) | 945 (1890) |
| Volume, MB | 8096 | 8096 | 8096 | 16192 | 16192 |
| Input / output bus | PCI Express 3.0 x16 | PCI Express 3.0 x16 | PCI Express 3.0 x16 | PCI Express 3.0 x16 | PCI Express 3.0 x16 |
| Performance | |||||
| Peak performance FP32, GFLOPS (based on maximum indicated frequency) | 10544 | 12665 | 13738 | 13107 | 13107 |
| Performance FP32 / FP64 | 1/16 | 1/16 | 1/16 | 1/16 | 1/16 |
| RAM bandwidth, GB / s | 410 | 484 | 484 | 484 | 484 |
| Image output | |||||
| Image Output Interfaces | HDMI 2.0, DisplayPort 1.4 | HDMI 2.0, DisplayPort 1.4 | HDMI 2.0, DisplayPort 1.4 | HDMI 2.0, DisplayPort 1.4 | HDMI 2.0, DisplayPort 1.4 |
| TDP, W | 210 | 295 | 345 | <300 | 350 |
| Retail price (US, without tax), $ | From 339 (newegg.com) | From 399 (newegg.com) | From 599 (amazon.com) | 999 (recommended at time of release) | 1499 (recommended at time of release) |
| Retail price (Russia), rub. | From 26 563 (market.yandex.ru) | From 35 940 (market.yandex.ru) | From 39 229 (market.yandex.ru) | Nd | Nd |
Initially, AMD considered the water-cooled Radeon RX Vega 64 as an offer for enthusiasts willing to donate a large sum of money for higher clock speeds: the base version of the Vega 64 went on sale at a recommended price of $ 499, and the Vega 64 LC was priced at a good $ 200 more. But the modern market for high-performance graphics cards looks completely different.
The lower border of the price range of the Radeon RX Vega 64 now lies in the region of $ 399, while the GeForce RTX 2070 costs at least $ 499. The last wave of discounts has not yet reached the Russian market, but Vega 64 in rubles has at least ceased to be more expensive than the RTX 2070. Depending on the specific modification, both devices are sold for an amount of 35-49 thousand rubles. But most importantly, Vega 64 LC (39-48 thousand) is now in this range – the only video card with a pre-installed liquid cooling system that can be bought for that kind of money.
Setting Up
Until now, a considerable part of all the Radeon RX Vega 64 video cards that are on sale is a reference model manufactured by SAPPHIRE. At AMD, we were ready for partners to soon launch production of devices of original design, and decided not to save on the design of reference samples. As a result, the Radeon RX Vega 56 and Vega 64 received a printed circuit board with an appropriately powerful voltage regulator and a rather efficient cooler, consisting of a radiator with an evaporation chamber and a radial type fan.
The Radeon Vega 64 LC has a lot in common with the usual Vega 64 reference card, but in terms of appearance and workmanship it is noticeable that this is a higher-level product. The circuit board and components of the cooling system are enclosed in an all-metal box, and the entire front part of the case is made of one thick sheet of aluminum. AMD adopted the love of metal from NVIDIA, but, unlike the Founders Edition video cards, the design of the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC is dominated by right angles, and the surface has a rough texture. The few case elements made of plastic are the Radeon inscription and the transparent red corner: when the board receives power, they glow brightly.
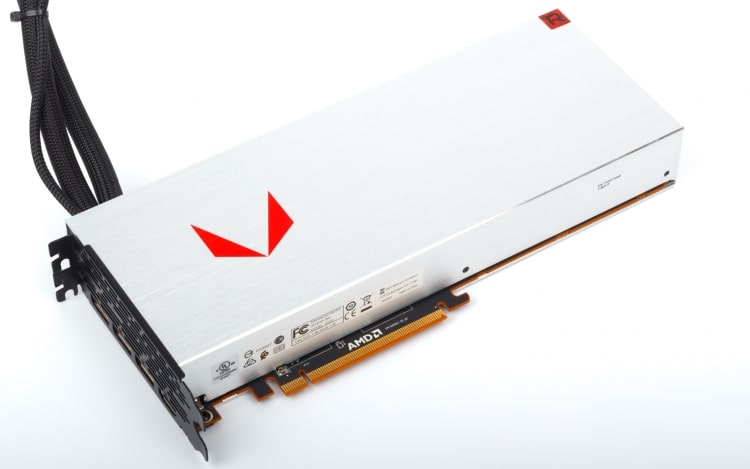
Changing the air cooler to the SJO almost did not affect the dimensions of the device, although the case was made a couple of millimeters longer and wider than the standard reference model to hide the edge of the printed circuit board at the junction of the metal plates.
But of course, the most interesting thing about the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC is its liquid cooling system. This is not the first time that water has found application in red video cards: after Radeon R9 295X2, Radeon R9 Fury X, and then Radeon Pro Duo based on two Fiji AMD chips, I gained enough experience to design a truly high-quality and durable solution. Indeed, in the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC everything is very well thought out.

The components of the SJO are manufactured by CoolerMaster on an individual order – it does not sell anything like this in retail. The system operates as follows. The liquid from the external radiator first enters the pump with an integrated water block – the copper base of this part is pressed against the GPU chips and the HBM2 memory assemblies. But the metal frame, under which almost the entire area of the printed circuit board is hidden, except for the GPU substrate and power connectors, also forms part of the cooling circuit: on the outside, a u-shaped cover is mounted on it, under which fluid heated by the GPU flows from the pump.
This is how the water cooling scheme of such a powerful video card as the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC should look like, because the VRM components here also need enhanced heat dissipation. But field effect transistors, drivers, capacitors and chokes are able to operate at a higher temperature than GPUs and HBM2 chips, so the latter have priority.
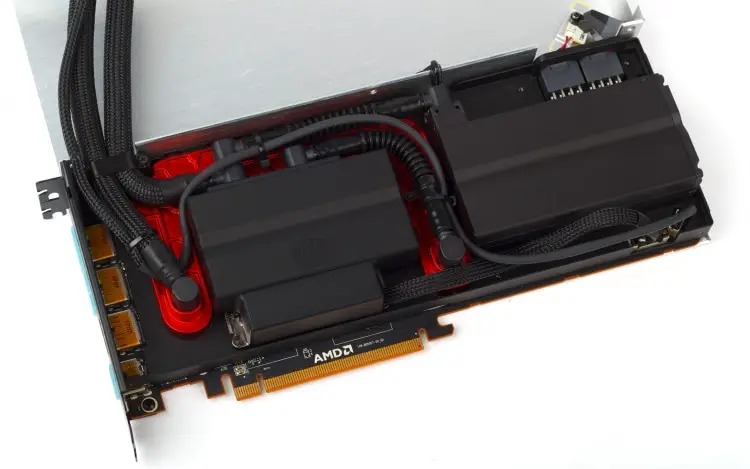
A typical factory-built coolant cooling system (CLLC – Closed Loop Liquid Cooler), which is installed on the central processors, is designed for a life of about five years. Due to the fact that the coolant gradually slides out of the circuit through the pores of the connecting hoses and is replaced by air, the internal lubricant dries in the pump – and the mechanics wear out quickly. To prevent this problem, AMD and CoolerMaster use hoses with an internal Teflon coating (be careful with bends!), And most importantly, they integrated a reservoir with a supply of liquid into the SJO – this is a plastic box that occupies the right side of the space under the casing. The tank is connected by a single tube to the pump inlet, and on the other hand it has an air valve – thus compensating for the slow loss of coolant from the main circuit.
The cooling ring closes a compact radiator with a single fan of size 120 mm. Although the Vega 64 LC has very serious heat dissipation, AMD did not make the heatsink thicker than the Radeon R9 Fury X (38 mm). In addition, he got rid of the expansion cavity, which sometimes complicates installation in seats for case fans, because there is already a separate tank under the cover of the video card. But the fan is the same Nidec Servo product, which is well known under the brand name Scythe Gentle Typhoon. The option for Fury X and Vega 64 LC (D1225C12B7ZP) has a ring connecting the blades, and can accelerate to 3000 rpm. But at a speed of rotation within 1200 rpm, which the Vega 64 LC lacks even under intense load, it is practically inaudible.

Printed circuit board
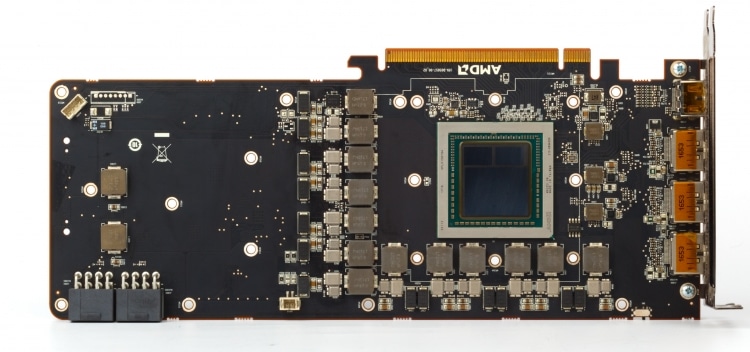
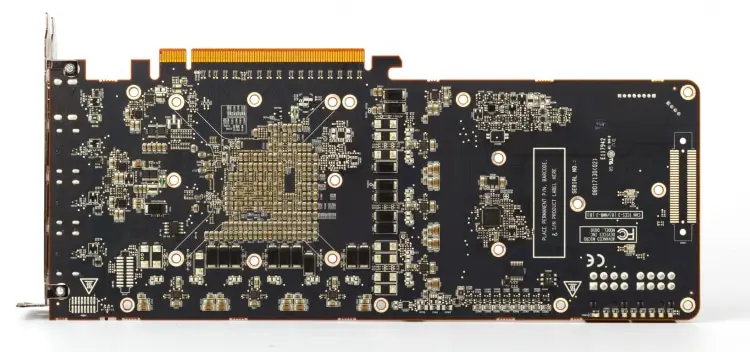
All reference versions of Vega accelerators, be it Vega 56, Vega 64 or Vega 64 LC, are based on the same circuit board. Due to the fact that the Vega 10 GPU and two HBM2 memory stacks are connected together with a silicon substrate, there is free space on the front side of the PCB. The manufacturer could shorten the PCB, as is done in the Radeon R9 Fury X, so that the Vega 64 LC becomes the same compact device, but then you would have to abandon the coolant reservoir, and in standard Vega versions, the dimensions are still determined by the air cooling system.
The lion’s share of the PCB is VRM. The voltage regulator consists of thirteen phases – a dozen for the GPU and one for the HBM2 chips. To simplify the control logic in the GPU power circuit and dispense with an eight-phase PWM controller (International Rectifier IR35217), AMD uses dual field-effect transistor drivers – one chip per pair of MOSFETs.
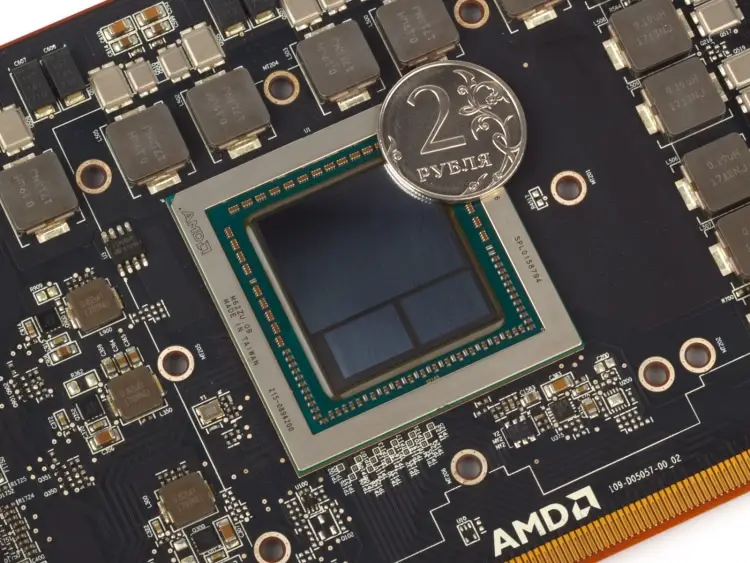
On most Vega 64s, the gaps between the GPU and the HBM2 chips are filled with epoxy compound.
Additional power is supplied to the board through two eight-pin connectors. Together with the power lines of the PCI Express slot, they provide the board with a rated power of 375 watts. This number usually does not say anything about real power consumption, but not in the case of the Radeon RX Vega 64 LC, which we will soon see. The LEDs next to the power connectors form a red indicator strip that indicates the load on the GPU. Using the DIP switch, for which a hole is made in the flap on the back of the PCB, you can turn off the LED or change their color to blue.
Not a single high-performance graphics card based on AMD chips can do without a backup UEFI chip, but for Vega this is not just insurance against a failed flashing: a second copy of the firmware limits the power, and hence the frequency, and heating of the GPU.