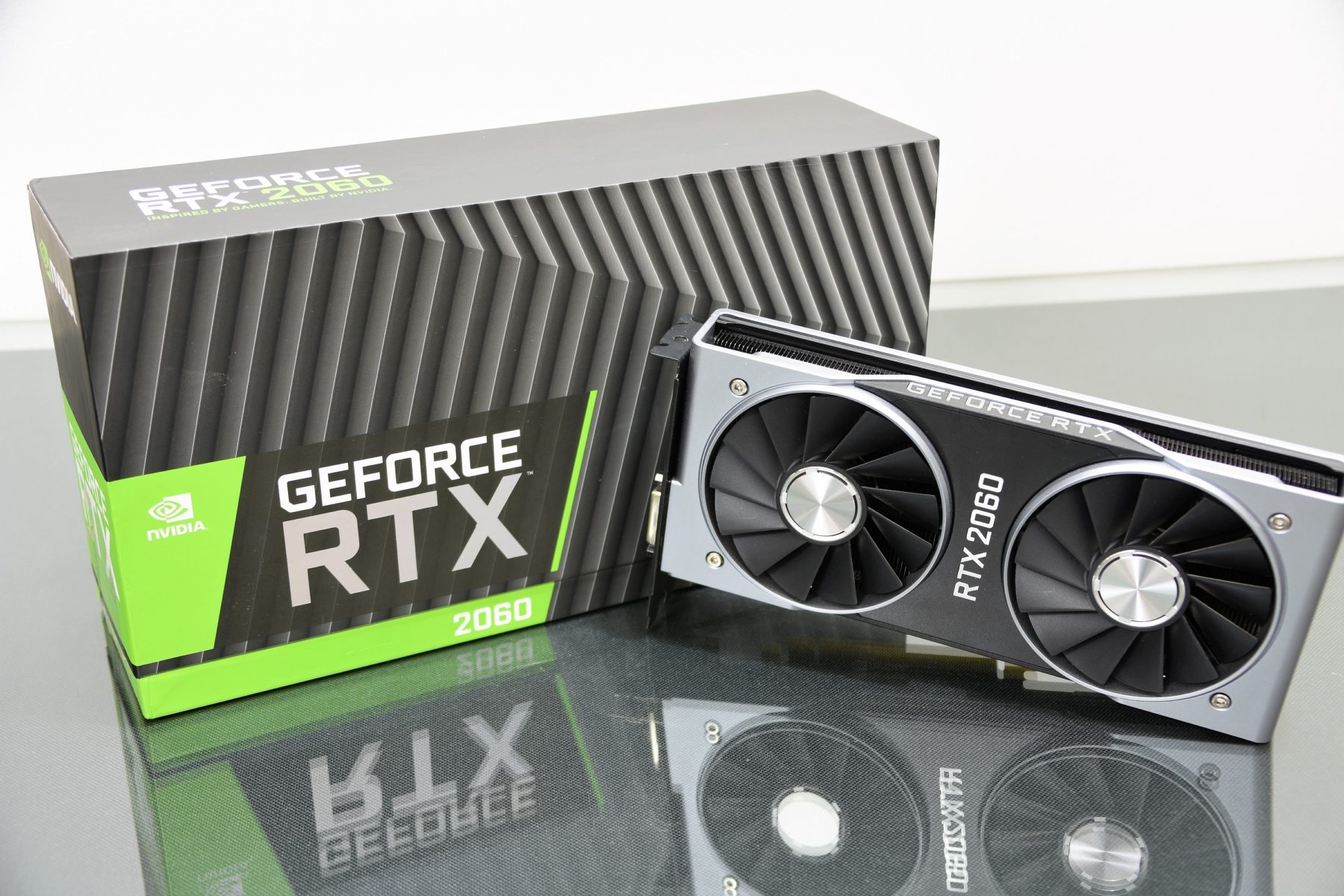
The NVIDIA RTX 2060 is the most modest model in the RTX series (so far), this model would be the transition from what are GTX models to RTX within their capabilities. After seeing what the GTX 1660 Ti and RTX 2070 models offer us, we needed to see how NVIDIA made the performance jump between one family and another, and thanks to NVIDIA for providing us with this copy of RTX 2060 we will know how it fits between these two models to market level
Turing architecture.
New transmission multiprocessor (SM).
Turing presents a new processor architecture, Turing SM, offering a dramatic increase in shading efficiency, achieving a 50% improvement in performance delivered by CUDA Core compared to the Pascal generation. These improvements are enabled by two key architectural changes. First, Turing SM adds a new independent integer data path that can execute instructions simultaneously with the floating-point mathematical data path. In previous generations, the execution of these instructions would have blocked the issuance of floating point instructions. Second, the SM memory path has been redesigned to unify shared memory, texture caching and memory caching in a drive. This translates into 2 times more bandwidth and more than 2 times more available capacity for L1 cache in common workloads.
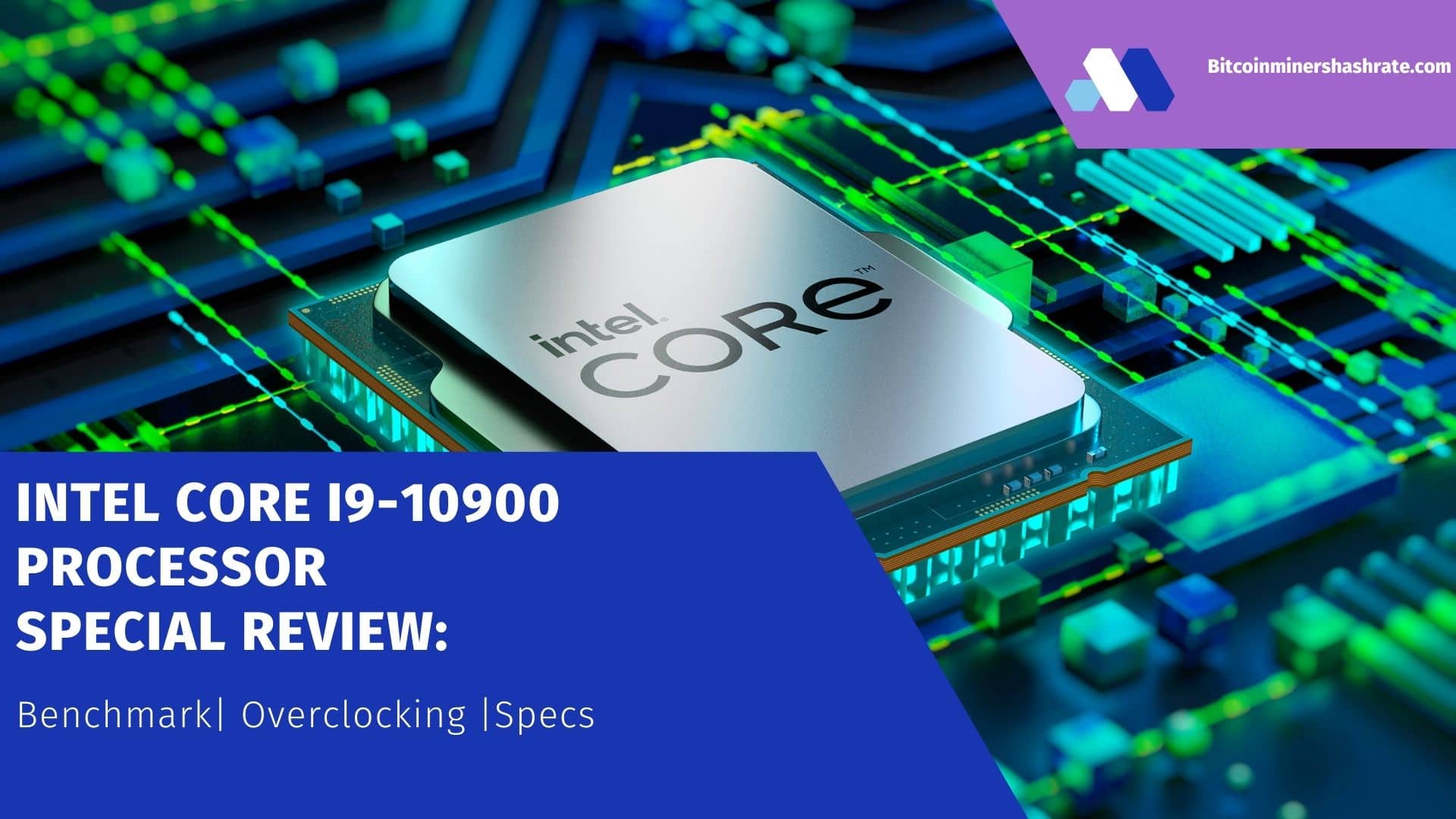
Turing Tensor Cores.
Tensor cores are specialized execution units, specifically designed to perform tensor / matrix operations that are the main computing function used in “Deep Learning”. Similar to the Volta Tensor Cores, the Turing Tensor Cores provide high accelerations for matrix calculations at the heart of deep neural network learning and inference operations. The Turing GPUs include a new version of the Tensor core design that has been improved for inference. Turing cores add new INT8 and INT4 precision modes for inference of workloads that can tolerate quantification and do not require FP16 accuracy. Turing Tensor offers for the first time new artificial intelligence capabilities based on deep learning for gaming PCs with GeForce and Quadro-based workstations. A new technique called Deep Learning Super Sampling (DLSS) is driven by Tensor Cores. DLSS leverages a deep neural network to extract the multidimensional features of the rendered scene and intelligently combine the details of multiple frames to build a high-quality final image. DLSS uses fewer input samples than traditional techniques such as TAA, while avoiding the algorithmic difficulties such techniques face with transparency and other complex scene elements.
Ray Tracing Acceleration in real time.
Turing introduces real-time ray tracing or Ray Tracing that allows a single GPU to render visually realistic 3D games and complex professional models with physically accurate shadows, reflections and refractions. Turing’s new RT Cores accelerate ray tracing and are leveraged by systems and interfaces such as NVIDIA Ray Tracing RTX technology and APIs such as Microsoft DXR, NVIDIA OptiX ™ and Ray Tracing Vulkan to deliver a real-time Ray Tracing experience .
New shading advances:
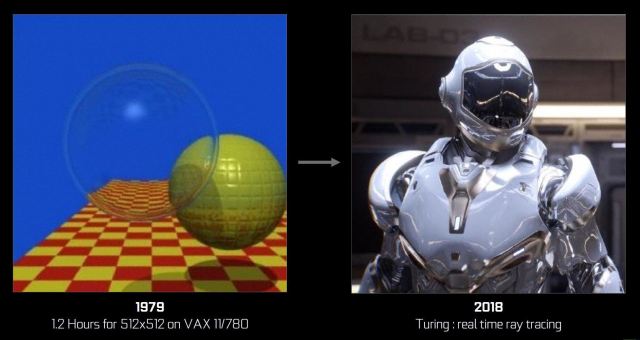
Mesh shading.
Mesh shading advances the NVIDIA geometry processing architecture by offering a new shading model for the shading stages of vertices, tessellations and geometries of the graphics pipe, which supports more flexible and efficient approaches to geometry calculation . This more flexible model makes it possible, for example, to admit an order of magnitude with more objects per scene, moving the bottleneck of the object lists outside the CPU towards highly parallel GPU mesh shading programs. Mesh shading also allows new algorithms for advanced geometric synthesis and LOD object handling.
Variable Rate Shading (VRS)
VRS allows developers to dynamically control the shading rate, shading only once every sixteen pixels or up to eight times per pixel. The application specifies the shading rate using a combination of a shading surface and a “per-primitive” value (triangle). VRS is a very powerful tool that allows developers to shade more efficiently, reducing work in regions of the screen where total resolution shading would not give any visible benefit to image quality, and therefore, would improve frame rate . Several classes of VRS-based algorithms have already been identified, which can vary the shading job according to the level of detail of the content (adaptive content shading), the speed of content movement (shading adaptable to the movement) and applications of virtual reality, lens resolution and eye position (Foveated Rendering).

Texture and space shading
With texture space shading, objects are shaded in a private coordinate space (a texture space) that is stored in memory, and pixel shaders sample that space instead of directly evaluating the results. With the ability to cache shading results in memory and reuse / resample them, developers can eliminate duplicate shading work or use different sampling approaches that improve quality.
Multiple view representation (MVR)
MVR powerfully extends Pascal’s single stereo step (SPS). While SPS allowed the representation of two views that were common, except for an X offset, MVR allows the representation of multiple views in a single pass, even if the views are based on completely different origin positions or view directions. Access is made through a simple programming model in which the compiler automatically considers the code independent of the view, while identifying the attributes dependent on the view for optimal execution.
Deep learning functions for graphics
NVIDIA NGX ™ is the new neural graphics framework based on deep learning of NVIDIA RTX technology. NVIDIA NGX uses deep neural networks (DNN) and a set of “neural services” to perform functions based on artificial intelligence that accelerate and improve graphics, representation and other client-side applications. NGX employs Turing Tensor Core for deep learning operations and accelerates the delivery of NVIDIA deep learning research directly to the end user. Features include ultra-high-quality NGX DLSS (Deep Learning Super-Sampling), AI InPainting image replacement with sensitive content, very high quality Slow-Mo AI and smooth slow motion, and AI Super Rez intelligent image change resolution .

Deep learning functions for inference
Turing GPUs offer exceptional inference performance. The Turing Tensor cores, together with the continuous improvements in the TensorRT (NVIDIA runtime inference framework), CUDA and CuDNN libraries, allow Turing GPUs to offer exceptional performance for inference applications. Turing Tensor Cores also add support for fast INT8 matrix operations to significantly accelerate inference performance with minimal loss of accuracy. New low precision INT4 matrix operations are now possible with Turing Tensor Cores and will allow research and development in sub 8-bit neural networks.
GDDR6 high performance memory subsystem
Turing is the first GPU architecture compatible with GDDR6 memory. GDDR6 is the next major advance in the design of DRAM GDDR high bandwidth memory. The GDDR6 memory interface circuits in the Turing GPUs have been completely redesigned for speed, energy efficiency and noise reduction, achieving transfer rates of 14 Gbps with an improved energy efficiency of 20% compared to the GDDR5X memory used in Pascal’s GPUs.
USB-C and VirtualLink
Turing GPUs include hardware support for USB Type-C ™ and VirtualLink ™ 4. VirtualLink is a new open industry standard that is being developed to meet the power, screen and bandwidth demands of upcoming VR headsets generation through a single USB-C connector. In addition to easing the inconvenience of configuration present in VR headsets today, VirtualLink will bring virtual reality to more devices.

Specs.
| GPU model | RADEON VII | NVIDIA RTX 2080 FE | NVIDIA GTX 1080Ti | NVIDIA RTX 2070 FE | NVIDIA RTX 2060 FE | NVIDIA GTX 1660 Ti | NVIDIA GTX 1060 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fabrication process | 7 nm | 12 nm | 16nm | 12 nm | 12 nm | 12 nm | 16nm |
| Codename | Vega 20 | Turing | Pascal | Turing | Turing | Turing | Pascal |
| GPU Core | Vega20 | TU104-400 | GP102 | TU106-400A-A1 | TU106 | TU116 | GP106 |
| CUDA Cores | 3840 | 2944 | 3584 | 2304 | 1920 | 1536 | 1280 |
| Texture Units | 240 | 184 | 224 | 144 | 120 | 96 | 80 |
| Tensor Cores | 368 | 288 | 240 | ||||
| ROPs | 64 | 64 | 88 | 64 | 48 | 48 | 48 |
| Core / Boost Clock | 1400 MHz / 1750 MHz | 1515 MHz / 1800 MHz | 1481 MHz / 1582 MHz | 1410 MHz / 1710 MHz | 1365 MHz / 1680 MHz | 1500 MHz / 1770 MHz | 1506 MHz / 1708 MHz |
| Memory clock | 2 Gbps | 14 Gbps | 11 Gbps | 14 Gbps | 14 Gbps | 12 Gbps | 8 Gbps |
| Memory | 16 GB HBM2 | 8 GB GDDR6 | 11 GB GDDR5X | 8 GB GDDR6 | 6 GB GDDR6 | 6 GB GDDR6 | 6 GB GDDR5 |
| Memory Bus | 4096-bit | 256-bit | 352-bit | 256-bit | 192-bit | 192-bit | 192-bit |
| Power Connectors | 2x 8 pin | 1x 8 pin + 1x 6 pin | 1x 8 pin + 1x 6 pin | 1x 8 pin | 1x 8 pin | 1x 8 pin | 1x 6 pin |
| TDP | 300 W | 225W | 250W | 175W | 160W | 120W | 120W |
| Price | MSRP: $ 699 | MSRP FE: $ 799 MSRP “NO FAITH”: $ 699 | MSRP: $ 699 | $ 490 | $ 350 | $ 280 | $ 200 |
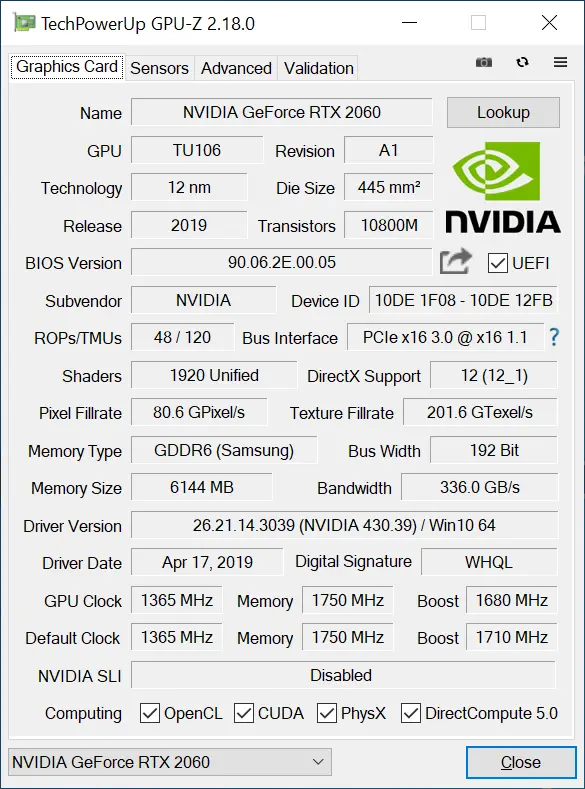
First look.
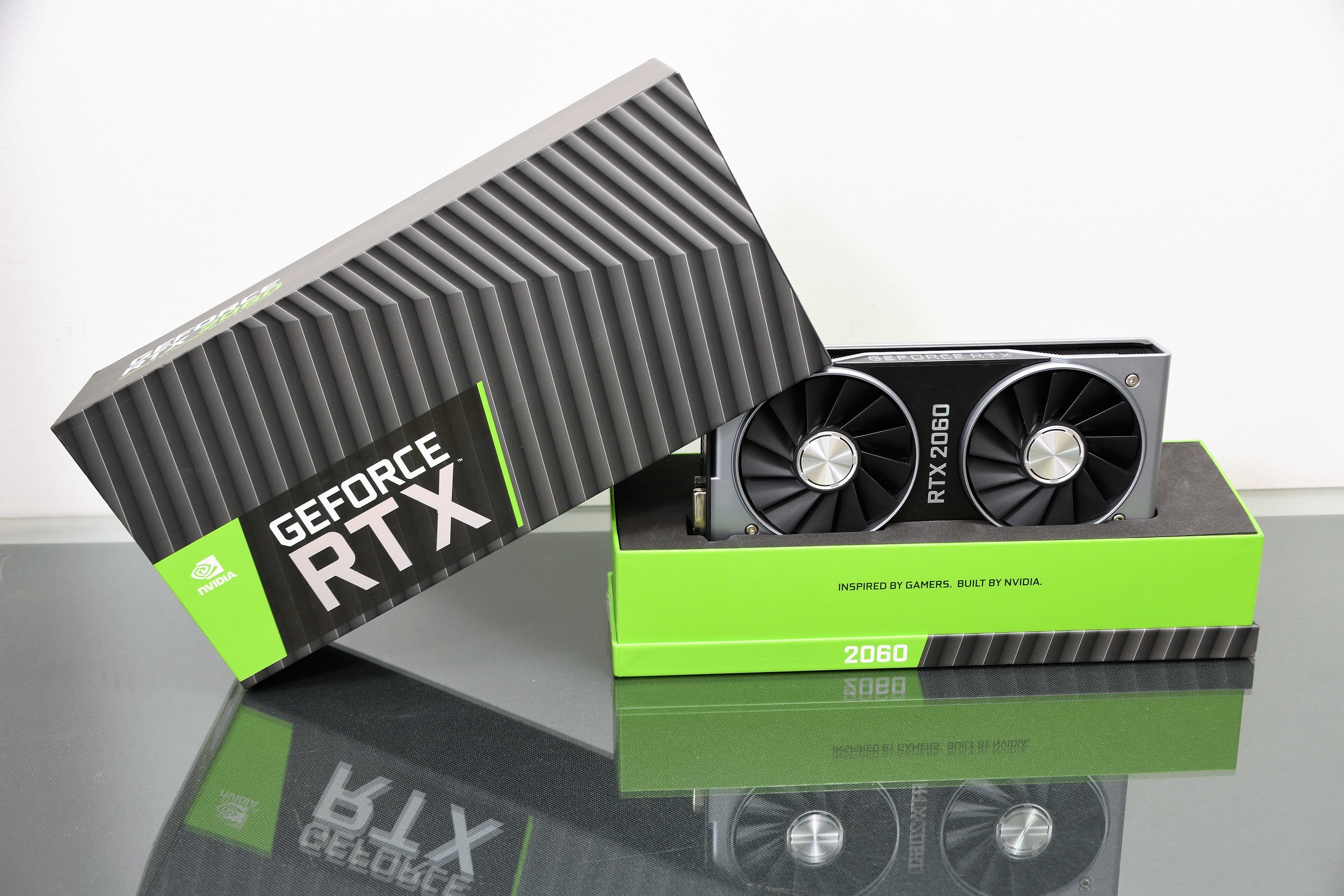
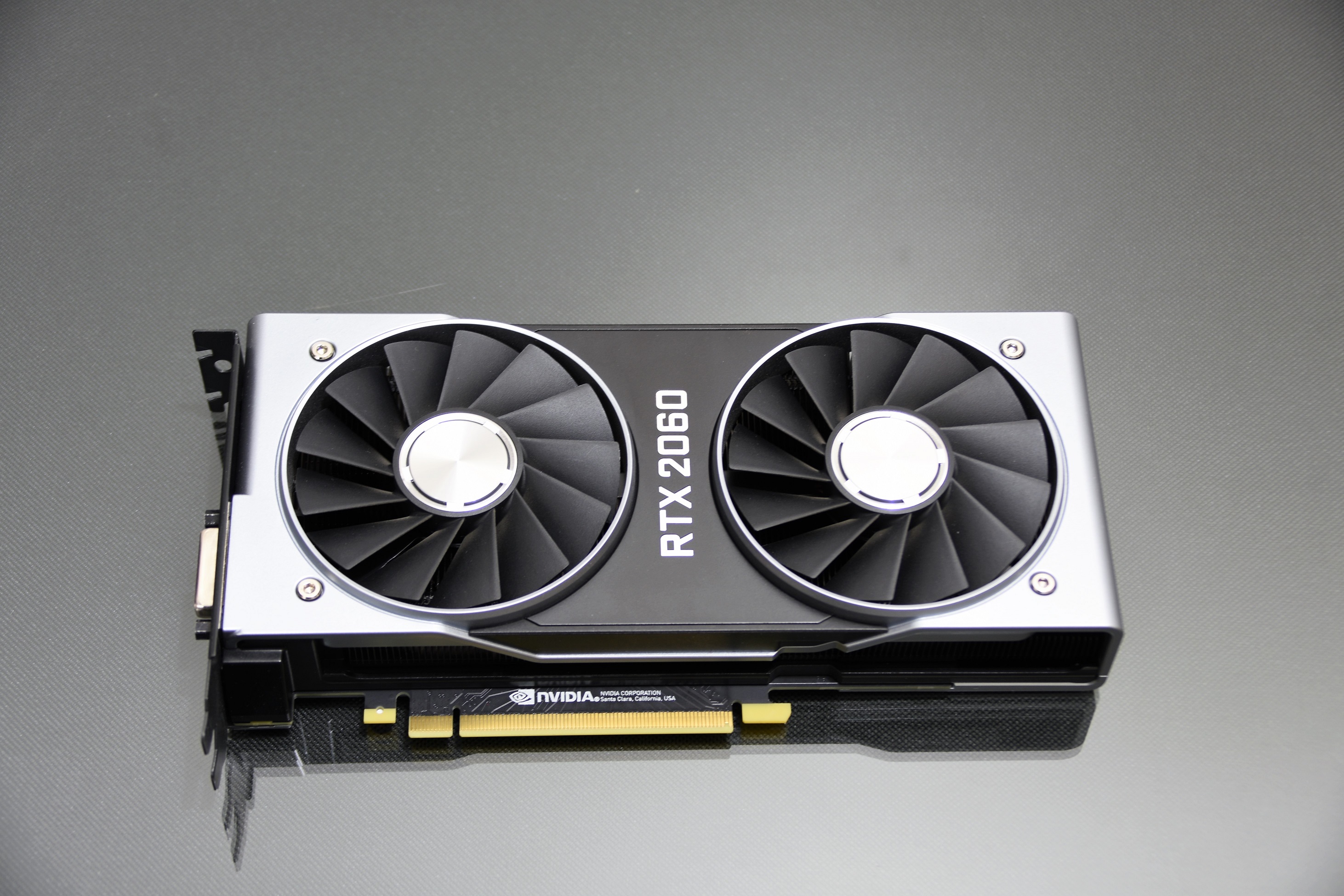


Characterizing NVDIA for its sober and futuristic models is how this NVIDIA RTX 2060 is presented, the smallest specimen of the RTX series whose differentiation is the Tensor Core, with respect to the GTX series.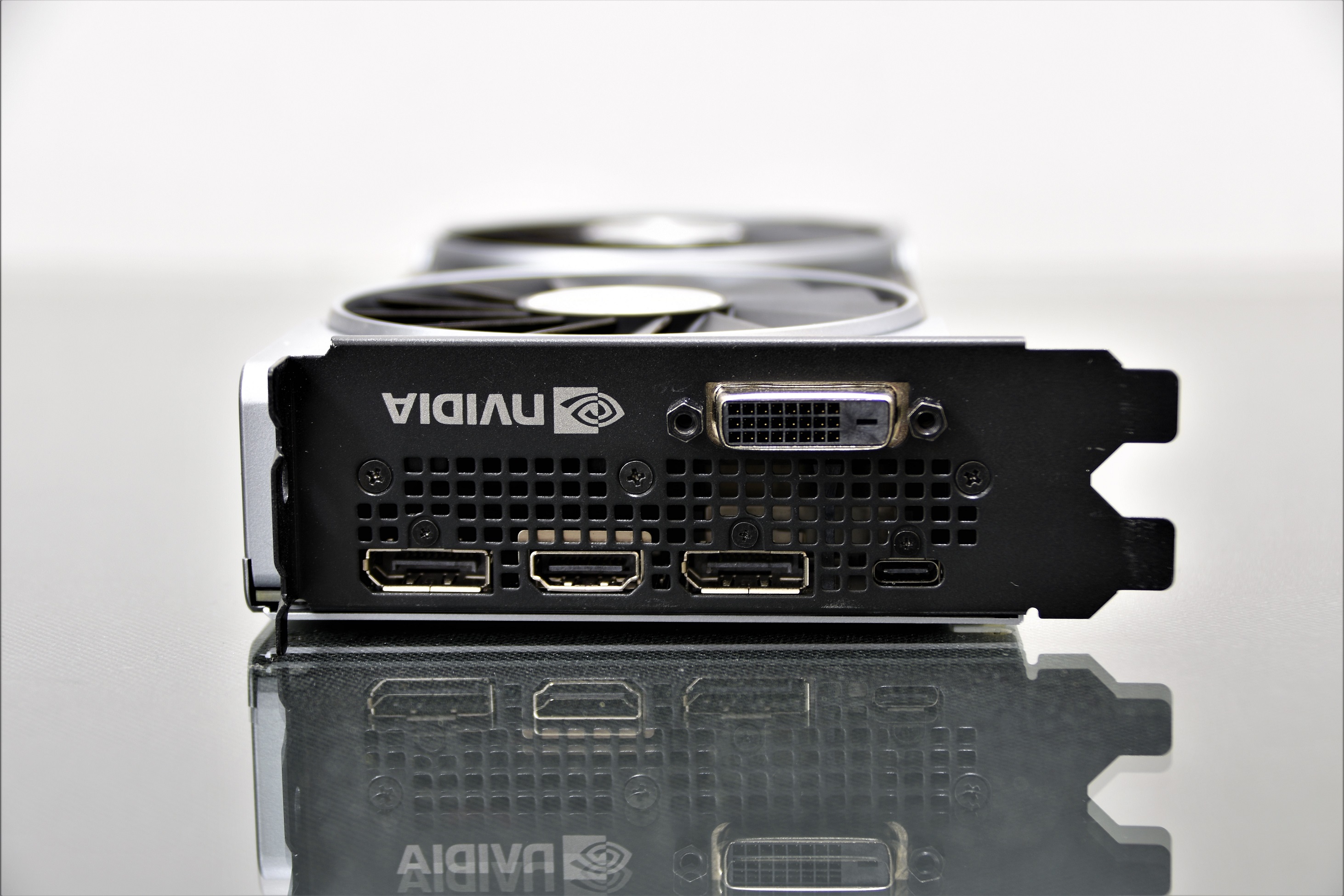 
2x Display Port, 1x HDMI, 1x DVI-D and USB Type-C for VR.
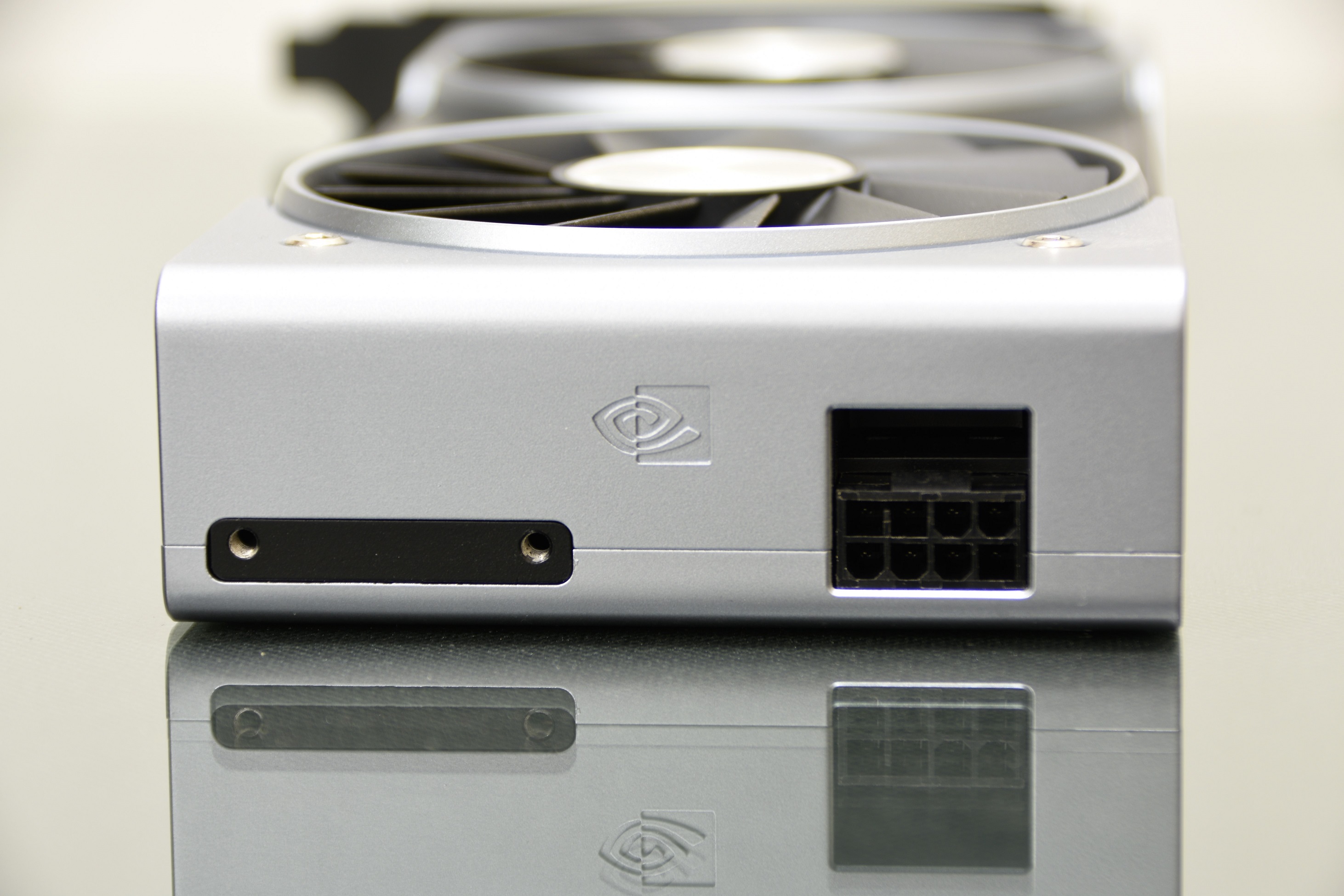

An 8-pin auxiliary connector for consumption that should be around 160W in relation to its TDP.
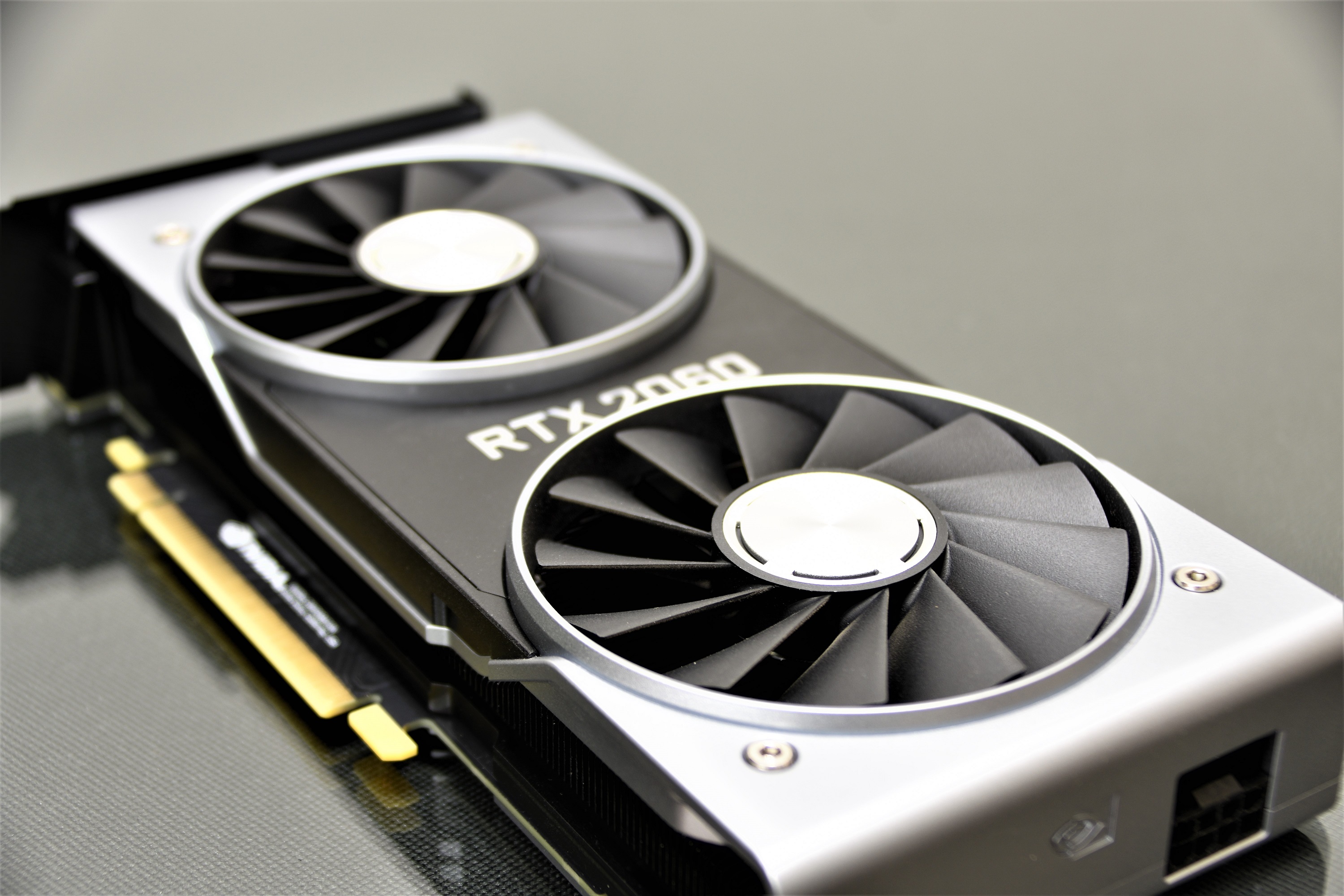

The design in the front view is remarkable in these NVIDIA RTX models, it clearly impresses us every time they launch a new generation. Avant-garde model that breaks the usual scheme in video cards (it doesn’t seem like a video card by far).
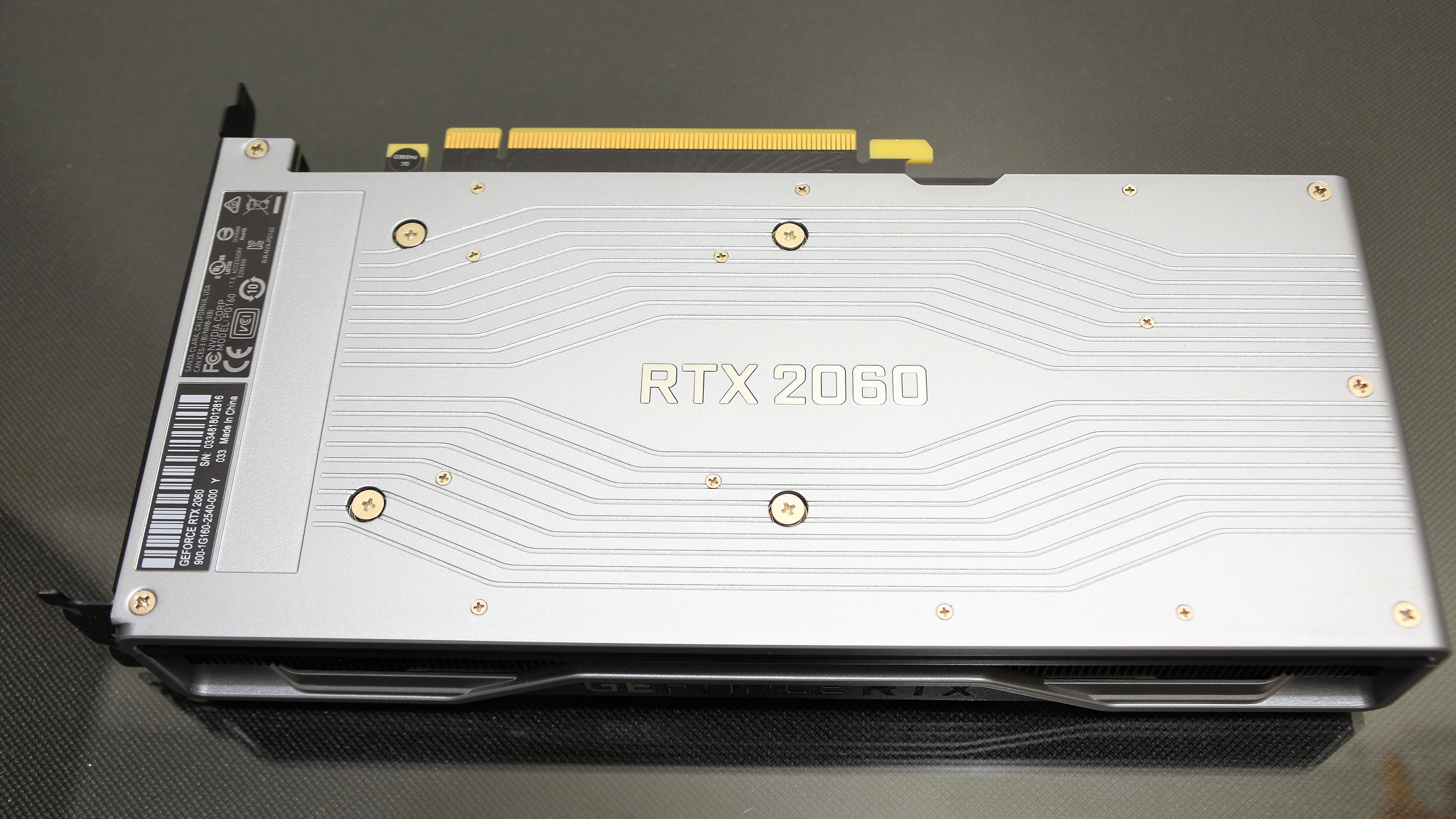

On the back side, an aluminum backplate follows the aesthetics of the front, visually creating a very attractive video card from different viewing angles.
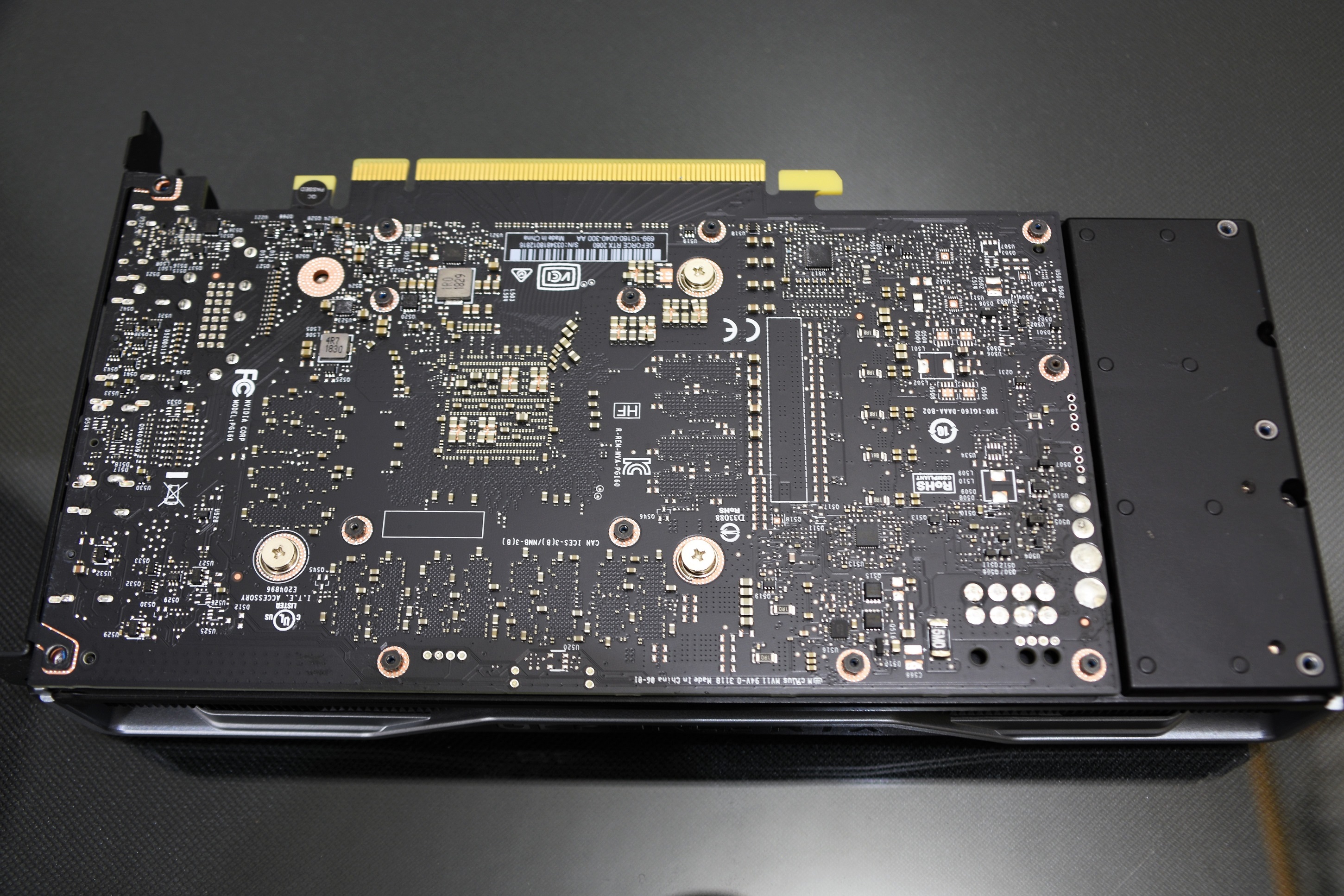
Under the backplate we do not find any thermal pad that involves temperature transfer. This is because the backplate is not made of a conductive material but rather offers protection and ultimately aesthetic. Looking at the PCB we see that this is only present in almost 3/4 of the card, the rest is complemented by an extension of the heatsink.
Testing and Methodology Platform.
| Test Platform | |
|---|---|
| Processor | – Intel Core i7 8086K |
| Motherboard | – ASUS ROG Maximus X APEX |
| Memories | – G. Skill TridentZ 3200MHz 2x8GB |
| Refrigeration | – EK-XLC Predator 240 |
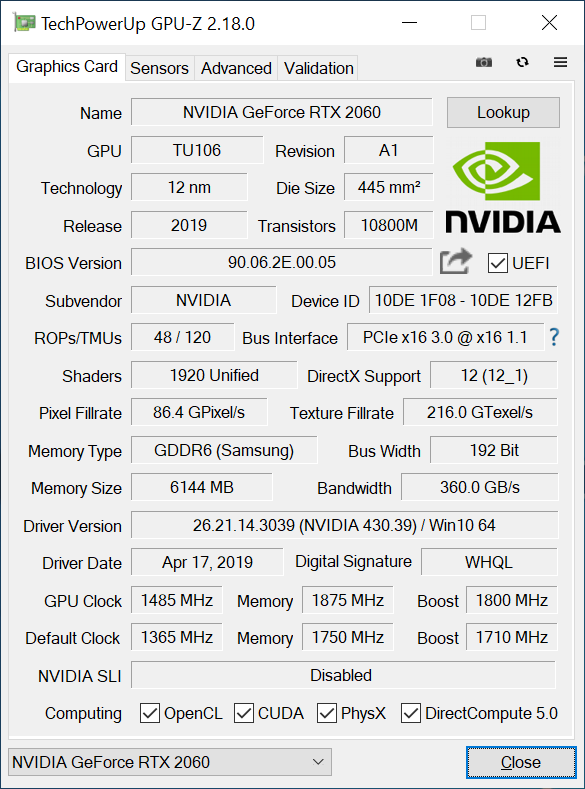
| Graphics card | – NVIDIA RTX 2060 8GB |
| Power supply | – Corsair RM1000X |
| Storage | – SAMSUNG 960PRO 512GB SSD M.2 |
| Monitor | – ASUS MG28UQ |
- Windows 10 Pro x64 operating system.
- The tests were performed in an environment with a temperature of approximately 25 ° C.
- The platform was used without a cabinet.
- The drivers used for the NVIDIA graphics cards: 425.31 WHQL
- The resolutions of the synthetic tests are the default ones for each of the benchmarks.
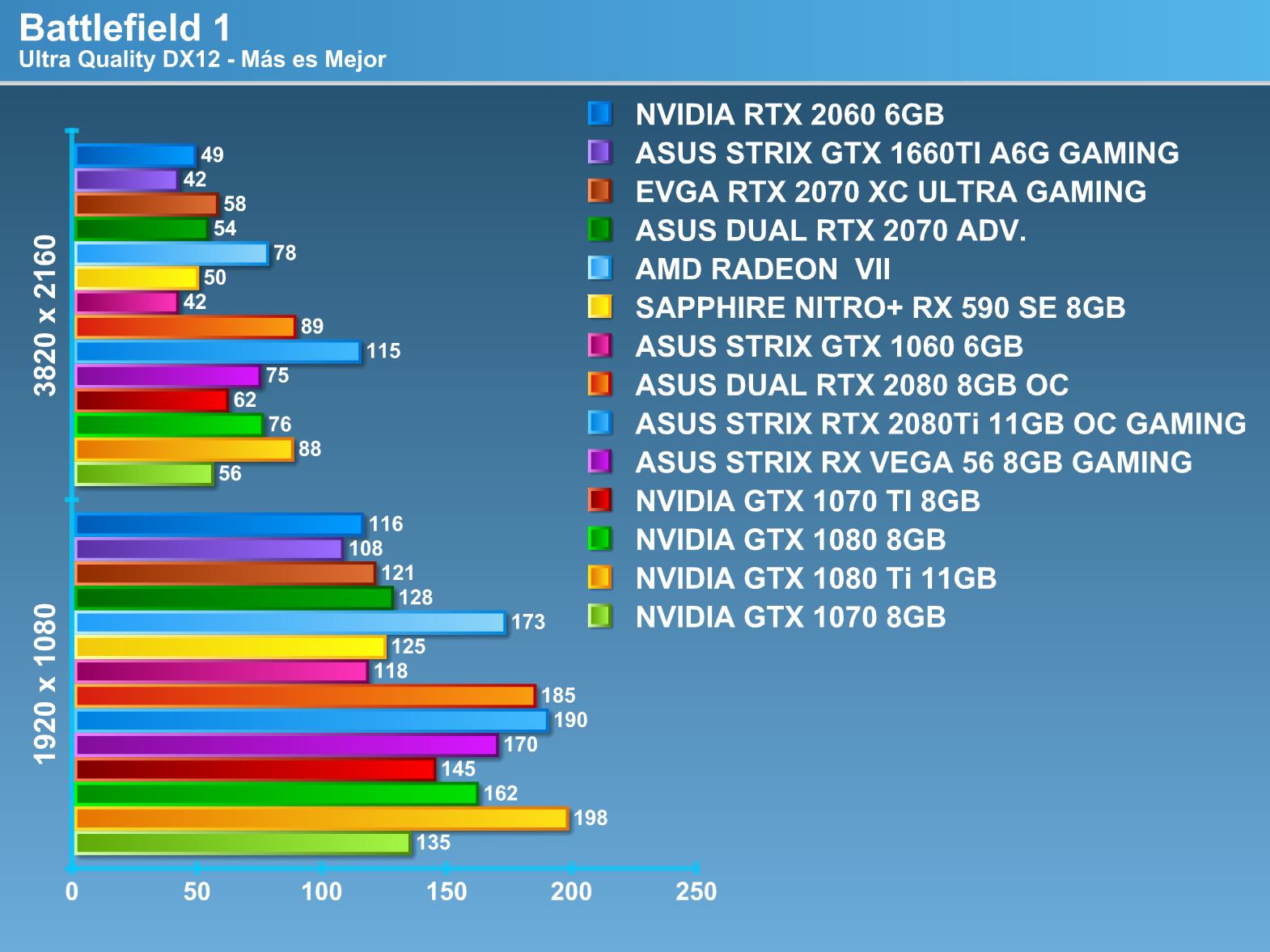
- The real test resolutions are 1920 × 1080 and 3820 × 2160 with all the maximum available graphics in each game.

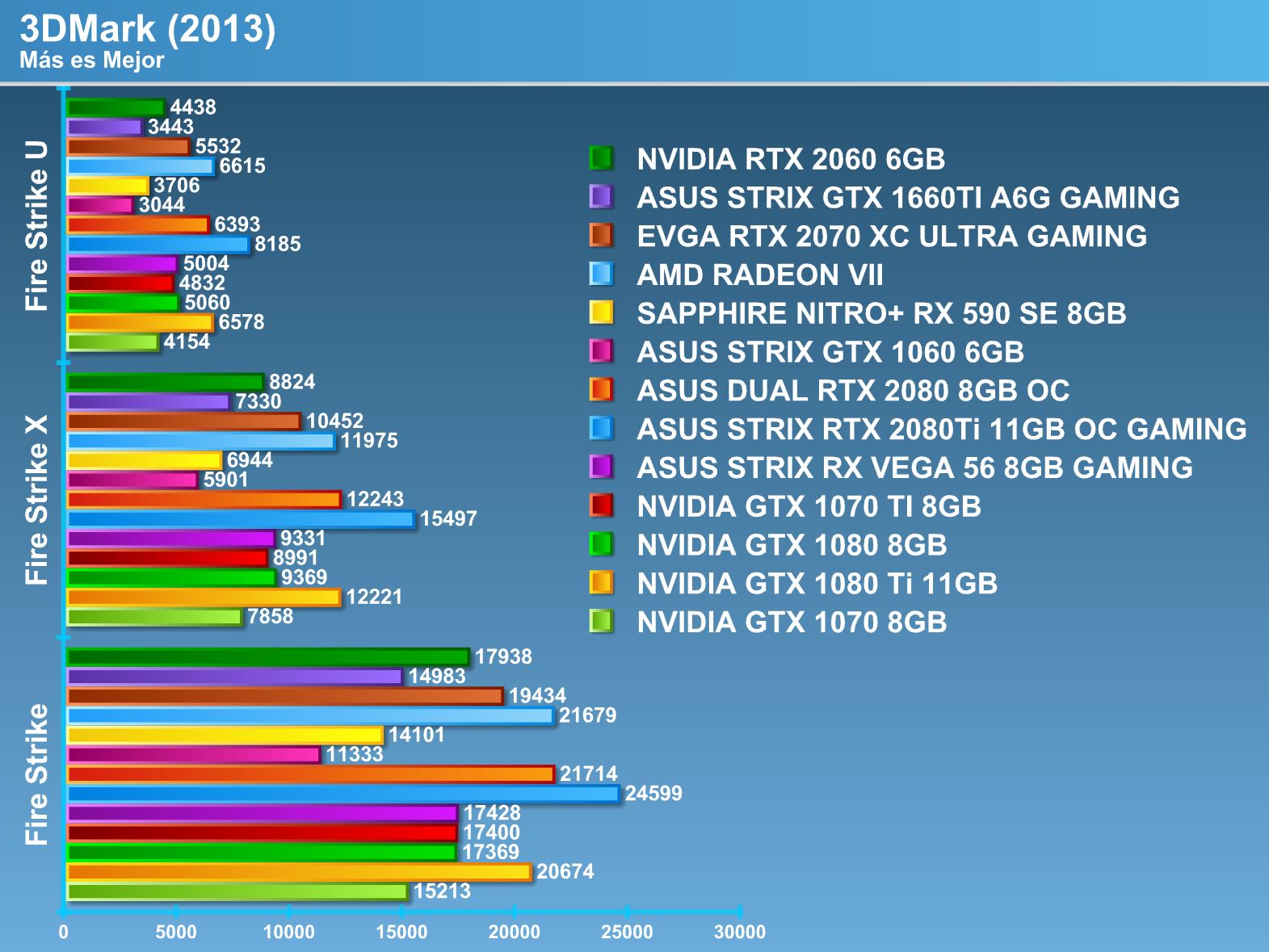
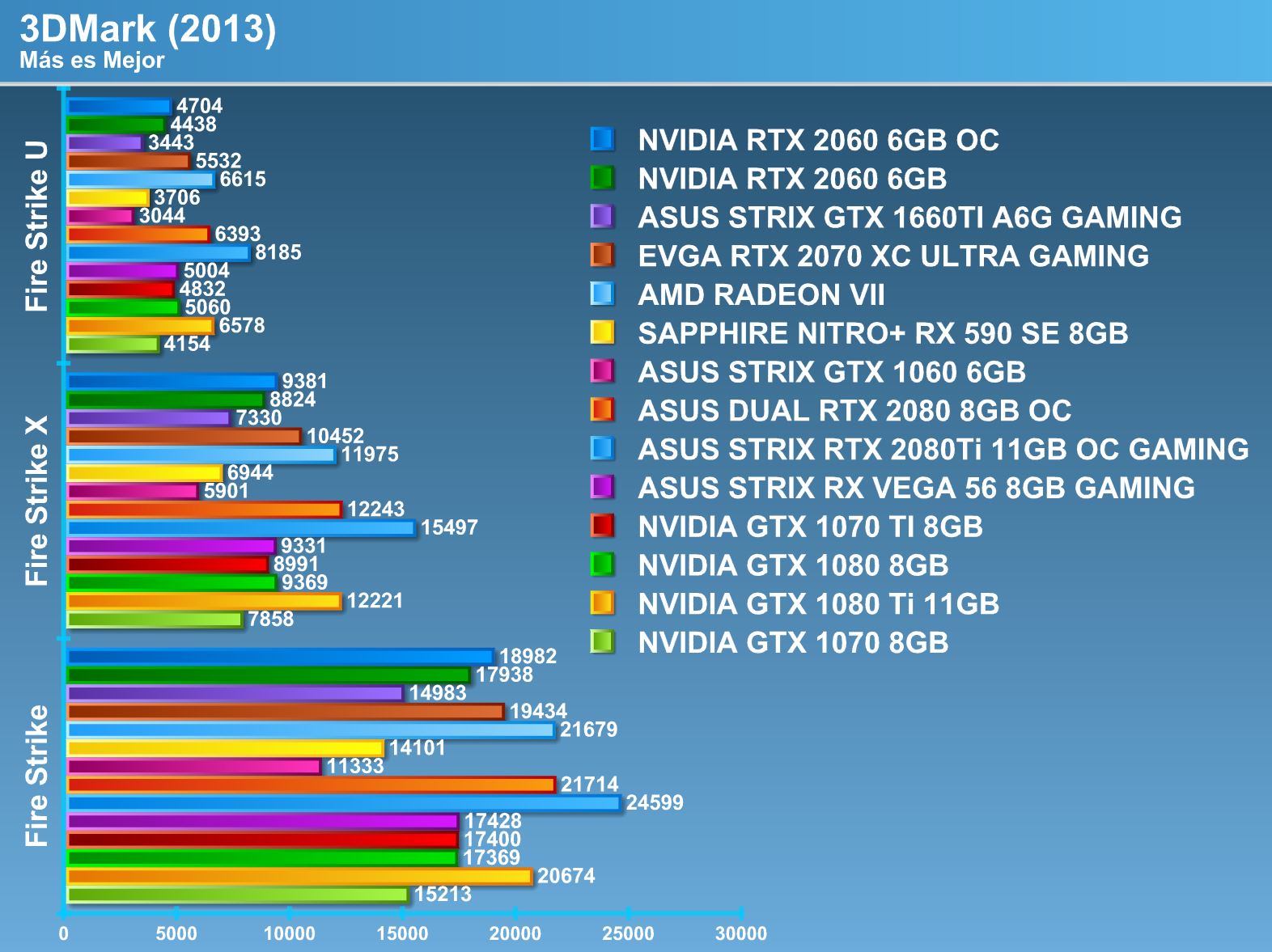
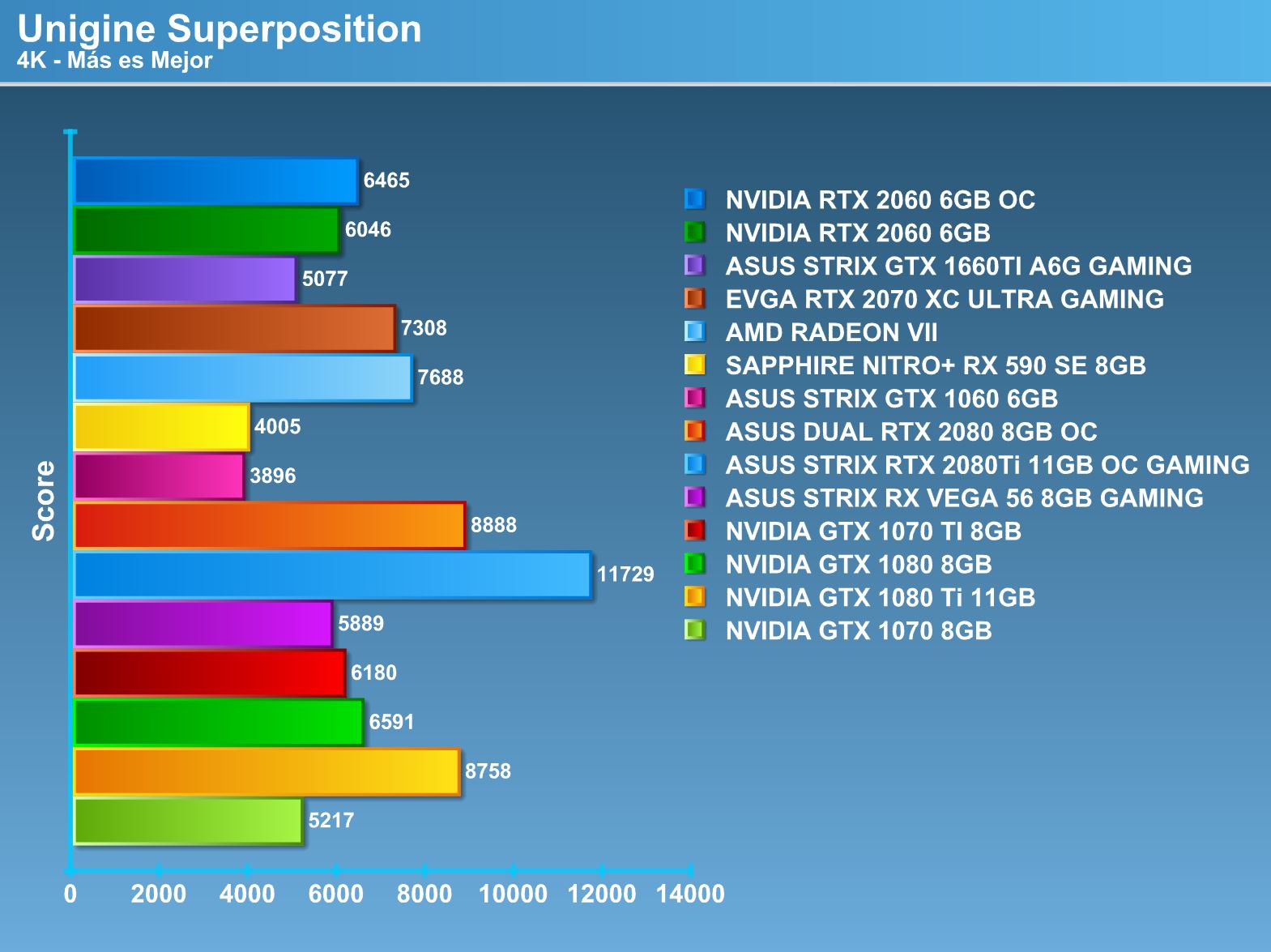
Synthetic tests

Real tests
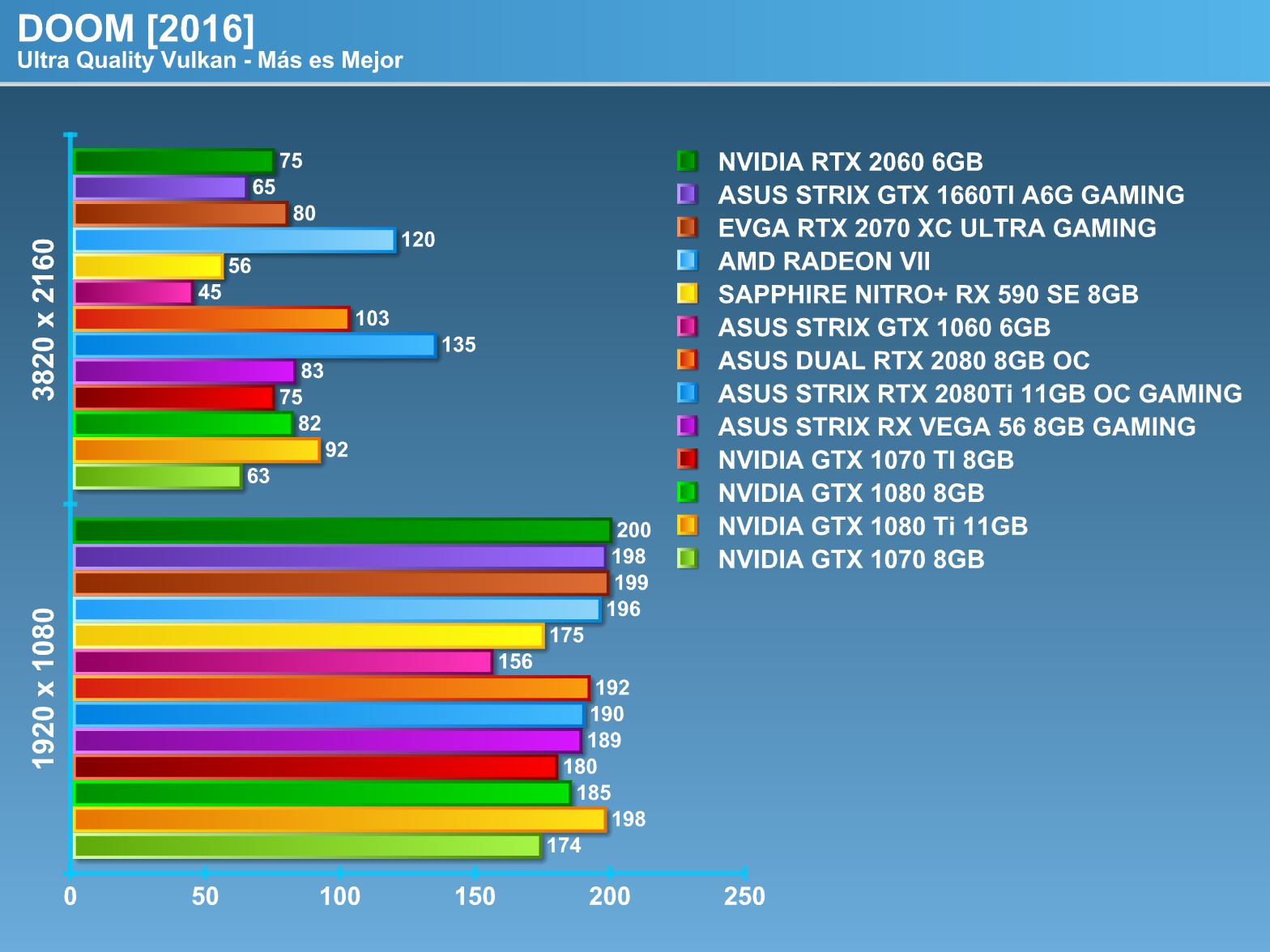
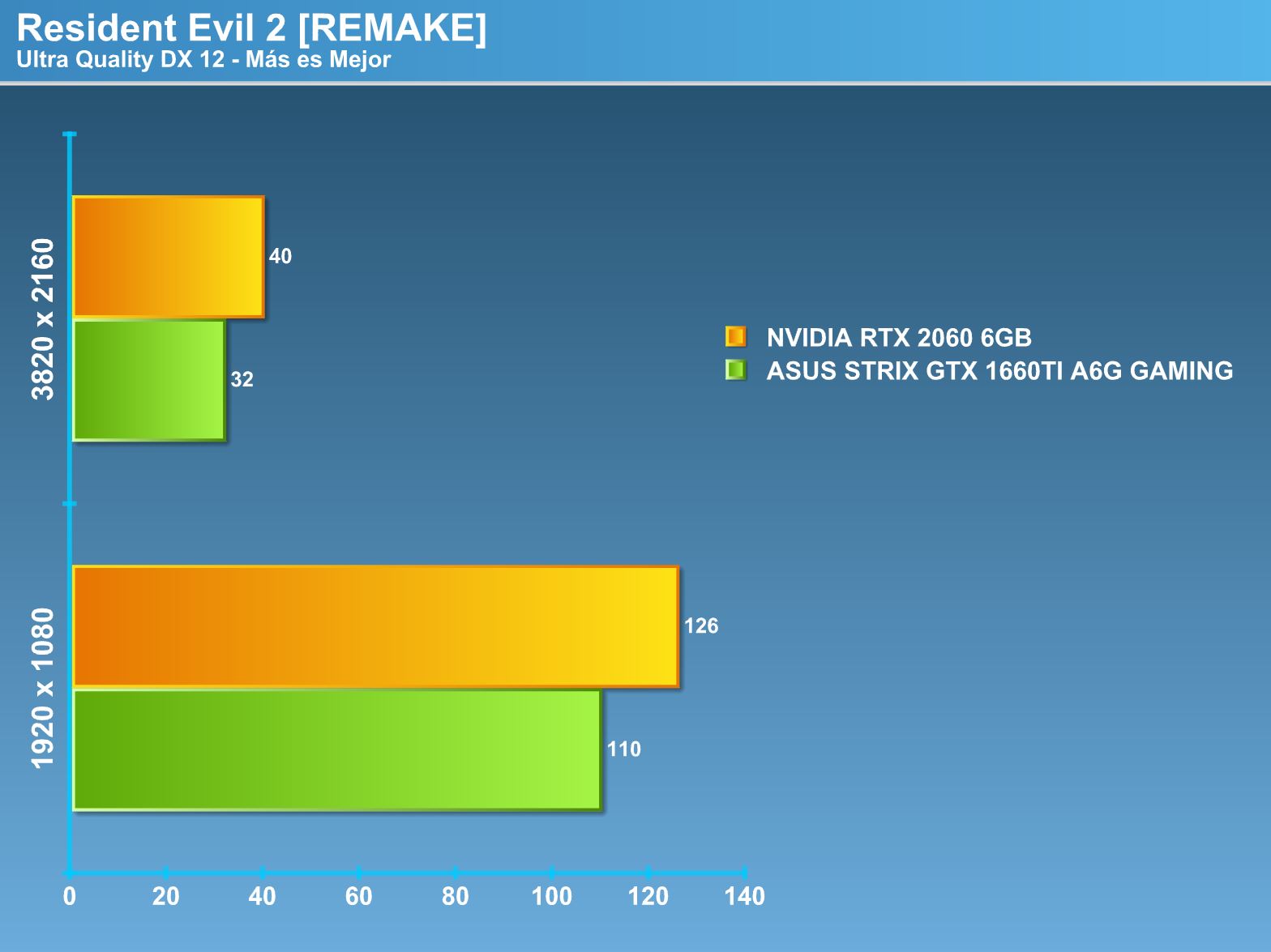
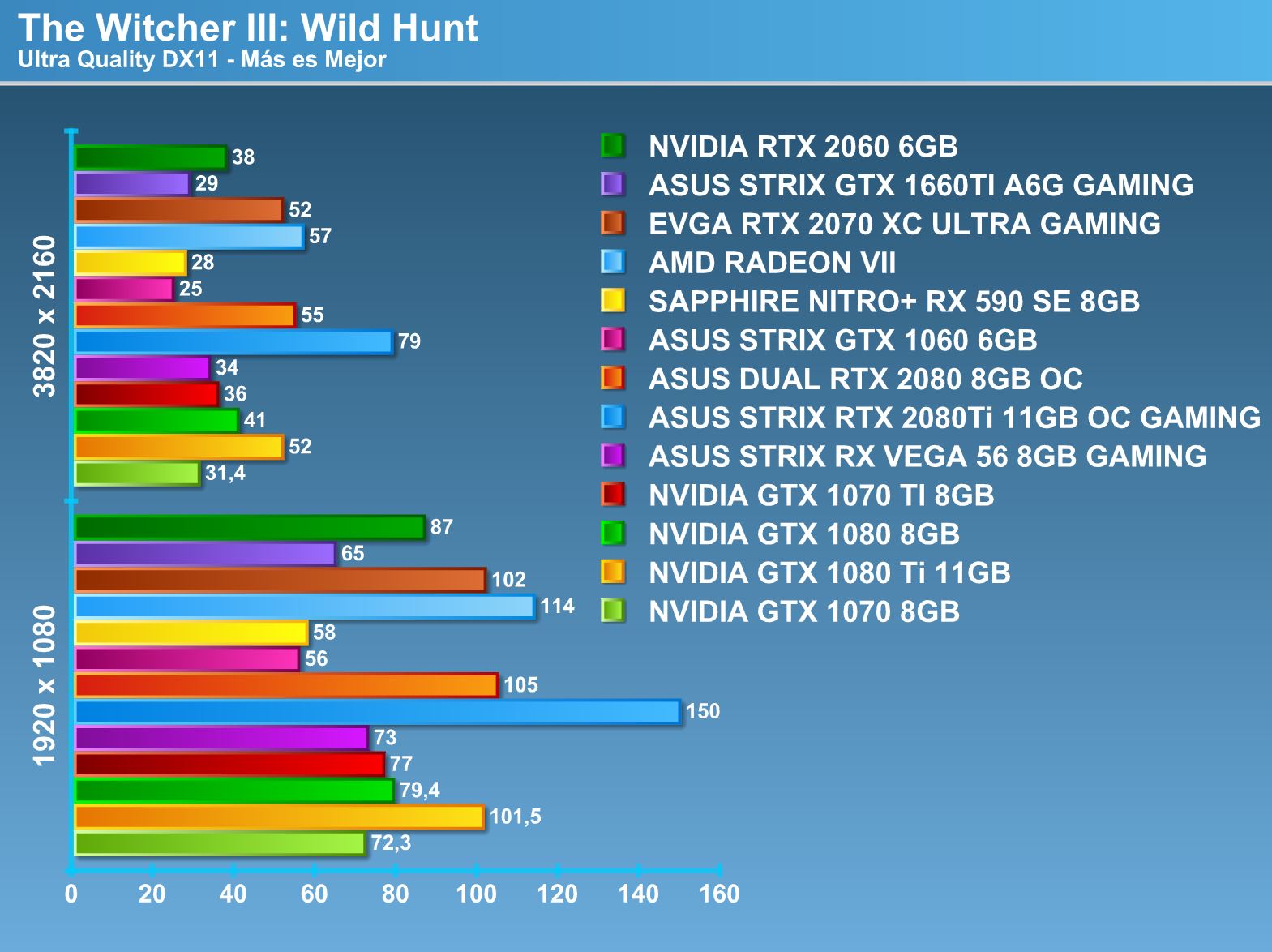
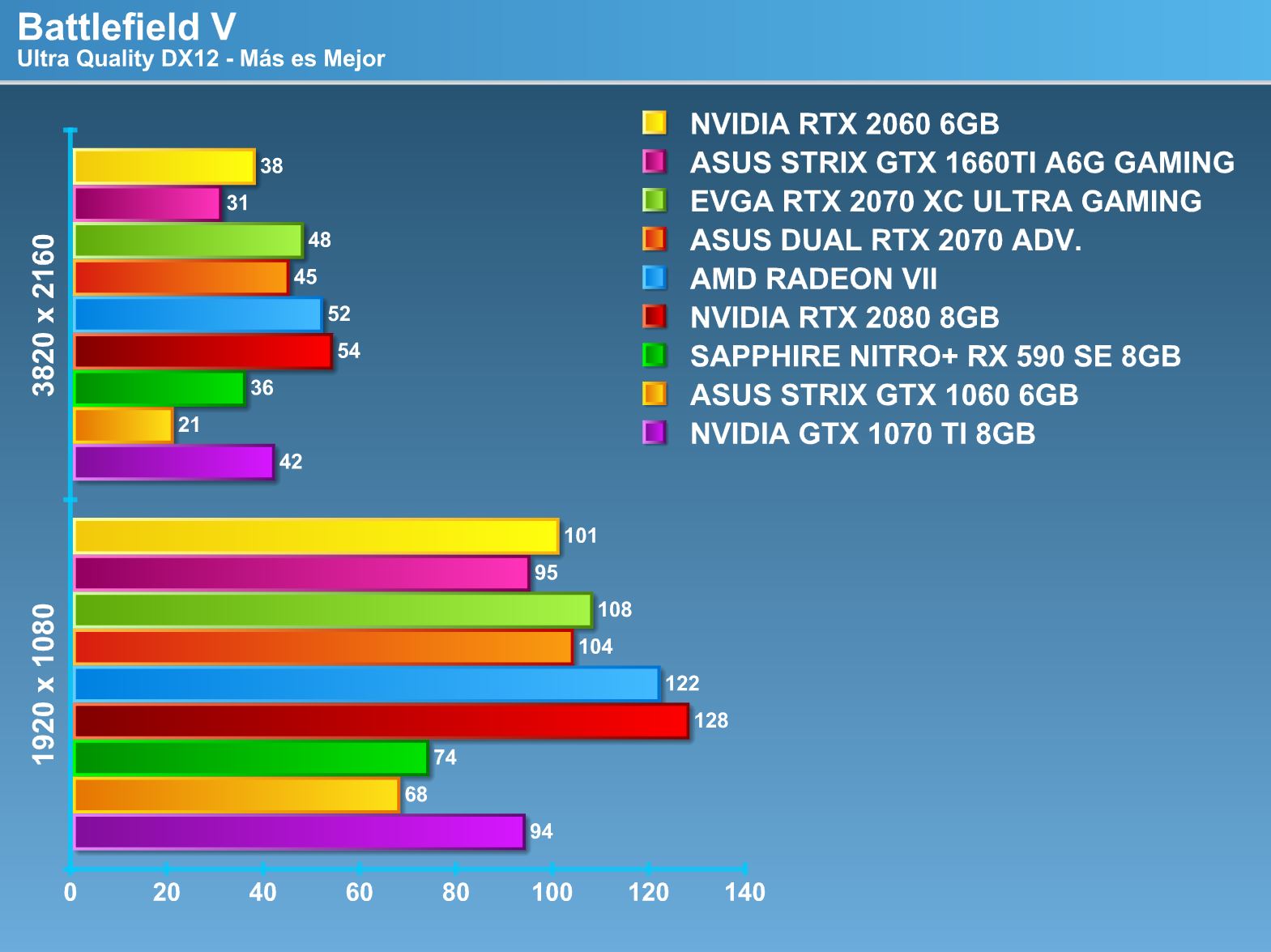
Overclocking.
The efficiency that NVIDIA has managed to develop in recent years has allowed it to deliver extra performance under overclocking, this is usually seen in the manufacturers of video cards that experiment with values over the preset ones. For the NVIDIA RTX 2060 there is no exception, you can see a GPU with potential due to its low temperature and consumption.
For this RTX 2060 model, the GPU was left at 1485MHz, an increase of 8.7% and in 1800 MHz memories this corresponds to 7.1% more. Let’s see how I scale this light overclocking.
Temperature.
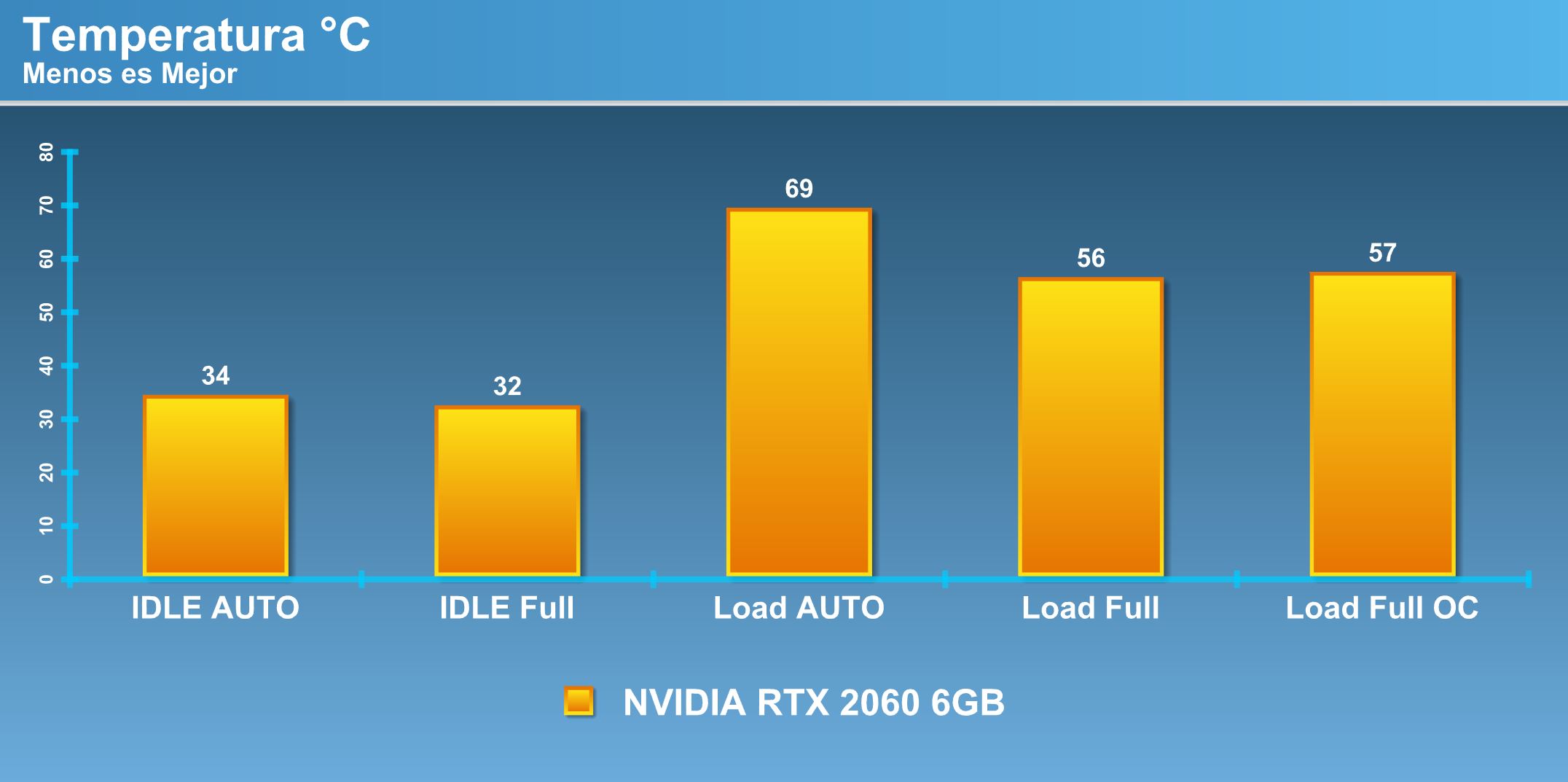
While it is a referential cooling system, it shows great potential to keep the video card at acceptable temperatures. The highest temperature pick is at 69 ° C, this is 100% loaded with fans at 44% of its speed, an acceptable value for a referential solution, while when it is brought to 100% of the speed, it falls sharply to the 56 ° C which rise slightly to 57 ° C when loaded under load overclocking.
Consumption.
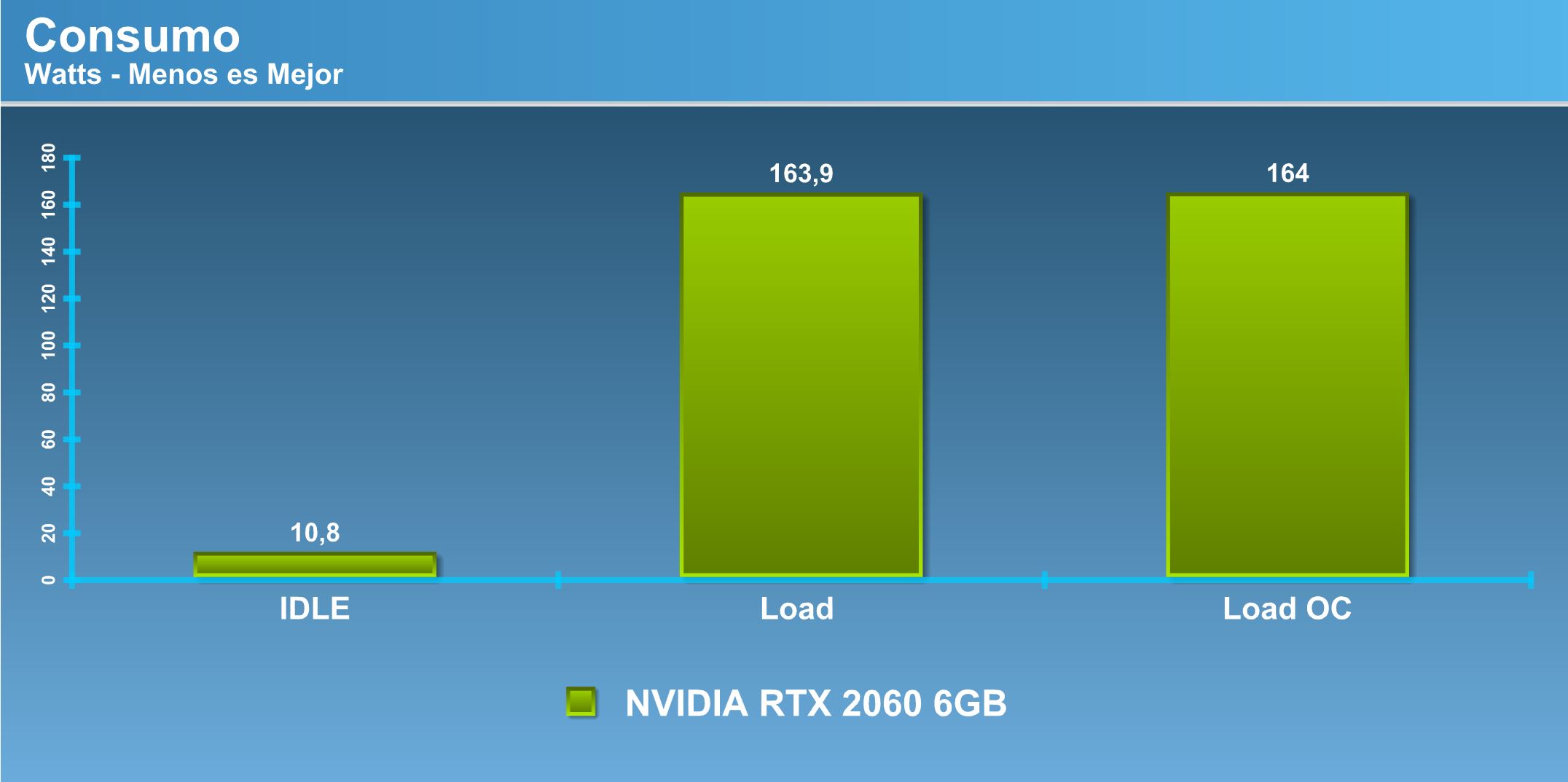
NVIDIA has been leading the efficiency section for a few generations, so in this section we can continue to trust that in this respect they make a big difference to the competition. Considering a TDP of 160W, the consumption that develops both in load and in load under overclocking, does not differ from that recorded in the TDP. It is surprising how even low overclocking consumption practically does not change.
Conclusion.
The NVIDIA RTX 2060 clearly fills the performance jump between the GTX 1660 Ti and the RTX 2070, a model more grounded within the RTX series that as a main feature are these Core Tensor that does not have the GTX 1660 Ti and make a difference in the narrow difference in performance between the two. At the moment, comparing these models of NVIDIA with the red side is somewhat ruthless considering that the RX 500 series has been on the market for quite some time, although we must not forget that if they have generated one or another problem with the price drops.
Aesthetically, NVIDIA surprises us with its referential models, although this is good for a few, and obtaining these referential models is not very easy considering that the manufacturers’ customized models arrive mainly on the market.
The temperature and low consumption are remarkable in this model, a consumption that is around 160W and is able to deliver all the experience in AAA games in high quality in 1080p and even in medium-high configuration is able to offer a pleasant experience in resolution 2K Following these factors of temperature and low consumption, this gives manufacturers the necessary tools to even find some ITX models of this version, which makes a GPU with great potential the possibility of adapting to different solutions.
Nowadays and with the large number of Turing-based models that NVIDIA has launched on the market, it is somewhat difficult to choose the model that best suits the striking “price / performance”, and that can also deliver the performance we are looking for. The medium-level market in video cards is very dense, and soon it will be even more so when Radeon launched its new Navi models.
With all that we manage to see this NVIDIA model we must give our approval as a recommended product, it meets the aspects of performance, temperature, consumption and price as the main factors in the choice of a video card