Halving (or halvening) is the hot word of these days: it is, for readers less familiar with the world of cryptocurrencies, the most important recurring event that concerns Bitcoin. More important because, in fact, it represents the heart of the economic model of the most famous currency in the world as it dictates its issue rate and, ultimately, the total circulating quantity. But let's go in order and try to understand what it is.
The origin of Bitcoin and the rules of the game
When Satoshi Nakamoto, the mysterious inventor of the algorithm that regulates the Bitcoin network, found himself determining the fundamental stakes of this technology, he faced an important question: what rate of issue to give to the cryptocurrency and whether to define a maximum ceiling on the working capital. One issue that Nakamoto addressed in an email:
"The production of new coins means that the money supply grows by a planned quantity, but this does not necessarily lead to inflation. If the money supply grows hand in hand with the number of people who use it, prices remain stable. If, on the other hand, it does not grow as fast as demand, there will be deflation and the first holders will see its value grow. The coins must be distributed in some way initially and a constant rhythm seems to be the best formula ".
This controlled rate of monetary inflation is one of the fundamental differences between cryptocurrencies and traditional fiat currencies, which in fact have an infinite issue due to the monetary policies of central banks. For this reason fiat coins are inflationary, while cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin are said to be deflationary. The main difference, at least in theory, is that fiat currencies tend to lose value over time while deflationary cryptocurrencies acquire value, or at least maintain it, over time. But how does the issue of "new currency" actually happen in the Bitcoin network? Nakamoto thought of linking the creation of new bitcoins to the process of verifying a new block of the blockchain.
Bitcoin: blockchain, mining and rewards
Small step back: the blockchain it is a shared and unchangeable data structure. It is a public and shared digital register, whose information is grouped into blocks which in turn are concatenated to each other in chronological order (hence the name blockchain). Concatenation occurs in a particular way whereby certain details of a block depend strictly on the previous block: this means that the manual compromise of a block would require, cascading and backwards, to modify all the previous blocks. The integrity of a blockchain is guaranteed by the use of encryption.
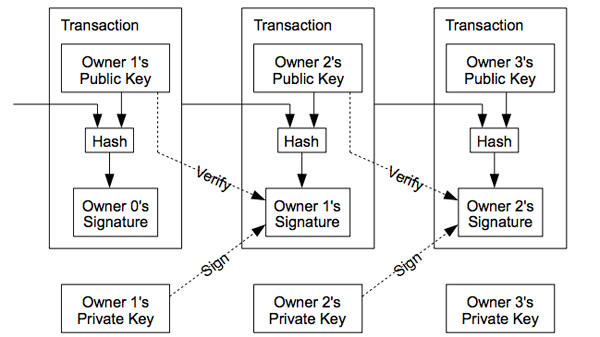
Bitcoin blockchain scheme
The Bitcoin network is based precisely on the principles of the blockchain and the distributed register: within this network there are entities, called "Miner" (simplifying: individuals who make available the computing power of one or more computers, or specialized hardware devices for the purpose) who have the task of verifying the legitimacy and correctness of the transactions that are grouped in the blocks. It is a process involving numerous miners and the first of them who manages to verify the transactions and then to confirm and create ("undermine") the new block, wins a reward: at the beginning the reward for each block was set at 50 bitcoins. In 2009 the monetary value of 50 bitcoins was less than 1 dollar.
However, this situation would not last forever: the rules of the Bitcoin algorithm require that the amount of the reward remains so for 210 thousand blocks, created which is reduced by half in a process that repeats over time. The halving of the reward (halving or halvening, in fact) is an event that therefore occurs with a certain periodicity, approximately every two years. The time required to verify a block is in fact roughly constant, about 10 minutes, also in this case due to the Bitcoin algorithm which dynamically regulates the difficulty of the mathematical question to be solved to verify the block of transactions, so as to compensate for the 'possible growth in the calculation capacity and keeping the issue of money constant.
Bitcoin halving: a recurring event
Given the rarity of the event, halving always generates an atmosphere of enthusiasm and euphoria in the cycles of the cryptocurrency market. On the other hand, as we said at the beginning, it is precisely the fundamental nucleus of the bitcoin economic model, because it ensures that the new coins are issued regularly and at a rate that follows a predictable trend. Since its birth, Bitcoin will face 32 halving, completed the last of which no new bitcoins will be issued since the maximum circulating quantity allowed and established by the algorithm will be reached, i.e. 21 million BTC.
Bitcoin's first halving took place on November 28, 2012, bringing the reward for miners from the original 50BTC to 25BTC. Back then the value of a single reward was around $ 12, but just a year later the value of bitcoins soared to over $ 1000 with an annual growth of 8500%. Instead, the second halving dates back to July 9, 2016, with the transition from 25BTC to 12.5BTC: then a single bitcoin was worth about $ 650, which grew to over $ 2,500 exactly one year later. But the true brake-free ride of the bitcoin value wore off in the following months, and as of December 17, 2017, the cryptocurrency hit its all-time high of over $ 20,000, the peak from which began a descent that ended a year later, on December 15, 2018, at a minimum of around 3,100 dollars. At the time of writing, the bitcoin value is around $ 8,700.
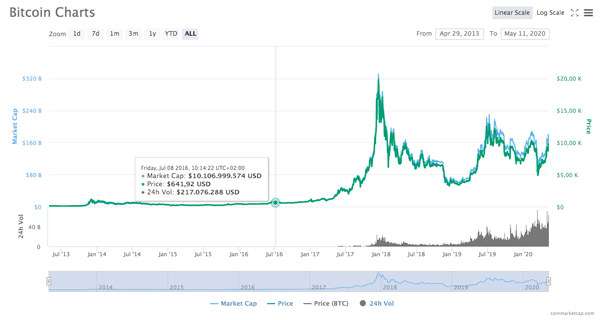
Linear scale
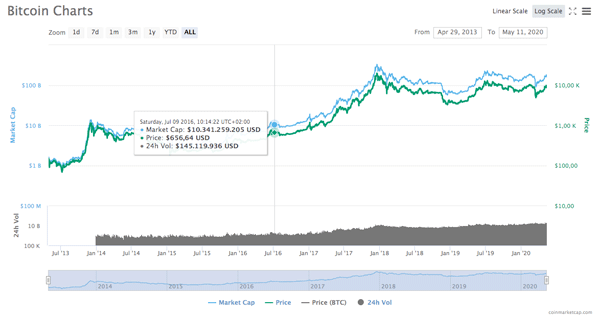
Log staircase
And we come to the present day: Bitcoin's third halving will take place today, May 11, 2020. The exact time cannot be estimated precisely as it depends on the time needed to identify the blocks that are missing before arriving at the fateful block number 630,000: indicatively the halving of the reward will take place around 10 pm Italian time: at that moment it will go from 12 , 5BTC to 6.25BTC which for miners means, at the present value, a prize of approximately 54 thousand dollars. The purpose of the reward is to cover the costs associated with the mining process which, as mentioned above, based on a series of mathematical operations, requires calculation power and ultimately consumes electricity. The reduction of the reward therefore has two effects on the entire bitcoin ecosystem: on the one hand it increases the scarcity, on the other it reduces the potential gain for the miners.
Bitcoin and the future
Actually the actual gain obviously also depends on the exchange rate of the bitcoins against the fiat currency. Theoretically, the increase in scarcity should also increase its value, as happened following the two previous halving: will this be the case again?
Obviously the future cannot be foreseen and an answer to this question is almost impossible: given that, at least by looking at the two previous cases, the growth in the value of bitcoin occurred over a period of 12-18 months after halving, it is also good to note that we are currently in a completely different scenario from the two previous halving.
The situation of the cryptocurrency market has changed profoundly: over the years numerous other cryptocurrencies have appeared on the market with more or less promising purposes and projects (Ethereum, just to mention the second largest-capitalization cryptocurrency after bitcoin) and many of them are shipwrecked while some continue on their way. The interest of the public, between speculators and users of the technology, has fragmented and after the bearish phase of the last two years many have moved away from the world of cryptocurrencies. Not to mention that precisely in these months, because of the COVID-19 pandemic, we are in an unprecedented global economic crisis.
Up to now the Bitcoin network, governed by the rules encoded in the algorithm devised by Satoshi Nakamoto, has seen the issue of over 85% of the total working capital of Bitcoin and the last digital coin will be issued no earlier than 2140. What will happen next? Miners will only be able to bear their costs by collecting network commissions which, at the moment, amount to less than 5% of the current reward. But this scenario will take place not earlier than a century: how many things can change in the meantime?













