Radeon RX 6600 XT Review: Test ( Proven) Specs| Hashrate | Overclocking| Benchmark| Testing: New solution on RDNA2 for Full HD with maximum settings.
The video cards of the Radeon RX 6000 family have brought back competition in the discrete GPU market, albeit nominally, since the market suffers greatly all year due to the situation with increased demand from cryptocurrency miners and, accordingly, greatly inflated prices.

AMD has turned out to be a solid family that competes well with the GeForce RTX 30 line in different price ranges. At first, AMD announced three models that came out at the end of last year, but then a less expensive model appeared – the Radeon RX 6700 XT, which we have already reviewed.
Many Read This as well – AMD Radeon RX 6800 vs RX 6800 XT: Hashrate | Specs | Test | Config | Profit
We will not write much about how everything changed due to the mining boom and insufficient production of semiconductor crystals, but these factors led to a severe shortage and a rise in market prices by two, or even three times! It is not surprising that manufacturers do not have much motivation to bring new solutions to the market, because miners are already grabbing everything that is produced, and even at exorbitant prices.
But the planned additions to the line were supposed to happen, and in August AMD rolled out the most budgetary (if you can say so now) solution of the new line.
Brief History – Radeon RX 6600 XT

The Radeon RX 6600 XT complements previously released GPUs in the lower mid-range (MSRP terms). It offers performance sufficient for any graphics setting at 1920 × 1080 in rasterized games and ray traced games under some conditions.
The new GPU incorporates all the advantages of the new RDNA 2 architecture – high-performance computing units with support for hardware ray tracing, a new type of Infinity Cache, albeit a reduced size in the version of the Navi 23 chip, on which the RX 6600 XT model is based, but all the same helping to improve effective memory bandwidth, and much more. Who needs this video card and why?
The answer is simple – to the most massive user. According to researchers from IDC, about two-thirds of monitors sold in the past year have a resolution of only Full HD (1920 × 1080). But there are quite a few models of such monitors with an increased screen refresh rate – up to 244-270 Hz, and all of them are intended mainly for gamers. The number of such fast gaming monitors on the market has grown dozens of times in recent years.
And the power of the most common video cards of past generations, such as the GeForce GTX 1060 and Radeon RX 480, is no longer enough to provide even 60 FPS in the most modern games at maximum quality settings. These solutions from AMD and Nvidia give only about 30 FPS in games such as Cyberpunk 2077, Godfall and Red Dead Redemption 2. And it is the owners of such GPUs that AMD offers an upgrade option to the Radeon RX 6600 XT model, which will provide 2- 2.5 times better performance in many games.

And the solutions of the previous generation AMD Radeon RX 5600 XT and RX 5700 can be replaced by the RX 6600 XT, because the new product provides 30% -40% higher performance compared to similar options from the previous family. And even if we take into account not the best situation on the market, the Radeon RX 6600 XT may well become one of the successful options in this price segment. After all, improvements in the RDNA 2 architecture have significantly increased the energy efficiency of the new product, and also new opportunities have appeared: hardware ray tracing and other DX12 Ultimate features that video cards of the past cannot boast.
Specifications – Radeon RX 6600 XT graphics card
The core of the Radeon RX 6600 XT model we are reviewing today is the new Navi 23 graphics processor, which is based on the second generation RDNA architecture, and it is closely related to both RDNA 1 and the latest generations of GCN. And before reading the article, it will be useful to familiarize yourself with our previous materials on AMD video cards:

| Graphics Accelerator Radeon RX 6600 XT | |
|---|---|
| Chip codename | Navi 23 |
| Production technology | 7 нм TSMC |
| Number of transistors | 11.1 billion (Navi 22 – 17.2 billion) |
| Core area | 237 mm (Navi 22 – 336 mm) |
| Architecture | unified, with an array of processors for streaming processing of any kind of data: vertices, pixels, etc. |
| DirectX hardware support | DirectX 12 Ultimate, with Feature Level 12_2 support |
| Memory bus | 128-bit: 2 independent 64-bit memory controllers with GDDR6 support |
| GPU frequency | 1968 (base) to 2589 MHz (turbo) |
| Computing units | 32 CUs with a total of 2048 ALUs for integer and floating point calculations (INT4, INT8, INT16, FP16, FP32 and FP64 formats are supported) |
| Ray tracing blocks | 32 Ray Accelerator blocks to calculate the intersection of rays with triangles and BVH bounding volumes |
| Texturing blocks | 128 texture addressing and filtering units with support for FP16 / FP32 components and support for trilinear and anisotropic filtering for all texture formats |
| Raster Operation Blocks (ROPs) | 8 wide 64-pixel ROPs with support for various anti-aliasing modes, including programmable and FP16 / FP32 framebuffer formats |
| Monitor support | support for up to six monitors connected via HDMI 2.1 and DisplayPort 1.4a |
| Specifications of the reference Radeon RX 6600 XT graphics card | |
|---|---|
| Core frequency (game / peak) | 2359/2589 MHz |
| Number of universal processors | 2048 |
| Number of texture units | 128 |
| Number of blending blocks | 64 |
| Effective memory frequency | 16 GHz |
| Memory type | GDDR6 |
| Memory bus | Page 128 |
| Memory | 8 GB |
| Memory bandwidth | 256 GB / s |
| Computational Performance (FP16) | to 21.2 teraflops |
| Computational Performance (FP32) | to 10.6 teraflops |
| Theoretical maximum fill rate | 165.7 gigapixels / s |
| Theoretical texture sampling rate | 331.4 gigatexels / s |
| Tire | PCI Express 4.0 x8 |
| Connectors | one HDMI 2.1, three DisplayPort 1.4a |
| Energy consumption | up to 160 watts |
| Additional food | 8 pin connector |
| The number of slots occupied in the system chassis | 2 |
| Recommended price | $ 379 (33 260 rubles) |
The name of the new video card model fully corresponds to the basic principle of naming for AMD solutions adopted several years ago – compared to the Radeon RX 5600 XT, only the generation number has changed. The XT suffix remained, and so far no other models of video cards based on the same chip have been released. And in comparison with the Radeon RX 6700 XT, the new video card is one step lower, and everything looks logical here.
The recommended price for the Radeon RX 6600 XT is $ 379 – a hundred less than that of the Radeon RX 6700 XT, and the price recommendation for the Russian market is 33 260 rubles, which looks like a slightly overpriced offer against the background of the GeForce RTX 3060 model, which seems to be cost less, despite the fact that the RTX 3060 Ti is only slightly more expensive. But all these reflections are purely theoretical, since the real retail prices are determined by the deficit, the efficiency of mining and the demand on the part of the participants in this business.
Interestingly, AMD does not have a reference version of the Radeon RX 6600 XT, we only saw it in renders. So there is no point in describing the cooling and power supply system, they will all be different. Note that the power consumption of the entire video card is 160 W, which is noticeably less than 230 W of the Radeon RX 6700 XT. Therefore, many cards use only one 8-pin power connector for additional power supply, although AMD partners may well decide the issue differently.

Many variants of the Radeon RX 6600 XT from different companies with their own PCB design and cooling systems have already entered the market. Unlike the RX 6700 XT, there are also very compact video cards, but there are also three-fan monsters, which for the budget RX 6600 XT seem to be a bit overkill.
Ready-made systems with the installed Radeon RX 6600 XT are already available for sale from Acer, Alienware, Dell and HP, and the corresponding video cards of the new model have been released by all AMD partners: ASRock, Asus, Biostar, Gigabyte, MSI, PowerColor, Sapphire, XFX and others – all of them are available for sale from August 11 in various versions, with their own options for printed circuit boards and cooling systems.
Architectural features
The Navi 23 GPU is a junior model compared to the Navi 22 chip, and it is also based on the RDNA 2 architecture, the main task in the development of which was to achieve the highest possible energy efficiency, as well as to implement the missing functionality that the competitor and which are included in the DirectX 12 Ultimate specifications – we have already talked about them in detail in the reviews of the Radeon RX 6800 and Radeon RX 6800 XT.
The basic blocks of any modern AMD chip are Compute Units (CUs), each of which has its own local storage for exchanging data or expanding the local register stack, as well as cache memory and a full-fledged texture pipeline with texture sampling and filtering units. Each of these CUs independently scheduling and scheduling work. Overall, the architecture of RDNA 2 is very similar to RDNA 1, although it has been heavily redesigned.
We draw the block diagram of Navi 23 in our head again on our own – the new chip contains 32 computational CUs, consisting of 2048 ALUs, 128 TMUs and 64 ROPs. The Radeon RX 6600 XT version uses the full version of Navi 23 in which all the chip blocks are active. Interestingly, the number of all execution units does not differ that much from their number of units in the full version of the older Navi 22 chip.
There is much more difference between these GPUs in the memory and data caching subsystem, the older chip has a 192-bit bus, while the Navi 23 has only a 128-bit bus. As you know, to improve the efficiency of using relatively narrow memory buses and compensate for the relatively low bandwidth of GDDR6, AMD came up with a large data cache – Infinity Cache, which really helps to improve the position of chips with low memory bandwidth. This global cache allows you to accelerate access to any data received by the GPU, and serves as an intermediary between the GPU and the slow video memory.
But if in the older Navi 22 this cache memory was as much as 96 MB, which is slightly less than 128 MB for top solutions, then in Navi 23 it was left quite a bit – only 32 MB. That is, Navi 23 has only 20% fewer computing units compared to Navi 22, but the memory bandwidth is noticeably lower, and the amount of cache memory is generally reduced by three times. So we won’t be surprised if the performance of the RX 6600 XT is more limited by the memory subsystem, especially when it comes to resolutions higher than Full HD.
To improve energy efficiency, AMD specialists redesigned all blocks in RDNA 2, rebalanced the pipeline, found and eliminated all bottlenecks, reworked data lines, processing geometry inside the chip, and also used the experience of designing CPUs with a high operating frequency. The result turned out to be the most impressive in terms of energy efficiency gain, but from the point of view of logic circuits, the roots of the previous version of the architecture are clearly visible in the computational units of RDNA 2.
Radeon RX 6600 XT has 8 GB of local memory, and at the moment this amount can be considered the right decision. It provides some margin for the future, because games are becoming more demanding, using more and more resources, and the same hardware ray tracing imposes additional requirements on the amount of memory. A fairly large number of modern games already take up more than 8 GB of memory at maximum graphics settings. It’s also useful because modern consoles have a lot of memory and fast SSDs, and future multiplatform and ported games may well start requiring 8GB of local video memory in the future.
Read the rest of the details about all the changes and innovations of the new graphics processor in the big review of the Radeon RX 6800 XT, where it is written about the new Infinity Cache, and about improved access to Smart Access Memory, and about changes in support for video codecs and input port standards -Output. The junior model of the RDNA 2 architecture is no different from the older GPUs in terms of functionality, although the chips are different, they can do all the same.
For example, the capabilities for hardware encoding and decoding of video data in the Radeon RX 6600 XT are very wide, the new solution supports all common codecs: H.264 (4K at 180 FPS decoding and 4K at 90 FPS encoding), H.265 (decoding 4K resolution at 90 FPS or 8K @ 24 FPS and encoding 4K @ 60 FPS and 8K @ 24 FPS), and the chip can decode VP9 (4K @ 90 FPS and 8K @ 24 FPS) and AV1 (4K @ 120 FPS or 8K @ 30 FPS) formats …
As for the performance of the new product, it must be remembered that the Radeon RX 6600 XT is designed for mid-range systems, the most common on the market. The new solution provides a sufficient level of performance for Full HD resolution in all modern games, including the ability to enable some effects using ray tracing. It is strange to demand more from the new GPU.
And if we compare the Radeon RX 6600 XT model we are considering today with the similarly priced GeForce RTX 3060, then the AMD video card is up to 15% faster than the competitor, judging by the measurements of the company itself:

Even with tracing turned on in Dirt 5 and Godfall. To be fair, AMD admits that their solution is inferior to the competitor in such games with ray tracing as Battlefield V, Doom Eternal, Metro Exodus, Shadow of the Tomb Raider and other games that use ray tracing more actively – most often these games were created for competitor graphics cards, which have a clear advantage due to dedicated hardware units dedicated to the task of ray tracing.
But in competitive online games, the new solution of the Radeon RX 6000 line should be slightly faster than the competing Nvidia video card, which is important for owners of the very high refresh rate gaming monitors that we talked about at the beginning of the article. We will definitely check all the comparative performance data in the practical part of the article, and now let’s talk about the company’s technologies.
AMD software technologies
We will also tell you about the software improvements and innovations associated with the announcement of the new solution. Introduced in August, the AMD graphics card supports all of the company’s modern technologies, such as Radeon Boost and Radeon Anti-Lag , which are useful for esports players in that the former increases FPS in dynamic scenes, and the latter reduces latency when playing online. Improvements to Radeon Boost allow variable rate shading (VRS) to be used in some games, which can be useful in multiplayer battles.
AMD is also proud of its Smart Access Memory technology , which is nothing more than the Resizable BAR feature available for modern Nvidia graphics cards. But AMD claims that it is their implementation of the GPU access technology to a part of the RAM that works much more efficiently – at least in their selected games.
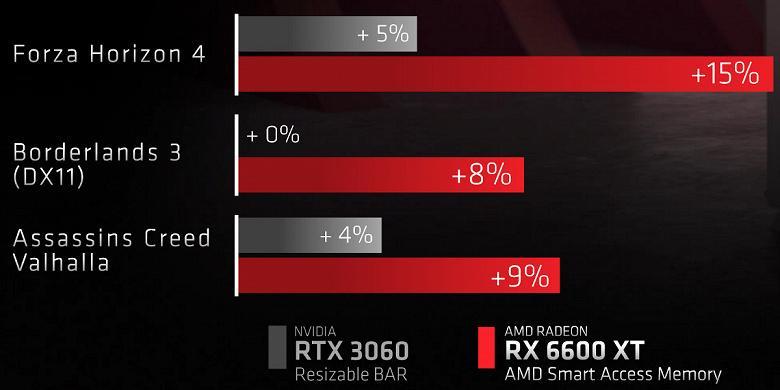
However, in other games with a significant impact of RBAR / SAM inclusion, the advantage of the new AMD solution over the RTX 3060 will be somewhat more modest – 6% -8%, but this is enough to proclaim a clear victory over the rival.
Of the new useful technologies, we note FidelityFX Super Resolution , which allows you to increase performance with a slight decrease in picture quality, which is almost imperceptible in dynamics at a sufficiently high output resolution. The technology works in part similar to DLSS of rival Nvidia, although it does not use data from previous frames and does not process it using a neural network. Rather, FSR is simply an advanced technique for improving the display of an image rendered at a lower rendering resolution.
But even in such a simple form, it allows you to significantly increase performance with a sufficiently high-quality picture, and even makes it possible to play with ray tracing (not always and only in a relatively low Full HD resolution). Well, without tracing, even the most modern and demanding games in Full HD just start to fly! And not the most demanding ones – they generally show 200 FPS and more:

FidelityFX technology is open source and available to everyone as part of the GPUOpen initiative, which simplifies its implementation in game projects and the corresponding optimization. Previously, one of the components of this technology was known to us as FidelityFX Contrast Adaptive Sharpening (CAS) – this part is responsible for increasing the clarity of the picture, but the FSR includes another important part that is involved in scaling a low-resolution image to a higher one, with high-quality restoration of details.
There are four FSR quality modes:
- Ultra Quality is the highest quality mode, rendering the picture with the quality that is as close as possible to rendering at full resolution, with a slight improvement in performance.
- Quality – good quality of restoration of image details and a decent increase in rendering speed – perhaps, it can be recommended in most cases.
- Balanced – a mode with a balanced increase in performance and still a fairly good quality of the final image, sometimes inferior to the native rendering resolution.
- Performance is the most productive mode with a high increase in speed, but with obvious losses in rendering quality, so it should be chosen only when there is a big lack of smoothness.

The good thing about FSR technology is that it works on a wide range of hardware, including older graphics cards, and not even just AMD. Yes, the technology is optimized for RDNA 1 and RDNA 2 architectures (Radeon RX 5000 and RX 6000), but it also works well on Radeon RX 500 and RX 400, and RX Vega with integrated graphics in AMD Ryzen processors. Also, importantly, FSR is supported on competing solutions – Nvidia GeForce RTX 30 and RTX 20 series graphics cards, as well as GeForce GTX 16 and GTX 10.
The new software technology is very easy to implement into the code, since it does not require access to the data of previous frames. In fact, it works like another post-filter, but it increases the output resolution, and in theory it can even be screwed onto old games if they require more performance. FSR is already available for the most common game engines Unity and Unreal Engine, so it is not surprising that almost since the announcement, FSR technology has been supported in several games at once, and their list is only expanding.
So, with all the theoretical data and potential capabilities of the new AMD video card, we got acquainted, it’s time to take a look at it before proceeding with the tests.

Features of the AMD Radeon RX 6600 XT graphics card
Manufacturer Information : Sapphire Technology (Sapphire trademark) was founded in 2001 in Hong Kong as a subsidiary of the largest concern for the production of PC components – PC Partner. Focused on the release of products based on cores (graphics processors) ATI (later became part of AMD). Headquartered in Hong Kong, production in China. The largest manufacturer of accelerators in the Radeon series. It also manufactures mini-PCs and other products. …
Subject of research : 3D graphics accelerator (video card) Sapphire Pulse Radeon RX 6600 XT 8 GB 128-bit GDDR6


Card characteristics
| Sapphire Pulse Radeon RX 6600 XT 8GB 128-bit GDDR6 | |
|---|---|
| GPU | Radeon RX 6600 XT (Navi 23) |
| Interface | PCI Express x8 4.0 |
| GPU frequency (ROPs), MHz | 2359(Boost)—2664(Max) |
| Memory frequency (physical (effective)), MHz | 4000 (16000) |
| Memory bus width, bit | 128 |
| GPU Computing Units | 32 |
| Number of operations (ALU) per block | 64 |
| Total number of ALUs | 2048 |
| Texture units (BLF / TLF / ANIS) | 128 |
| ROP units | 64 |
| Number of Ray Tracing blocks | 32 |
| Number of tensor blocks | — |
| Dimensions, mm | 240×120×44 |
| The number of slots in the system unit occupied by the video card | 3 |
| PCB color | black |
| Peak power consumption in 3D, W | 135 |
| Power consumption in 2D mode, W | 20 |
| Power consumption in sleep mode, W | 4 |
| Noise level in 3D (maximum load), dBA | 21,0 |
| Noise level in 2D (video viewing), dBA | 18,0 |
| Noise level in 2D (idle), dBA | 18,0 |
| Video outputs | 1 × HDMI 2.1, 3 × DisplayPort 1.4a |
| Multiprocessor support | No |
| Maximum number of receivers / monitors for simultaneous image display | 4 |
| Power: 8-pin connectors | 1 |
| Power: 6-pin connectors | 0 |
| Maximum Resolution / Frequency, Display Port | 3840 × 2160 @ 120Hz, 7680 × 4320 @ 60Hz |
| Max Resolution / Frequency, HDMI | 3840 × 2160 @ 120Hz, 7680 × 4320 @ 60Hz |
| approximate cost | 58-66 thousand rubles at the time of preparation of the review |
Memory

The card has 8 GB of GDDR6 SDRAM located in 4 16 Gbit chips on the front side of the PCB. Samsung memory chips (GDDR6, K4ZAF325BM-HC16) are designed for a nominal nominal operating frequency of 4000 (16000) MHz.
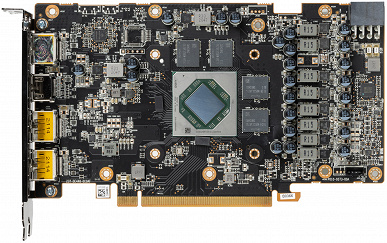
Card features and comparison with AMD Radeon RX 6700 XT
| Sapphire Pulse Radeon RX 6600 XT 8 ГБ | AMD Radeon RX 6700 XT 12 ГБ |
|---|---|
| front view | |
 |  |
| back view | |
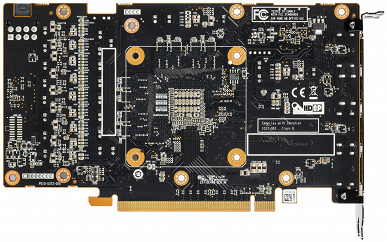 |  |
We traditionally compare this card with its older sister, in this case, the Radeon RX 6700 XT. It is clear that due to different memory buses (128 versus 192 bits), printed circuit boards will be different. Nevertheless, we observe that AMD partners are using the most modern and very high-capacity 16 Gbit memory chips with might and main, which allows you to get 8 GB with just 4 chips on a 128-bit bus. For a 256-bit bus, for example, it would be possible to supply 8 usual 8 Gbps microcircuits. The GPU Radeon RX 6600 XT itself has decreased even more compared to the Radeon RX 6700 XT (we remember what monsters the GPU accelerators of the Radeon RX 6800/6900 line look like because of the huge cache).

In total, the “feed” has 10 phases. The power supply circuit for the core (8 phases) is marked in green, the memory (2 phases) – in red. If we could see an expensive 16-phase PWM controller XDPE132G5D (Infineon) for powering the GPU in flagship boards based on the Radeon RX 6800/6900, then the PWM controller IR35217 (International Rectifier, which is now part of Infineon) is used here.

On boards with Radeon RX 6800/6900, it was also used to control the power phases of memory chips. In this case, a PWM controller NCP81022N (On Semiconductor) is used for this purpose, it controls two phases of the power supply of memory chips.

Both controllers are located on the front side of the board.
In the power converter, traditionally for all modern video cards, DrMOS transistor assemblies are used – in this case, manufactured by On Semiconductor: NCP302155 (up to 50A) for the core power phases and NCP302045 (up to 45A) for the memory power phases.


The card has 1 power connector: 8-pin. As for the video outputs, everything is familiar, they are 4: 3 DP and 1 HDMI.
As for the dimensions of the Sapphire card, it is 240 × 120 × 44 mm, that is, the video card is very compact. At first glance, it seems that it occupies 2 slots in the system unit, but in reality the card still fits into the third slot, albeit only by 4 mm.
The nominal memory frequencies are equal to the reference values. The boost value of the core frequency is also equal to the reference analog, but the maximum achievable frequency is slightly higher than the reference maximum. On average, this has little or no effect on performance. Manual overclocking was tested using the standard AMD utility included in the driver control panel. With the maximum possible frequencies, provided that the core and memory frequencies were maintained, the maximum frequencies of 2975/17600 MHz were obtained. At the same time, the performance gain relative to the reference card was just over 6%.
At low GPU load, the fans stop regardless of the selected mode.
The card’s operation is traditionally controlled using the proprietary Sapphire Trixx utility.
Heating and cooling
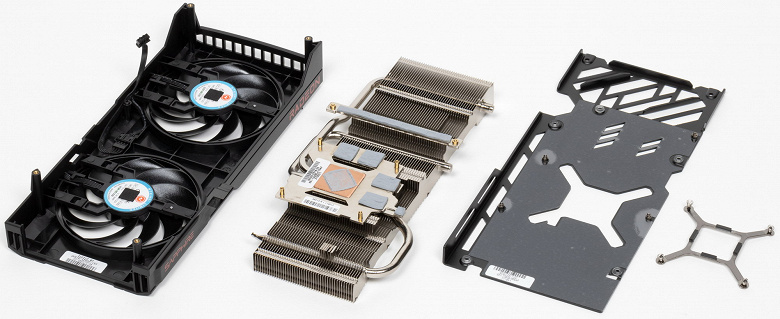
Traditionally, a relatively massive copper nickel-plated radiator is used. The ribs are made in the longitudinal direction, so hot air is blown out through the short ends of the video card (through the mounting bar – outside the system unit and behind the video card). The copper sole is in direct contact with the GPU. The plate surrounding the sole cools the memory chips through a thermal interface, and the heatsink has its own pads for cooling the VRM power converters. The back plate is purely protective (although it is metal, not plastic).

The casing carries two fans (∅90 mm), the ends of the blades of which are connected by a ring (we have already seen similar designs).
We have long been accustomed to the fact that mid-range and top-end video cards stop their fans when idle, when working in 2D, if the GPU temperature drops below about 55-60 degrees, and the CO becomes silent at the same time. This video card works in the same way. Below is a video on this topic.
https://cdn.embedly.com/widgets/media.html?src=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.youtube.com%2Fembed%2Fcz8nvllRQRg%3Ffeature%3Doembed&display_name=YouTube&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.youtube.com%2Fwatch%3Fv%3Dcz8nvllRQRg&image=https%3A%2F%2Fi.ytimg.com%2Fvi%2Fcz8nvllRQRg%2Fhqdefault.jpg&key=0ab080c1948f4b70823c97de31f6895f&type=text%2Fhtml&schema=youtube
Thermal Monitoring with MSI Afterburner:

After a 2-hour run under load, the maximum core temperature did not exceed 75 degrees, which can be called an acceptable result.

We filmed and accelerated the 8-minute warm-up by 50 times:
https://cdn.embedly.com/widgets/media.html?src=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.youtube.com%2Fembed%2FpaAWVQxw1Zg%3Ffeature%3Doembed&display_name=YouTube&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.youtube.com%2Fwatch%3Fv%3DpaAWVQxw1Zg&image=https%3A%2F%2Fi.ytimg.com%2Fvi%2FpaAWVQxw1Zg%2Fhqdefault.jpg&key=0ab080c1948f4b70823c97de31f6895f&type=text%2Fhtml&schema=youtube
The maximum heating was observed in the area of the power converters and the GPU itself.


Note again and again that the Radeon family cards have sensors that indicate heating up to 100 degrees and even higher. These sensors can be called Hot Spot or Junction.

The temperature readings from these sensors can significantly exceed the values we are used to when evaluating the heating of the GPU under load. The fact is that the Hot Spot (Junction) is a sensor for the maximum heating of the graphics core. The temperature according to its readings can reach 110 ° C , and it is safe! The driver will continue to increase the frequency of the GPU blocks until the Hot Spot sensor reads close to this critical value. This achieves the maximum that the GPU crystal can provide in the current environment. Of course, a specific chip instance, as well as the type / type, efficiency and mode of operation of the CO, plus the load on the GPU, will affect the possibility of reaching the maximum heating, and hence the maximum operating frequencies. Therefore, these values may differ for different cards, but, we repeat once again, there is no need to be afraid of such temperatures , GPUs tolerate them quite normally (the silicon heating limit is even higher).
Noise
The noise measurement technique assumes that the room is noise-insulated and damped, and reverberations are reduced. The system unit, in which the noise of video cards is examined, does not have fans and is not a source of mechanical noise. The background level of 18 dBA is the noise level in the room and the noise level of the sound level meter itself. Measurements are taken from a distance of 50 cm from the video card at the level of the cooling system.
Measurement modes:
- Idle mode in 2D: loaded internet browser with iXBT.com website, Microsoft Word window, a number of internet communicators
- 2D mode with movie viewing: SmoothVideo Project (SVP) is used – hardware decoding with insertion of intermediate frames
- 3D mode with maximum load on the accelerator: using FurMark benchmark
The assessment of the noise level gradations is as follows:
- less than 20 dBA: conditionally silent
- 20 to 25 dBA: very quiet
- from 25 to 30 dBA: quiet
- 30 to 35 dBA: clearly audible
- 35 to 40 dBA: loud but bearable
- above 40 dBA: very loud
In idle mode in 2D, the temperature was no higher than 39 ° C, the fans did not work, the noise level was equal to the background noise level – 18 dBA.
When watching a movie with hardware decoding, nothing changed, so the noise remained at the same level.
Under maximum load in 3D, the temperature reached 75 ° C. At the same time, the fans spun up to 1000 rpm, the noise grew up to 21.0 dBA: it’s very quiet. The map is almost inaudible! The video below shows how the noise grows (noise was recorded for a couple of seconds every 30 seconds).
https://cdn.embedly.com/widgets/media.html?src=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.youtube.com%2Fembed%2FMqf_TiUNroc%3Ffeature%3Doembed&display_name=YouTube&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.youtube.com%2Fwatch%3Fv%3DMqf_TiUNroc&image=https%3A%2F%2Fi.ytimg.com%2Fvi%2FMqf_TiUNroc%2Fhqdefault.jpg&key=0ab080c1948f4b70823c97de31f6895f&type=text%2Fhtml&schema=youtube
Backlight
The card has no backlight. So she only knows how to shine with reflected light, if there are sources of it in the body.

Scope of delivery and packaging
The package is the simplest: a few paper instructions and the card itself.



Testing: synthetic tests
Test bench configuration
- Computer based on AMD Ryzen 9 5950X (Socket AM4) processor :
- Platform:
- AMD Ryzen 9 5950X processor (overclocked to 4.6 GHz across all cores);
- ЖСО Cougar Helor 240;
- Asus ROG Crosshair Dark Hero motherboard based on AMD X570 chipset;
- RAM TeamGroup T-Force Xtreem ARGB (TF10D48G4000HC18JBK) 32 GB (4 × 8) DDR4 (4000 MHz);
- Intel 760p NVMe SSD 1 ТБ PCI-E;
- Seagate Barracuda 7200.14 3TB SATA3 hard drive;
- Seasonic Prime 1300 W Platinum (1300 W) power supply;
- Thermaltake Level20 XT case;
- operating system Windows 10 Pro 64-bit; DirectX 12 (v.21H1);
- LG 55Nano956 TV (55 ″ 8K HDR, HDMI 2.1);
- AMD drivers 21.7.1 / 21.8.1;
- Nvidia drivers version 471.41;
- VSync is disabled.
- Platform:
We tested the Radeon RX 6600 XT graphics card at standard frequencies in our synthetic benchmark suite. It continues to change, sometimes new tests are added, and obsolete ones are gradually removed. We would like to add even more examples with calculations, but there are certain difficulties with this. We will try to expand and improve the set of synthetic tests, and if you have clear and well-grounded suggestions, write them in the comments to the article or send them to the authors.
From more or less new benchmarks, we began to use several examples included in the DirectX SDK and the AMD SDK (compiled examples of the use of D3D11 and D3D12), as well as several various tests to measure the performance of ray tracing, software and hardware. As semi-synthetic tests, we also use a set of subtests from the rather popular 3DMark package: Time Spy, Port Royal, DX Raytracing, etc.
Synthetic tests were carried out on the following video cards:
- Radeon RX 6600 XT with standard parameters ( RX 6600 XT )
- Radeon RX 6700 XT with standard parameters ( RX 6700 XT )
- Radeon RX 5700 XT with standard parameters ( RX 5700 XT )
- Standard GeForce RTX 3060 Ti ( RTX 3060 Ti )
- Standard GeForce RTX 3060 ( RTX 3060 )
This time, to analyze the performance of the new AMD video card, we took one solution from the company from the last two generations. We did not touch the full analogue in positioning from the previous line of Radeon RX 5600 XT, instead of it we took the more powerful and interesting RX 5700 XT, but we took the modern model Radeon RX 6700 XT in order to understand how far behind the older model on the more powerful Navi 22 is a fresh budget solution based on the Navi 23 chip of the same RDNA2 architecture.
Due to the difficult market situation, it is still not easy to talk about direct price rivals of the new product from Nvidia, but this is clearly one of a couple of models: GeForce RTX 3060 and RTX 3060 Ti. The first of them is somewhat cheaper than today’s novelty, and the second is a little more expensive, so the RX 6600 XT is favorably located between them, based on the recommended prices (real ones may differ and still differ).
Benchmarks from 3DMark Vantage
Мы традиционно рассматриваем устаревшие синтетические тесты из пакета 3DMark Vantage, ведь в них зачастую можно найти что-то интересное, чего нет в других, более современных тестах. Feature тесты из этого тестового пакета имеют поддержку DirectX 10, они до сих пор более-менее актуальны и при анализе результатов новых видеокарт мы всегда делаем какие-то полезные выводы.
Feature Test 1: Texture Fill
Первый тест измеряет производительность блоков текстурных выборок. Используется заполнение прямоугольника значениями, считываемыми из маленькой текстуры с использованием многочисленных текстурных координат, которые изменяются каждый кадр.

Эффективность работы видеокарт AMD и Nvidia в текстурном тесте компании Futuremark довольно высока, и тест обычно показывает результаты, близкие к соответствующим теоретическим параметрам, хотя иногда они все же получаются несколько заниженными для некоторых GPU. В этом тесте чип Navi 23 в его полном виде выступил очень неплохо, уступив старшей модели RX 6700 XT примерно столько же, насколько оказался быстрее более мощного и дорогого решения предыдущего поколения в виде RX 5700 XT.
Если сравнивать новинку с конкурирующими видеокартами компании Nvidia, то мы снова отмечаем высокую скорость текстурирования у всех новых Radeon, имеющих достаточно большое количество текстурных блоков, что типично для решений AMD. Поэтому они и справляются с такими задачами несколько лучше видеокарт конкурента примерно того же ценового позиционирования. В этот раз условный конкурент в виде RTX 3060 остался далеко позади, и новая видеокарта Radeon даже обошла чуть более дорогую RTX 3060 Ti.
Feature Test 2: Color Fill
Вторая задача — тест скорости заполнения. В нем используется очень простой пиксельный шейдер, не ограничивающий производительность. Интерполированное значение цвета записывается во внеэкранный буфер (render target) с использованием альфа-блендинга. Используется 16-битный внеэкранный буфер формата FP16, наиболее часто используемый в играх, применяющих HDR-рендеринг, поэтому такой тест является вполне современным.

Цифры из второго подтеста 3DMark Vantage обычно показывают производительность блоков ROP, без учета величины пропускной способности видеопамяти, и тест обычно измеряет именно производительность подсистемы ROP. Так получилось и сегодня, ведь RX 6600 XT показала производительность на уровне старшей модели этого же поколения — RX 6700 XT (даже чуть лучше, но это может быть погрешностью), так как обе они имеют по 64 блока ROP и такие результаты неудивительны.
А вот модель из предыдущего поколения RX 5700 XT в этом тесте оказалась сильно быстрее. И все же, противостоять видеокартам компании Nvidia по скорости заполнения сцены хватило и этого, новая RX 6600 XT обогнала и GeForce RTX 3060 Ti, а более дешевая RTX 3060 осталась далеко позади.
Feature Test 3: Parallax Occlusion Mapping
Один из самых интересных feature-тестов, так как подобная техника давно используется в играх. В нем рисуется один четырехугольник (точнее, два треугольника) с применением специальной техники Parallax Occlusion Mapping, имитирующей сложную геометрию. Используются довольно ресурсоемкие операции по трассировке лучей и карта глубины большого разрешения. Также эта поверхность затеняется при помощи тяжелого алгоритма Strauss. Это тест очень сложного и тяжелого для видеочипа пиксельного шейдера, содержащего многочисленные текстурные выборки при трассировке лучей, динамические ветвления и сложные расчеты освещения по Strauss.

Результаты этого теста из пакета 3DMark Vantage зависят не исключительно от скорости математических вычислений, эффективности исполнения ветвлений или скорости текстурных выборок, а от нескольких параметров одновременно. Для достижения высокой скорости в этой задаче важен правильный баланс GPU, а также эффективность выполнения сложных шейдеров. Это довольно полезный тест, так как результаты в нем нередко хорошо коррелируют с тем, что получается в игровых тестах.
Тут важны и математическая и текстурная производительность, и в этой «синтетике» из 3DMark Vantage новая модель видеокарты Radeon RX 6600 XT показала неплохой результат заметно впереди RX 5700 XT из прошлого поколения, относящейся к более высокому ценовому диапазону. Правда, старшая RX 6700 XT существенно обогнала новинку, что и должно было произойти, так как чип Navi 22 имеет большее количество исполнительных блоков ALU и TMU, а также лучшую подсистему памяти и кэширования. Новые графические процессоры AMD в этом тесте показывают хорошие результаты, но RX 6600 XT все же немного уступила более дорогой RTX 3060 Ti, обойдя лишь RTX 3060.
Feature Test 4: GPU Cloth
Четвертый тест интересен тем, что в нем рассчитываются физические взаимодействия (имитация ткани) при помощи GPU. Используется вершинная симуляция, при помощи комбинированной работы вершинного и геометрического шейдеров, с несколькими проходами. Используется stream out для переноса вершин из одного прохода симуляции к другому. Таким образом, тестируется производительность исполнения вершинных и геометрических шейдеров и скорость stream out.

Скорость рендеринга в этом тесте должна зависеть сразу от нескольких параметров, и основными факторами влияния должны являться производительность обработки геометрии и эффективность выполнения геометрических шейдеров. Сильные стороны чипов Nvidia должны были проявиться, но мы постоянно получаем явно некорректные результаты для них в этом тесте, поэтому учитывать результаты видеокарт GeForce просто нет смысла. Сравниваем только Radeon между собой, и получаем еще один необычный результат — Radeon RX 6600 XT оказалась лидером сравнения, опередив даже RX 6700 XT — похоже, больше всего тут важна частота GPU. Неудивительно, что больше всего от новинки отстала RX 5700 XT из предыдущего семейства.
Feature Test 5: GPU Particles
Тест физической симуляции эффектов на базе систем частиц, рассчитываемых при помощи графического процессора. Используется вершинная симуляция, где каждая вершина представляет одиночную частицу. Stream out используется с той же целью, что и в предыдущем тесте. Рассчитывается несколько сотен тысяч частиц, все анимируются отдельно, также рассчитываются их столкновения с картой высот. Частицы отрисовываются при помощи геометрического шейдера, который из каждой точки создает четыре вершины, образующие частицу. Больше всего загружает шейдерные блоки вершинными расчетами, также тестируется stream out.

Во втором геометрическом тесте из 3DMark Vantage мы также видим далекие от теории результаты, хотя они чуть ближе к истине, чем в прошлом подтесте этого же бенчмарка. Видеокарты Nvidia и в этот раз необъяснимо медленны, но хотя бы не так сильно отстают. Но это им не помогает в сравнении даже с Radeon RX 5700 XT из предыдущего поколения, не говоря уже о моделях архитектуры RDNA 2. Интересно, что новинка не смогла обогнать RX 5700 XT, показав результат на ее уровне, но и отстала от RX 6700 XT не так уж сильно.
Feature Test 6: Perlin Noise
Последний feature-тест пакета Vantage является математически-интенсивным тестом GPU, он рассчитывает несколько октав алгоритма Perlin noise в пиксельном шейдере. Каждый цветовой канал использует собственную функцию шума для большей нагрузки на видеочип. Perlin noise — это стандартный алгоритм, часто применяемый в процедурном текстурировании, он использует много математических вычислений.

В этом математическом тесте производительность решений хоть и также не совсем соответствует теории, но она обычно ближе к пиковой производительности видеочипов в предельных задачах. В тесте используются операции с плавающей запятой, но новая архитектура Ampere не раскрывает свои уникальные возможности, так что видеокарты Nvidia могли бы выглядеть более впечатляюще.
Недавно вышедшее бюджетное решение компании AMD на основе архитектуры RDNA 2 в этом тесте уступило показателям GeForce RTX 3060 Ti, но выступило быстрее RTX 3060, так что тут все соответствует рекомендованным ценам. А вот сравнение с другими картами AMD совсем не радужное, ведь Radeon RX 5700 XT оказалась быстрее новинки в этом тесте, да и RX 6700 XT заметно впереди. Впрочем, все это объяснимо с точки зрения теории. Рассмотрим более современные тесты, использующие повышенную нагрузку на GPU.
Direct3D 11 benchmarks
Переходим к Direct3D11-тестам из пакета разработчиков SDK Radeon. Первым на очереди будет тест под названием FluidCS11, в котором моделируется физика жидкостей, для чего рассчитывается поведение множества частиц в двухмерном пространстве. Для симуляции жидкостей в этом примере используется гидродинамика сглаженных частиц. Число частиц в тесте устанавливаем максимально возможное — 64 000 штук.
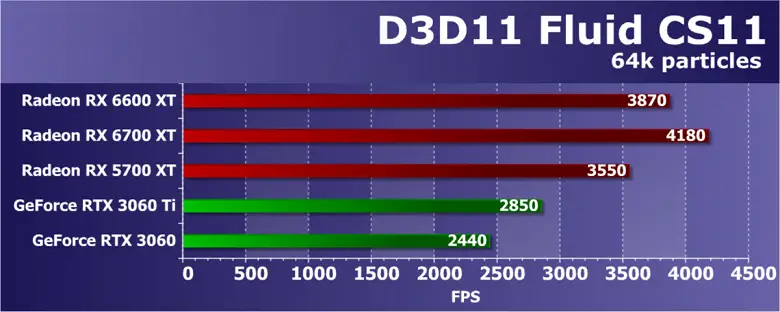
В первом Direct3D11-тесте новая Radeon RX 6600 XT опередила Radeon RX 5700 XT, но по понятным причинам уступила старшей модели RX 6700 XT. Так что тут ничего необычного, хотя разница между ними невеликая. Важнее то, что и GeForce RTX 3060 и RTX 3060 Ti остались позади, и новинка AMD оказалась заметно быстрее представленных решений архитектуры Ampere. Впрочем, судя по крайне высокой частоте кадров, вычисления в этом примере из SDK уже слишком просты для столь мощных видеокарт.
Второй D3D11-тест называется InstancingFX11, в этом примере из SDK используются DrawIndexedInstanced-вызовы для отрисовки множества одинаковых моделей объектов в кадре, а их разнообразие достигается при помощи использования текстурных массивов с различными текстурами для деревьев и травы. Для увеличения нагрузки на GPU мы использовали максимальные настройки: число деревьев и плотность травы.

Производительность рендеринга в этом тесте больше всего зависит от оптимизации драйвера и командного процессора GPU, но не только. С этим всегда было отлично у решений Nvidia, но видеокарты семейства RDNA 2 улучшили позиции конкурирующей компании и местами даже обогнали конкурента. Если рассматривать сегодняшнюю новинку Radeon RX 6600 XT, сравнивая ее с решениями конкурента из семейства Ampere, то результат снова тот же — новый Radeon расположился строго между RTX 3060 и RTX 3060 Ti. Конечно же, RX 6700 XT опередила более бюджетную новинку, а RX 5700 XT из прошлого поколения проиграл всем.
Ну и третий D3D11-пример — VarianceShadows11. В этом тесте из SDK AMD используются теневые карты (shadow maps) с тремя каскадами (уровнями детализации). Динамические каскадные карты теней сейчас широко применяются в играх с растеризацией, поэтому тест довольно любопытный. При тестировании мы использовали настройки по умолчанию.

Производительность в этом примере из SDK зависит как от скорости блоков растеризации, так и от пропускной способности памяти. Новая видеокарта Radeon RX 6600 XT показала результат лишь чуть выше, чем у старенькой Radeon RX 5700 XT, а и вот более мощная RX 6700 XT оказалась позади, что вполне нормально. Сравнение с GeForce чуть более приятно для AMD, ведь новинка куда ближе к RTX 3060 Ti, чем к отстающей RTX 3060. Частота кадров и в этом тесте слишком высока — очередная задача является слишком простой для современных GPU.
Direct3D 12 benchmarks
Переходим к примерам из DirectX SDK компании Microsoft — все они используют последнюю версию графического API — Direct3D12. Первым тестом стал Dynamic Indexing (D3D12DynamicIndexing), использующий новые функции шейдерной модели Shader Model 5.1. В частности — динамическое индексирование и неограниченные массивы (unbounded arrays) для отрисовки одной модели объекта несколько раз, при этом материал объекта выбирается динамически по индексу.
Этот пример активно использует целочисленные операции для индексации, поэтому особенно интересен нам для тестирования графических процессоров семейства Turing и Ampere, но не только. Для увеличения нагрузки на GPU мы модифицировали пример, увеличив число моделей в кадре относительно оригинальных настроек в 100 раз.

Общая производительность рендеринга в этом тесте зависит от видеодрайвера, командного процессора и эффективности работы мультипроцессоров GPU в целочисленных вычислениях. Решения Nvidia отлично справились с такими операциями, а вот все Radeon ранее были в разы хуже любой из GeForce. Но все новые модели семейства RX 6000 показывают одинаковый и странный результат почти на уровне решений конкурента. Вероятно, дело в недостатке программной оптимизации или какой-то ошибки в драйвере. В любом случае, RTX 3060 оказалась далеко позади, а RTX 3060 Ti чуть впереди.
Очередной пример из Direct3D12 SDK — Execute Indirect Sample, он создает большое количество вызовов отрисовки при помощи ExecuteIndirect API, с возможностью модификации параметров отрисовки в вычислительном шейдере. В тесте используется два режима. В первом на GPU выполняется вычислительный шейдер для определения видимых треугольников, после чего вызовы отрисовки видимых треугольников записываются в UAV-буфер, откуда запускаются посредством ExecuteIndirect-команд, таким образом на отрисовку отправляются только видимые треугольники. Второй режим отрисовывает все треугольники подряд без отбрасывания невидимых. Для увеличения нагрузки на GPU число объектов в кадре увеличено с 1024 до 1 048 576 штук.

Очередной странный результат. Да, в этом тесте видеокарты Nvidia доминировали всегда, производительность в нем зависит от драйвера, командного процессора и мультипроцессоров GPU, и наш опыт говорит также о большом влиянии программной оптимизации драйвера на результаты теста. Но очень уж странные цифры получаются, все видеокарты AMD показывают отличающиеся результаты, необъяснимые теоретически. Скорее всего, дело в постоянных оптимизациях драйверов AMD. И все же, Radeon RX 6600 XT не достала своих конкурентов из стана Nvidia в этом тесте.
И последний пример подраздела с поддержкой D3D12 — известный тест nBody Gravity. В этом примере из SDK показана расчетная задача гравитации N-тел (N-body) — симуляция динамической системы частиц, на которую воздействуют такие физические силы, как гравитация. Для увеличения нагрузки на GPU число N-тел в кадре было увеличено с 10 000 до 64 000.

Снова явно некорректная работа большого количества новинок в очередном тесте. Вообще все Radeon показывают идентичные результаты, чего быть явно не должно. Скорее всего, такое положение дел снова можно объяснить недостаточной оптимизацией драйвера. Что касается пары видеокарт GeForce, то младшая RTX 3060 наравне с конкурентами, а RTX 3060 Ti почти вдвое быстрее в этом тесте, что тоже довольно странно. Этот тест — еще один кандидат на выбывание из нашего синтетического набора.
В качестве дополнительного вычислительного теста с поддержкой Direct3D12 мы взяли известный бенчмарк Time Spy из 3DMark. В нем нам интересно не только общее сравнение GPU по мощности, но и разница в производительности с включенной и отключенной возможностью асинхронных вычислений, появившихся в DirectX 12. Для верности мы протестировали видеокарты сразу в двух графических тестах.


Если рассматривать производительность новой модели Radeon RX 6600 XT в этой задаче по сравнению с Radeon RX 5700 XT — более дорогой картой прошлого поколения, то мы видим небольшое превосходство представителя новой архитектуры. Сегодняшняя новинка заметно быстрее более дорогого решения архитектуры RDNA первого поколения. Конечно, RX 6700 XT заметно быстрее, но эта разница вполне в ожидаемых рамках, с учетом разницы в количестве исполнительных блоков, ПСП и объеме кэш-памяти. Сравнение с видеокартами GeForce RTX тоже показало ожидаемый результат, новинка во всех условиях отстает от условного соперника в виде RTX 3060 Ti, но почти на столько же опережает RTX 3060. Пока что наши ожидания в основном оправдались.
Ray tracing tests
Специализированных тестов трассировки лучей со временем выходит все больше. Одним из первых тестов производительности трассировки лучей является бенчмарк Port Royal создателей известных тестов серии 3DMark. Полноценный тест работает на всех графических процессорах с поддержкой DXR API. Мы проверили несколько видеокарт в разрешении 2560×1440 при различных настройках, когда отражения рассчитываются при помощи трассировки лучей (в двух режимах), а также традиционным для растеризации методом.

Бенчмарк показывает сразу несколько новых возможностей применения трассировки лучей через DXR API, в нем используются алгоритмы отрисовки отражений и теней с применением трассировки, но тест в целом не слишком хорошо оптимизирован и довольно сильно загружает в том числе даже мощные GPU. Самые лучшие видеокарты сегодняшнего сравнения с трудом достигли уровня производительности 30-35 FPS, и то лишь в среднем. Но для сравнения производительности разных GPU тест нам подходит.
Первый же тест трассировки в очередной раз наглядно показывает разницу между ее ускорением в версиях AMD и Nvidia. Если на видеокартах GeForce включение среднего уровня трассировки вызывает небольшое падение производительности, то на обеих моделях Radeon оно гораздо больше. Настолько, что новинка сразу проигрывает RTX 3060, а до RTX 3060 Ti ей совсем далеко. Правда, включение высокого уровня трассировки приносит Radeon чуть меньшее падение скорости, чем на GeForce, но это не особенно помогает — трассировка явно лучше дается решениям конкурента.
Позднее вышел еще один подтест 3DMark, направленный на тестирование производительности трассировки лучей — DirectX Raytracing. В отличие от предыдущего, он не гибридный, и не использует растеризацию вовсе, а только трассировку лучей, поэтому гораздо лучше отражает скорость GPU именно по возможностям аппаратного ускорения трассировки. Сцена в бенчмарке используется уже известная нам по другим подтестам 3DMark, и она довольно небольшая — BVH-структура в теории может поместиться в Infinity Cache.

Снова видно, что по скорости аппаратной трассировки лучей решения архитектуры RDNA 2 уступают Ampere, ведь новая Radeon RX 6600 XT показала уровень производительности вдвое ниже, чем RTX 3060! Вторая условно конкурирующая с новинкой модель RTX 3060 Ti еще быстрее, и с ней можно даже и не сравнивать. Налицо разница в реализации аппаратной трассировки в исполнении AMD и Nvidia. Первой пришлось срочно делать реализацию аппаратной трассировки малыми затратами. Возможно, в следующем поколении своих GPU они исправят эту ситуацию.
Рассмотрим полусинтетический бенчмарк, который сделан на игровом движке, соответствующий игровой проект должен выйти в скором времени. Это Boundary — один из китайских игровых проектов с поддержкой RTX. Они выпустили бенчмарк с очень серьезной нагрузкой на GPU, трассировка лучей в нем используется весьма активно — и для сложных отражений с несколькими отскоками луча, и для мягких теней, и для глобального освещения. Так как в тестах участвуют видеокарты AMD, мы не используем технологию DLSS, с ней отрывы GeForce были бы еще больше.
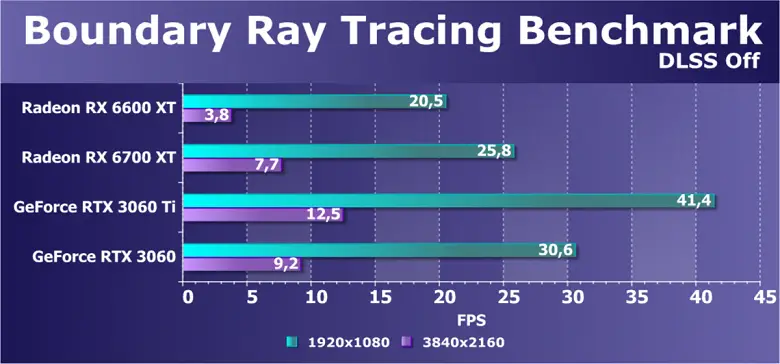
Результат новой модели Radeon RX 6600 XT почти повторяет то, что мы видели в предыдущем тесте, только в 4K все стало еще хуже (но в таком режиме нет смысла). В этом бенчмарке GeForce RTX 3060 заметно быстрее новинки, а ведь у Nvidia есть еще один козырь в виде DLSS 2.0, включение этой технологии в этой игре сделает разгром Radeon еще более печальным. Хотя у AMD теперь есть своя технология улучшения производительности FSR, но ее поддержки в этой игре можно не ждать.
Отметим еще один интересный момент — RX 6600 XT провалилась в 4K-разрешении куда сильнее, чем RX 6700 XT, и это связано, скорее всего, с нехваткой ПСП и недостаточным объемом Infinity Cache. Но в 4K на таких картах не играют, тем более с включенной трассировкой лучей. Хотя и в Full HD дела RX 6600 XT довольно печальны: 20 FPS в среднем, по сравнению с 30 FPS у RTX 3060.
Computational tests
Мы продолжаем поиск бенчмарков, использующих OpenCL для актуальных вычислительных задач, чтобы включить их в состав нашего пакета синтетических тестов. Пока что в этом разделе остается довольно старый и не слишком хорошо оптимизированный тест трассировки лучей (не аппаратной) — LuxMark 3.1. Этот кроссплатформенный тест основан на LuxRender и использует OpenCL.

Новая модель Radeon RX 6600 XT показала не совсем ожидаемый результат в LuxMark, заметно отстав от старшей модели RX 6700 XT в паре подтестов, но оказавшись даже быстрее ее в третьем — самом сложном. Последнее мы не можем объяснить ничем, кроме как некорректной работой теста на Navi 22, ведь у Navi 23 нет преимущества ни по одному из теоретических параметров.
Новая модель также обходит Radeon RX 5700 XT из предыдущего поколения почти вдвое, но тоже не везде — в самом простом тесте новинка уступает. Обе GeForce тут явно быстрее, даже RTX 3060 во всех подтестах смогла опередить новинку AMD, а уж RTX 3060 Ti еще намного быстрее. Математически-интенсивные нагрузки с большим влиянием кэширования явно лучше исполняются на новой архитектуре Ampere, а RDNA двух поколений они не слишком хорошо подходят.
Увы, но еще два теста вычислительной производительности графических процессоров: V-Ray Benchmark и OctaneRender, просто не работают на видеокартах Radeon. Производительность трассировки лучей без применения аппаратного ускорения в профессиональных 3D-приложениях сравнить непросто и придется пока что обойтись без таких тестов.
Но зато мы рассмотрим еще один вид неграфических вычислений на GPU — криптографические вычисления и связанный с ними майнинг криптовалют. Таким тестом будет интересное приложение — hashcat. Это очень быстрый инструмент для «восстановления паролей» (ну, или их взлома, хотя такое наименование разработчики не любят, конечно). Программное обеспечение использует как возможности CPU, так и GPU при помощи OpenCL, а алгоритмов хеширования поддерживаются очень много, среди них хеши Microsoft LM, MD4, MD5, семейство SHA, форматы Unix Crypt, MySQL и Cisco PIX.
Многие алгоритмы можно взломать («восстановить») за короткое время при помощи ускорения подбора на графическом процессоре. Кроме банальной атаки «грубой силой» (brute-force), поддерживаются маски — например, стандартная маска для многих паролей в виде первой заглавной буквы и двух или четырех цифр в конце, обозначающих год. На GPU подобные задачи исполняются очень быстро — заметно быстрее, чем на CPU, и ненадежные пароли взломать становится гораздо проще.

Как это бывает, результаты получились довольно интересными. Radeon RX 6600 XT показала скорость точно на уровне GeForce RTX 3060, да и пара RTX 3060 Ti и RX 6700 XT также весьма близки друг к другу в этом тесте. Такое впечатление, что именно по хешрейту и выставляют рекомендуемые цены производители, и относят современные GPU к ценовым диапазонам, а не по игровым тестам. А может это и не впечатление вовсе. Чтобы окончательно разобраться с вопросом, предлагаем посмотреть результаты в реалистичных тестах майнинга криптовалют, которые приведены ниже — в практической части материала.
Testing: game tests, mining
Testing tool list
All gaming tests used the maximum graphics quality in the settings.
- Hitman III (IO Interactive/IO Interactive)
- Cyberpunk 2077 (Softclub / CD Projekt RED), patch 1.2
- Death Stranding (505 Games/Kojima Productions)
- Assassin’s Creed Valhalla (Ubisoft/Ubisoft)
- Watch Dogs: Legion (Ubisoft/Ubisoft)
- Control (505 Games/Remedy Entertainment)
- Godfall (Gearbox Publishing/Counterplay Games)
- Resident Evil Village (Capcom/Capcom)
- Shadow of the Tomb Raider (Eidos Montreal/Square Enix), HDR включен
- Metro Exodus (4A Games/Deep Silver/Epic Games)
To calculate the hashrate when mining “ether” (Ethereum / ETH / ETC) and “crows” (Ravencoin / RVN), the T-Rex miner (0.21.04) was used, the average indicator for 2 hours was recorded in two modes:
- by default (consumption limit reduced to 70%, GPU frequency reduced by 200 MHz, memory frequency by default, fans set in manual mode by 70%)
- optimization (the consumption limit is reduced to 70%, the GPU frequency is reduced by 200 MHz, the memory frequency is increased by 500-1000 MHz (depending on the card), the fans are set in manual mode by 80%)
To test the GeForce RTX 3060, we used the same “leaked” driver version 470.05, in which the protection against mining is disabled, with other versions of the hashrate driver it drops to 24/26 MH / s.
Test results in 3D games
Standard benchmark results without hardware ray tracing at 1920 × 1200, 2560 × 1440, and 3840 × 2160
| Исследуемая карта | в сравнении с | 1920×1200 | 2560×1440 | 3840×2160 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 3060 | +23,7 | +19,8 | +13,3 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 | +25,3 | +22,1 | +11,5 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 5700 XT | +6,8 | +0,8 | +1,5 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 6700 XT | −3,1 | −18,6 | −21,8 |
| Исследуемая карта | в сравнении с | 1920×1200 | 2560×1440 | 3840×2160 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 3060 | +8,1 | 0,0 | −30,8 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 | +9,8 | 0,0 | −33,3 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 5700 XT | +11,7 | +8,1 | −37,9 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 6700 XT | −19,3 | −28,6 | −56,1 |
| Исследуемая карта | в сравнении с | 1920×1200 | 2560×1440 | 3840×2160 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 3060 | +19,1 | +16,1 | +12,2 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 | +19,1 | +13,5 | +12,2 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 5700 XT | −1,4 | −1,9 | −5,2 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 6700 XT | −11,6 | −17,9 | −21,4 |
Assassin’s Creed Valhalla
| Исследуемая карта | в сравнении с | 1920×1200 | 2560×1440 | 3840×2160 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 3060 | +31,7 | +25,5 | +3,2 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 | +38,6 | +25,5 | +3,2 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 5700 XT | 0,0 | −1,7 | +3,2 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 6700 XT | −17,7 | −20,3 | −28,9 |
| Исследуемая карта | в сравнении с | 1920×1200 | 2560×1440 | 3840×2160 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 3060 | +25,0 | +11,6 | 0,0 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 | +18,6 | +9,1 | −7,1 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 5700 XT | +4,5 | +4,3 | +4,0 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 6700 XT | −12,5 | −23,8 | −29,7 |
| Исследуемая карта | в сравнении с | 1920×1200 | 2560×1440 | 3840×2160 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 3060 | 0,0 | +4,3 | −13,0 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 | +5,6 | +4,3 | −13,0 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 5700 XT | +5,6 | +2,1 | −13,0 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 6700 XT | −20,0 | −26,2 | −35,5 |
| Исследуемая карта | в сравнении с | 1920×1200 | 2560×1440 | 3840×2160 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 3060 | +25,9 | +10,6 | +3,8 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 | +25,9 | +13,0 | +8,0 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 5700 XT | +7,4 | +10,6 | +12,5 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 6700 XT | −35,4 | −37,3 | −41,3 |
| Исследуемая карта | в сравнении с | 1920×1200 | 2560×1440 | 3840×2160 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 3060 | +15,8 | +9,1 | +8,0 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 | +13,9 | +11,6 | +14,9 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 5700 XT | −0,7 | +1,1 | +3,8 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 6700 XT | −26,5 | −28,4 | −23,9 |
Shadow of the Tomb Raider
| Исследуемая карта | в сравнении с | 1920×1200 | 2560×1440 | 3840×2160 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 3060 | +24,7 | +9,4 | +6,7 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 | +41,3 | +25,0 | +14,3 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 5700 XT | +19,1 | +9,4 | −5,9 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 6700 XT | −8,6 | −21,3 | −29,4 |
| Исследуемая карта | в сравнении с | 1920×1200 | 2560×1440 | 3840×2160 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 3060 | +11,7 | +1,6 | 0,0 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 | +10,3 | +5,1 | −2,4 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 5700 XT | +3,6 | −3,1 | +2,5 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 6700 XT | −23,9 | −33,3 | −14,6 |
In general, the Radeon RX 6600 XT was somewhere between the GeForce RTX 3060 and the GeForce RTX 3060 Ti, closer to the first than to the second, and it also outperformed its predecessor of a higher level, the Radeon RX 5700 XT, by about 11%.

Since previously released AMD video cards do not support ray tracing technologies, we are forced to disable both tracing and DLSS for mass testing in order to adequately compare all cards. However, today half of the 28 video cards we regularly test support RT technology, so we conducted tests not only using conventional rasterization methods, but also with RT enabled. Of course, so far only Nvidia GeForce RTX and AMD Radeon RX 6000 series graphics cards are on this list.
Test results with hardware ray tracing enabled at 1920 × 1200, 2560 × 1440, and 3840 × 2160
| Исследуемая карта | в сравнении с | 1920×1200 | 2560×1440 | 3840×2160 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 3060 | −50,0 | −58,3 | −66,7 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 | −48,7 | −58,3 | −68,8 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 Super | −53,5 | −63,0 | −70,6 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 6700 XT | −20,0 | −28,6 | −28,6 |
Watch Dogs: Legion, RT
| Исследуемая карта | в сравнении с | 1920×1200 | 2560×1440 | 3840×2160 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 3060 | −18,8 | −13,0 | −23,1 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 | −13,3 | −9,1 | −23,1 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 Super | −23,5 | −16,7 | −28,6 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 6700 XT | −27,8 | −23,1 | −28,6 |
| Исследуемая карта | в сравнении с | 1920×1200 | 2560×1440 | 3840×2160 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 3060 | −19,5 | −25,9 | −50,0 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 | −17,5 | −16,7 | −41,7 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 Super | −26,7 | −31,0 | −53,3 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 6700 XT | −15,4 | −23,1 | −46,2 |
Resident Evil Village, RT
| Исследуемая карта | в сравнении с | 1920×1200 | 2560×1440 | 3840×2160 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 3060 | −16,9 | −11,5 | −16,7 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 | −12,9 | −9,8 | −14,3 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 Super | −22,9 | −22,0 | −25,0 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 6700 XT | −25,0 | −25,8 | −31,8 |
Shadow of the Tomb Raider, RT
| Исследуемая карта | в сравнении с | 1920×1200 | 2560×1440 | 3840×2160 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 3060 | −17,6 | −16,2 | −20,8 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 | −8,7 | −3,1 | −17,4 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 Super | −34,4 | −22,5 | −26,9 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 6700 XT | −20,8 | −20,5 | −29,6 |
| Исследуемая карта | в сравнении с | 1920×1200 | 2560×1440 | 3840×2160 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 3060 | −9,5 | −10,0 | −31,6 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 | −5,0 | −12,9 | −31,6 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | GeForce RTX 2070 Super | −20,8 | −22,9 | −43,5 |
| Radeon RX 6600 XT | Radeon RX 6700 XT | −26,9 | −27,0 | −23,5 |
In the Radeon RX 6600 XT, we see the same very serious performance drop as in all Radeon RX 6000s, when the RT technology is activated: in games with ray tracing, the Radeon RX 6600 XT sometimes drops even to the level of the GeForce RTX 2060. Alas, this is the Achilles heel of the current generations of Radeon accelerators. Yes, the use of ray tracing in general causes a drop in performance for all cards that support this technology, but the competing GeForce RTX 30, firstly, have more powerful blocks of RT cores, so the drop in speed is not as dramatic as that of the GeForce RTX 20, but secondly, there is support for “smart” DLSS anti-aliasing, which helps to increase the speed, compensating for the drop from turning on RT (and even bringing the accelerator “plus”). The promised analogue of DLSS – AMD FidelityFX Super Resolution – was released, but today in our set of games, unfortunately, it is
IXBT.com Rating
The iXBT.com accelerator rating demonstrates to us the functionality of video cards relative to each other and is presented in two versions:
- IXBT.com rating option without RT included
The rating is compiled for all tests without the use of ray tracing technologies. This rating is normalized for the weakest accelerator – GeForce GTX 1650 Super (that is, the combination of speed and features of the GeForce GTX 1650 Super is taken as 100%). Ratings are carried out for 28 accelerators that we study monthly as part of the Best Video Card of the Month project. In this case, a group of cards for analysis was selected from the general list, which includes the Radeon RX 6600 XT and its competitors.
The rating is given in total for all three resolutions.
| № | Accelerator model | IXBT.com Rating | Utility rating | price, rub. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | RTX 2070 Super 8 ГБ, 1770—1950/14000 | 310 | 48 | 64 000 |
| 15 | Sapphire RX 6600 XT Pulse, 2359—2664/16000 | 300 | 54 | 56 000 |
| 16 | RTX 3060 12 GB 1807-1950 / 15000 | 280 | 46 | 61 000 |
| 17 | RTX 2070 8GB 1710-1850 / 14000 | 280 | 45 | 62 000 |
| 18 | RX 5700 XT 8 GB, 1755—1905 / 14000 | 270 | 36 | 75 000 |
The rating confirms that the Radeon RX 6600 XT has taken an intermediate position between the GeForce RTX 3060 Ti, GeForce RTX 2070 Super and GeForce RTX 3060/2070: closer to the latter. Let us emphasize once again that this is exactly the average! In a particular game, the balance of forces can be significantly different, as indicated by the diagrams with test results (we ask readers not only to read the conclusions, but also delve into the diagrams). It is clear that with higher prices for GeForce RTX cards, the novelty can be very interesting, although it is still wild for us to see a price of more than 50 thousand rubles for a mid-budget video card.
- IXBT.com rating option with RT included
The rating is based on 6 tests using ray tracing technology. Today RT is supported by Nvidia GeForce RTX and AMD Radeon RX 6000 series accelerators. This rating is normalized to GeForce RTX 2060 (that is, the combination of speed and features of the GeForce RTX 2060 is taken as 100%).
The rating is given in total for all three resolutions.
| № | Accelerator model | IXBT.com Rating | Utility rating | price, rub. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | RTX 2070 Super 8 ГБ, 1770—1950/14000 | 150 | 23 | 64 000 |
| 14 | RTX 3060 12 GB 1807-1950 / 15000 | 140 | 23 | 61 000 |
| 16 | RTX 2070 8GB 1710-1850 / 14000 | 130 | 21 | 62 000 |
| 17 | RTX 2060 Super 8 ГБ, 1650—1950/14000 | 130 | 23 | 56 000 |
| 18 | Sapphire RX 6600 XT Pulse, 2359—2664/16000 | 100 | 18 | 56 000 |
| 19 | RTX 2060 6 GB 1680-1920 / 14000 | 100 | 20 | 51 000 |
We will not say anything new here. In ray tracing games, the rivalry between the new Radeon and the GeForce RTX is one level lower: the Radeon RX 6600 XT is weaker than the GeForce RTX 2060 Super. However, it is difficult to compare in price, because the GeForce RTX 20 series cards have disappeared from retail.
Utility rating
The utility rating of the same cards is obtained if the indicators of the previous rating are divided by the prices of the corresponding accelerators. To calculate the utility rating, the retail prices at the end of August 2021 were used .
- Utility rating option without including RT
| № | Accelerator model | Utility rating | IXBT.com Rating | price, rub. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 02 | Sapphire RX 6600 XT Pulse, 2359—2664/16000 | 54 | 300 | 56 000 |
| 07 | RTX 2070 Super 8 ГБ, 1770—1950/14000 | 48 | 310 | 64 000 |
| 11 | RTX 3060 12 GB 1807-1950 / 15000 | 46 | 280 | 61 000 |
| 12 | RTX 2070 8GB 1710-1850 / 14000 | 45 | 280 | 62 000 |
| 20 | RX 5700 XT 8 GB, 1755—1905 / 14000 | 36 | 270 | 75 000 |
Surprising but true. AMD’s new product turned out to be the most useful for today in its group of accelerators (the first place in the overall standings is taken by the GeForce RTX 3070 Ti, but it is from a different price segment). Alas, the price tags of all these mid-range accelerators are much higher than 50 thousand rubles.
- Utility rating option with RT included
| № | Accelerator model | Utility rating | IXBT.com Rating | price, rub. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 06 | RTX 2070 Super 8 ГБ, 1770—1950/14000 | 23 | 150 | 64 000 |
| 07 | RTX 2060 Super 8 ГБ, 1650—1950/14000 | 23 | 130 | 56 000 |
| 08 | RTX 3060 12 GB 1807-1950 / 15000 | 23 | 140 | 61 000 |
| 11 | RTX 2070 8GB 1710-1850 / 14000 | 21 | 130 | 62 000 |
| 13 | RTX 2060 6 GB 1680-1920 / 14000 | 20 | 100 | 51 000 |
| 14 | Sapphire RX 6600 XT Pulse, 2359—2664/16000 | 18 | 100 | 56 000 |
It is clear that the drop in speed when RT is turned on significantly changes the previous conclusions. But it is worth considering the still relatively small percentage of RT games in the total range of PC games.
Test results in mining (mining, hashrate)
Tests have shown that the Radeon RX 6600 XT is not very suitable for mining at its price. Its hashrate is at the level of GeForce RTX 2060 (somewhere worse, somewhere better), and the same Radeon RX 5600 XT is definitely better for these purposes (we are already silent about the Radeon RX 5700 XT). But you can still get 30 MH / s from the card if you wish. Note that Radeon cards do not have any protection against being used for mining, they work as they can physically.

If we start mining ETH with the default settings of the card’s operation parameters, we get about 28 MH / s with a GPU consumption of 104 W (the card generally consumes more). Heating within normal limits.

RVN, as you know, is more demanding on the power consumption of video cards, so the GPU alone already “eats” 134 watts. Heating in general is also slightly higher. In this case, we have 15.2 MH / s. (Different cryptocurrencies have different hash rates, you cannot compare them with each other, you can compare cards only within the framework of the same algorithm.)

Optimizing the settings of video cards for mining in our case does not provide for strong overclocking of video memory, and external cooling of video cards is also required. With a strong underestimation of the core frequency and voltage, a slight increase in the memory frequency and increased cooling, we got 30 MH / s in ETH, while the GPU consumption almost halved. Now that’s a completely different matter. However, the same GeForce GTX 1660 Super still looks better, and you can find it cheaper.

For the kawpow (RVN) algorithm, our optimization gives almost nothing, because a strong decrease in PL leads to a drop in the hash rate (in the case of ethash, it was the decrease in PL that saved a lot, because the hash rate remained the same with much less consumption). As a result, the gain is minimal.
conclusions
In general, AMD Radeon RX 6600 XT demonstrated its belonging to the middle-level accelerators such as GeForce RTX 3060 / Ti, hitting right between them, and showed speed at the level of the previous GeForce RTX 2070/2060 Super, overtaking the Radeon RX 5700 XT (if we are talking about games without ray tracing). With ray tracing, the Radeon RX 6600 XT delivers performance on par with the GeForce RTX 2060 or slightly better. Alas…
In practice, this means that the Radeon RX 6600 XT will allow you to play comfortably in Full HD resolution at maximum graphics settings, in this AMD did not deceive us. However, all this is true if we do not consider ray tracing games (or rather, we do not consider the use of this technology in them). Of course, today there are not so many games with support for ray tracing, but in general, the trend is that the future belongs to games with RT, especially in light of the fact that the new generation consoles also support this technology (albeit in a greatly reduced form, so as the same AMD graphics cores are used there).
As for the trump card in the form of DLSS in the GeForce RTX 30, which significantly increases performance, compensating for the drop in speed from turning on RT, we know that AMD has released its counterpart – FidelityFX Super Resolution. Unfortunately, we cannot yet compare them directly: there is not a single game that supports both DLSS and FSR at the same time. Moreover, in our set of games there is not a single one where FSR would be implemented with real impact. We are waiting for the updates of the games released under the patronage of AMD.

As for the specific video card Sapphire Pulse Radeon RX 6600 XT (8 GB) , it is simply excellent from the point of view of consumer characteristics: the board is quite compact (but still occupies 3 slots in the system unit), practically silent, and the heat generated by the video card is partially blown out for the limits of the system unit.
Traditionally, you should also pay attention to a number of new interesting AMD solutions accompanying the Radeon RX 6000 family, including support for the HDMI 2.1 standard. We also note support for hardware decoding of video data in AV1 format, Smart Access Memory technology, which can provide a small performance increase when new accelerators work together with Ryzen 3000/5000 processors (this also works on the Intel Z490 / 590 platform on those motherboards for which new BIOS versions that include resized BAR), as well as Radeon Anti-Lag latency reduction technology, useful for esports players.
In conclusion, we state once again: the Radeon RX 6600 XT is excellent for playing in Full HD resolution with maximum graphics quality, but when RT is turned on, the new accelerator is able to provide acceptable comfort only with a slight decrease in the quality settings.
In the Original Design nomination, the AMD Radeon RX 6600 XT (8GB) card won:
Testbed : AMD Ryzen 9 5950X CPU courtesy of AMD ,
ROG Crosshair Dark Hero motherboard courtesy of Asus