It looks like something out of a science fiction movie or series, but no, this is real, since a group of researchers from AMD has filed a patent application for a more efficient and reliable quantum computing architecture.
It appears that AMD is investigating a system that aims to use quantum teleportation to increase the reliability of a quantum system, while reducing the number of qubits required for a calculation. The objective is to alleviate scale problems and calculation errors derived from system instability.
There are two major obstacles on the road to quantum development and quantum supremacy, one is scalability and the other is stability. Quantum states are so sensitive that they can become destabilized at the slightest provocation, and the sensitivity of a quantum system tends to increase with the presence of more qubits in a system.
AMD’s patent, titled “Advance Teleportation for Reliable Computing on a Multi-SIMD Quantum Processor,” aims to improve quantum stability, scalability, and performance in new and more efficient ways.
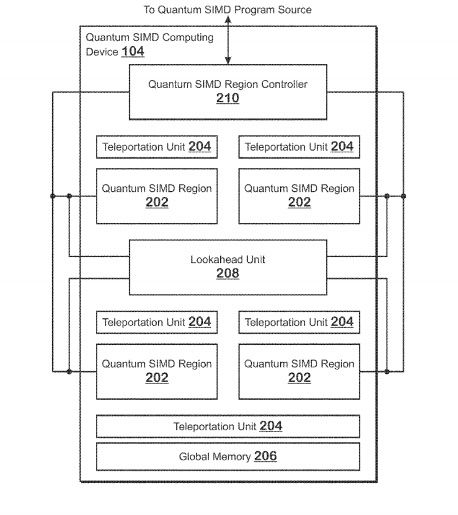
The patent describes a quantum architecture based on quantum processing regions: areas of the chip that contain or may contain qubits, waiting their turn to be used by a process.
AMD’s approach aims to improve existing quantum architectures by actually reducing the number of qubits required to perform complex calculations, through the sci-fi concept of quantum teleportation.
AMD is working on quantum computing, the next great computing career.
AMD’s design aims to teleport qubits across processor regions, allowing workloads that would theoretically require running in order to be processed in an out-of-order philosophy.
As a quick update, executing in order has dependencies between one statement and the next, which means that a workload must be processed sequentially, and subsequent steps depend on the previous step being fully processed and its result known before that the chip can advance with the calculation.
The AMD patent also includes a processor, which would analyze the input workload, it would predict which steps can be tackled in parallel (and which cannot) and properly distribute the workload between qubits, using quantum teleportation.
How this quantum teleportation occurs is not described in the patent. Perhaps we are seeing the beginning of AMD’s “Zen 128” design (this is a joke), or perhaps this will never materialize. But it does show, to an AMD who is working on quantum computing, that it seems to be the next great computing career.















