AMD’s next generation game-oriented graphics card with RDNA 3 architecture is planned for the second half of 2022. The company’s patent reveals that a chiplet-based design for graphics processors is under development, which may be relevant already for RDNA 3. The data circulating around the Navi 31 circuit speaks of both a Multi-Chip Modulessolution (MCM) and 15 360 stream processors.
Specifications are now also reported for Navi 32 and Navi 33, which are relevant for what is assumed to be the Radeon RX 7700 XT and Radeon RX 7600 XT, respectively. The figures are compiled from a number of different delicacies and are not entirely improbable, but should be taken with a pinch of salt. The next generation is still at a relatively early stage, which means that most numbers, even if they are correct, can change before launch.
Specifications for Radeon RX 7700 XT and RX 7600 XT
| Product name | RX 7700 XT | RX 6700 XT | RX 7600 XT | RX 6600 XT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| District name | Navi 32 | Navi 22 | Navi 33 | Navi 23 |
| Processnod | 5 nm/6 nm | 7 nm | 6 nm | 7 nm |
| Circuit type | MCM | Monolithic | Monolithic | Monolithic |
| Kernels | 10 240 | 2 560 | 5 120 | 2 048 |
| Memory bus | 192-bit | 192-bit | 128-bit | 128-bit |
| Infinity Cache | 384 MB | 96 MB | 256 MB | 32 MB |
| TBP | 300 W | 230 W | 200 W | 160 W |
(Names and specifications are speculative and based on rumors.)
According to the information, Navi 32 looks like Navi 31 is based on one chiplet-design with several smaller circuits on a substrate. Navi 32 replaces Navi 22 and quadruples the number of cores, from 2,560 to 10,240. With current pricing, it is difficult to say that graphics cards like the RX 6700 XT belong to an intermediate segment, but the RX 7700 XT seems to be moving even further away from it. Possibly the specification may refer to an RX 7800 XT rather than the RX 7700 XT. Infinity Cache looks up from 96 to 384 MB, but the memory bus remains at 192 bits.
Unlike its two larger siblings, the Navi 33 retains the same monolithic circuit type as before. Compared to Navi 22, this is a little more than twice as many cores, 5,120 instead of 2,048. The RX 7600 XT is also the same 128-bit memory bus as its predecessor, the RX 6600 XT. However, the unchanged memory bus is offset by an eightfold increase in Infinity Cache, which goes from 32 MB to 256 MB.
If the figures are correct, it is a real step up in performance for all products, at least on paper. Just as with the Navi 31, the same width of the memory bus remains as the current generation graphics card has, which could be somewhat narrow. It remains to be seen how well the properly increased amount of Infinity Cache will compensate for that. It should be noted, however, that no specifications have been confirmed by AMD at present and thus may change a lot during the remaining year.
RX 7700 XT Faster Than The 6900 Xt For 500 Dollars
RDNA 3 could revolutionize the mid-range: Possible specifications of the Radeon RX 7700 XT and RX 7600 XT
The RDNA 3 architecture will give life to the Radeon 7900 XT RX, RX Radeon 7800 XT and Radeon RX 7800, and will also be present in the Radeon 7700 XT and Radeon RX 7600 RX XT. According to the latest information that I have been able to read, AMD will make the leap to an MCM design, but with nuances , since it will maintain, in theory, a monolithic core design in the Radeon RX 7600 XT and lower.
I know what you are thinking, why would AMD do such a thing? Well, very simple, to maximize the value of an MCM design by limiting it only to those graphics solutions with such a high shader count that, in short, it is not economically viable under a monolithic core design. Our more advanced readers will already know what I mean, when you transfer the design of a chip to the wafer, it has certain chances of success that depend, among other factors, on:
- How advanced, and mature, is the process used.
- The complexity of the chip.
- The minimum number of functional elements that each chip must have.
This means that moving a chip with 15,360 shaders to the wafer will be much more complex, and expensive , than bringing a chip with 7,680 shaders to the wafer. In the first case, you are more likely to get a high number of non-functional chips, that is, of GPUs that do not come out with all those shaders running smoothly. That would, in theory, be the shader count of the Radeon RX 7900 XT .
Under a monolithic core design, we could only fall back on that chip option with 15,360 shaders, and it would be very difficult to achieve a high success rate on the wafer. In contrast, with an MCM design, we could combine two 7,680 shader chips to create a 15,360 shader GPU , keeping a lower cost on the wafer due to the greater simplicity of that chip, which will translate into more functional units per wafer.
In graphics cards with a lower shader count, such as the mid-range and low-end, the MCM model would not have as much weight, since the chips needed to manufacture them would be perfectly viable, both economically and technically, under a monolithic core design. . This helps us understand why the Radeon RX 7700 XT would have an MCM design, while the Radeon RX 7600 XT will retain a monolithic core GPU.

Navi 31 GPU Concept Diagram
Possible specifications of the Radeon RX 7700 XT and Radeon RX 7600 XT
Now that we have a clear distinction between MCM and monolithic core design, it is the perfect time to review the possible specifications of the Radeon RX 7700 XT and Radeon RX 7600 XT from AMD. The first will be a mid-range graphics card based on the Navi 32 graphics core , and will use an MCM architecture, while the second will be a mid-range graphics card based on the Navi 33 chip , and will maintain a monolithic core architecture. .
Both will be manufactured in the 5nm process, although the possibility that AMD will use the 6nm process to free up TSMC a bit is not ruled out. The Radeon RX 7700 XT will feature:
- MCM architecture at 5 nm / 6 nm.
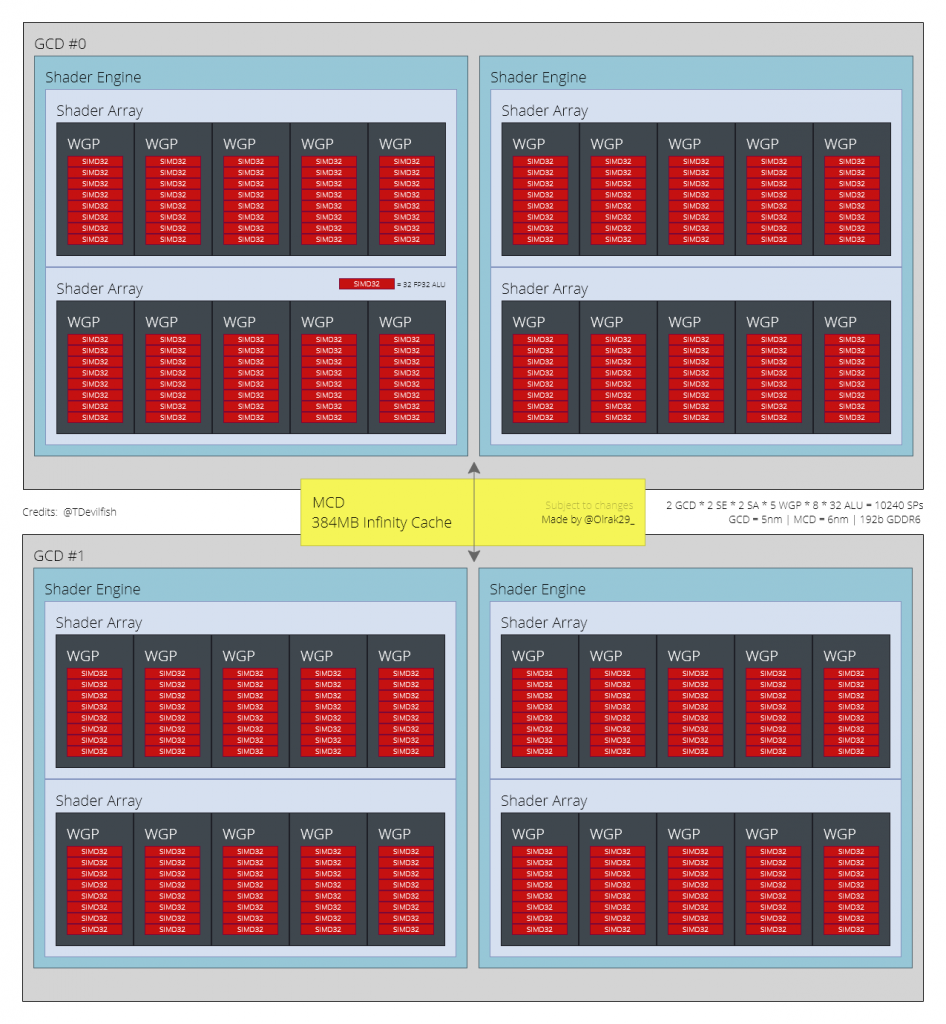
- Two interconnected GPUs, each chip will have 5,120 shaders, which leaves us 10,240 shaders in total.
- 160 CUs (computing units, 80 for each chip).
- 160 ray tracing acceleration units, if AMD keeps the base we have seen in RDNA 2.
- 192-bit bus.
- 384 MB infinite cache.
- GDDR6 memory (quantity and speed not specified).
- TBP (Total Board Consumption) of about 300 watts
Navi 32 GPU Diagram
For its part, the Radeon RX 7600 XT would have a much more modest configuration, although if the specifications that we are going to see are met, there is no doubt that it would be very powerful , even for a mid-range model. These are its keys:
- Monolithic core architecture in 5 nm / 6 nm.
- GPU con 5.120 shaders.
- 80 CUs (computer units).
- 80 units of ray tracing acceleration, if AMD keeps the base that we have seen in RDNA 2.
- 128-bit bus.
- 384 MB infinite cache.
- GDDR6 memory (quantity and speed not specified).
- TBP (Total Board Consumption) of about 200 watts.
Although some rumors are beginning to say that the first graphics cards based on the RDNA 3 architecture will arrive later this year, I think it clearly does not make any sense. This is a date that is practically around the corner, and AMD just introduced the Radeon RX 6600 XT .
Ignore these information, it is most likely that the first graphics cards based on RDNA 3 will arrive from the second half of 2022 , and that the Radeon RX 7700 XT and RX 7600 XT will debut between the end of that year and the beginning of the next.
















