/ data, / recovery, / system … These are all memory partitions on your Android
In this article we will talk about Android Partitions: what they are and what they are for. If you’ve ever ventured into the world of root, to change the operating system or other advanced procedures of the Android universe, you have surely had to deal with terms like / data, / system , / recovery, ecc. These strange names refer to the different partitions found in the memory of your Android smartphone.
The goal of these partitions is that all files stored in your terminal are organized correctly according to their role. Knowing them well will help you better understand how your device works “inside”.
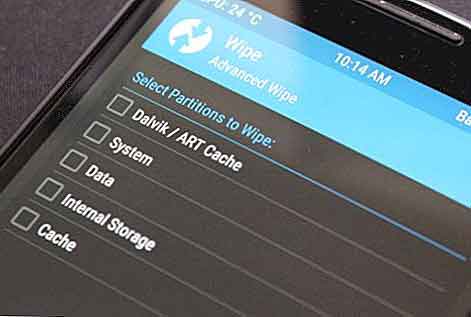
The main partitions, which you will find on all smartphones, are / boot, / system, / recovery, / data, / cache and / misc. They may seem like a lot, but you have to think of them as the drawers where you keep your clothes.
If all the clothes were kept in the same drawer, it would be impossible to know where the underwear, shirts and pants are. It’s easier if each drawer contains one type of garment, right? Well, exactly the same thing happens with system files and now you will know why.
Explanations about Android partitions: boot, system, recovery, data, cache and misc
/boot
The partition / boot is, in a nutshell, what ensures that the phone “starts up” . In it is the kernel (which would be the brain of the operating system) and the ramdisk (a small virtual memory that is used to perform some startup and configuration processes). If this partition isn’t there, it’s like removing the ignition mechanism from a car: it won’t start.
/ system
As you have already guessed, / system contains all operating system files, namely: the visual interface of Android, system apps and bloatware. Basically, you could say that it contains everything you see on your mobile when you first turn it on. If you delete it, which you can’t easily do unless you have a custom recovery installed, it’s as if delete the operating system from the terminal.
/ recovery
All operating systems have a recovery partition which is used for “emergencies”. Simply put, the / recovery partition is like one sort of alternative / boot, which contains a console with maintenance commands: clear memory, restore factory settings, upload files via ADB… The “recovery”, as the command console is called, can be changed into a modified / customized one to expand its functionality. These are known as “Custom Recovery”, and the most famous are ClockworkMod or TWRP.
/data
This partition is explained quickly. / data contains all user data, i.e. the apps you have installed, the files you have downloaded, your contacts, messages, settings, etc. It is what people know as “internal memory”. Eliminating it means losing everything you have saved inside it. When you reset your mobile to factory settings, what you are actually doing is resetting this partition.
/ cache
The already famous cache, right? In simple terms, memory or partition / cache stores the data and files that both you and the Android operating system access often. If you spend the day on Instagram, for example, the cache will be filled with profile photos, photos and videos you’ve seen, etc. So that? So you don’t have to download them again and save time and resources. Eliminating it is useless – in the long run – because sooner or later it will fill up again as you use your mobile.
/ misc
It is the most boring partition and you need to take care of the most. / misc saves the settings related to the operator and some aspects of the hardware of your mobile phone. If there are corrupt files in / misc, it is possible that some of your terminal functions stop working. For example, a problem in / misc could leave you with no signal / data or no USB connection.
These are the partitions that you will always find on all Android smartphones, albeit there may be two more, depending on whether or not you have microSD support. These are as follows:
- / sdcard: equivalent to / data but on the microSD card.
- / sd-ext: let’s say it is an expansion of / data in / sdcard. It is used, or used, a lot in custom ROMs to install apps on external storage. In fact, deleting / sd-ext is the same as deleting / data.
As you can see, something that can look messy like your device’s memory partitions, this is no longer the case when you know what function each one performs. Now that you know what / boot, / system, / recovery, / data, / cache and / misc are and what they are for, you also know that we must respect them.