How to test the open source alternative to Firefox LibreWolf on Linux
Firefox is a great browser. Firefox developers do a lot for the web, and without it, we’d all be stuck using Chromium on Linux. However, as time has passed, Firefox has gotten worse with its practices. If you’re tired of Mozilla’s business practices and experiments, there’s LibreWolf.
LibreWolf is a fork of Firefox proper. It is open source and works on Mac OS, Linux, and Windows. Best of all, it removes all the shady stuff Mozilla has been doing. Here’s how you can test LibreWolf on Linux.
Installing LibreWolf on Linux
LibreWolf is an excellent project and offers users the option of getting a more open version of Firefox on their Linux computers. However, the application is not installed by default on any conventional Linux operating system.
Since the application is not pre-installed, we will have to go over how to install it on Linux. LibreWolf is officially compatible with Ubuntu, Debian, Arch Linux, Fedora, OpenSUSE, and Flatpak. Open a terminal window on the Linux desktop by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T on the keyboard to start the installation process.
Ubuntu
The LibreWolf team includes an AppImage package on their website that you can use to install the LibreWolf application on your Ubuntu (or Ubuntu-derived) PC. To get your hands on the latest version of AppImage, use the following wget download command below.
wget https://gitlab.com/librewolf-community/browser/appimage/-/jobs/1580351789/artifacts/raw/LibreWolf-92.0-1.x86_64.AppImage
After downloading the AppImage package to your computer, update the file permissions with the chmod command.
sudo chmod +x LibreWolf-92.0-1.x86_64.AppImage
You can then start LibreWolf by running the following command or by double-clicking the LibreWolf AppImage file in Ubuntu’s file manager.
./LibreWolf-92.0-1.x86_64.AppImage
Debian
Debian users can install LibreWolf on their systems through the Debian Unstable software repository. Follow these instructions only if you are using Debian Unstable. If you are on Debian stable or testing, follow Flatpak’s instructions.
echo 'deb http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/home:/bgstack15:/aftermozilla/Debian_Unstable/ /' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/home:bgstack15:aftermozilla.list curl -fsSL https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/home:bgstack15:aftermozilla/Debian_Unstable/Release.key | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/home_bgstack15_aftermozilla.gpg > /dev/null sudo apt update sudo apt install librewolf
Arch Linux
Arch Linux users can get the latest version of LibreWolf working on their system by installing it through the AUR. In order for it to work in AUR, you will first need to configure the Trizen AUR helper tool using the commands below.
sudo pacman -S git base-devel git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/trizen.git cd trizen/ makepkg -sri
With Trizen running, you can get the LibreWolf app up and running.
trizen -S librewolf-bin
Fedora / OpenSUSE
If you want to use LibreWolf on Fedora or OpenSUSE Linux, you will have to download the latest AppImage file on your computer and run it. To get the file, use the wget command below.
wget https://gitlab.com/librewolf-community/browser/appimage/-/jobs/1580351789/artifacts/raw/LibreWolf-92.0-1.x86_64.AppImage
Update the file permissions using the chmod command.
sudo chmod +x LibreWolf-92.0-1.x86_64.AppImage
After updating the permissions, run the following command to start the application. Or run it through Linux file manager.
./LibreWolf-92.0-1.x86_64.AppImage
Flatpak
To use LibreWolf on Linux as Flatpak, you will first need to configure the Flatpak runtime. You can do it by following our guide here. After configuring the runtime, run the following two commands to get the application working on your system.
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo flatpak install flathub io.gitlab.librewolf-community
Browse with LibreWolf on Linux
To navigate LibreWolf on your Linux PC, start by launching the application on your computer. Once the app is open, follow the step-by-step instructions below.
Paso 1: Look for the “Search with DuckDuckGo or enter address” text bar within LibreWolf. Then click on it with the mouse.
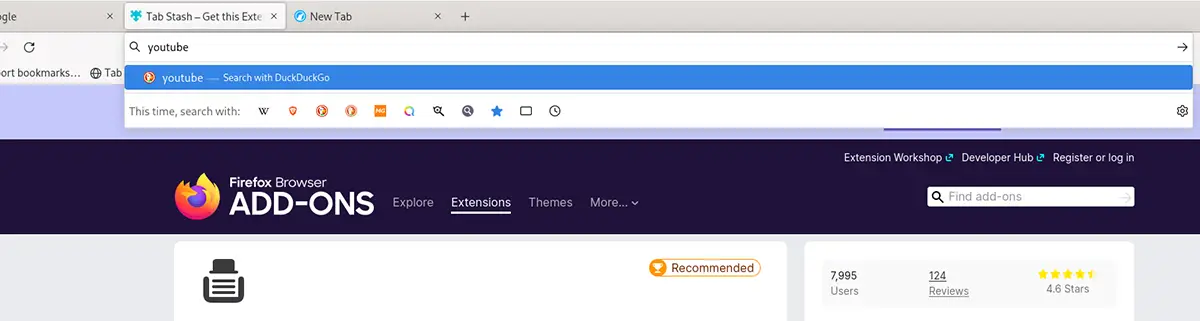
Paso 2: Start typing what you want to see. For example, if you want to search for something, start typing your query in the text box. Then press the Get into on the keyboard to view the search results. Or, if you want to go to a website, type a URL in the URL bar and press Get into.
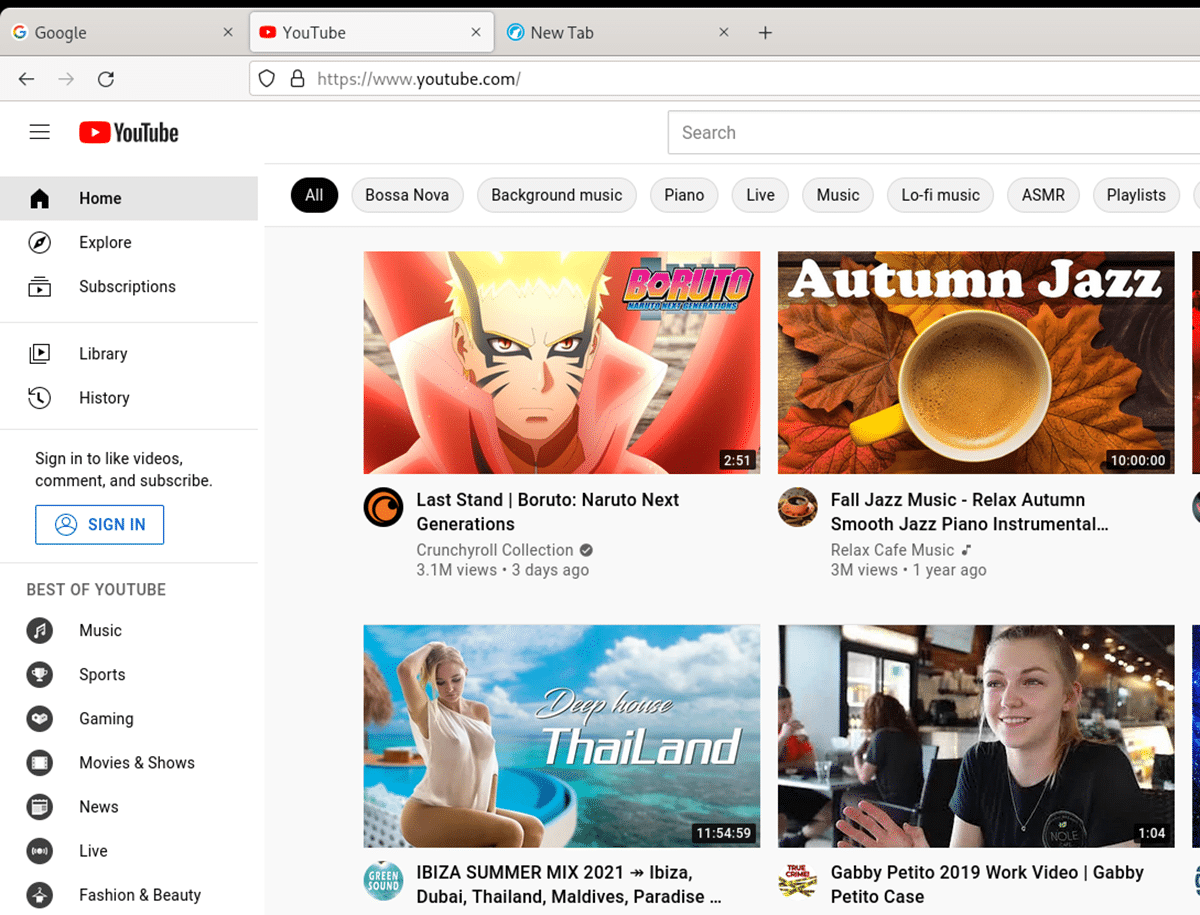
Bookmarks
Do you need to bookmark your favorite website within LibreWolf? Do the following. First, open a web page within the LibreWolf application. When the website is open, locate the star icon and click on it with your mouse.
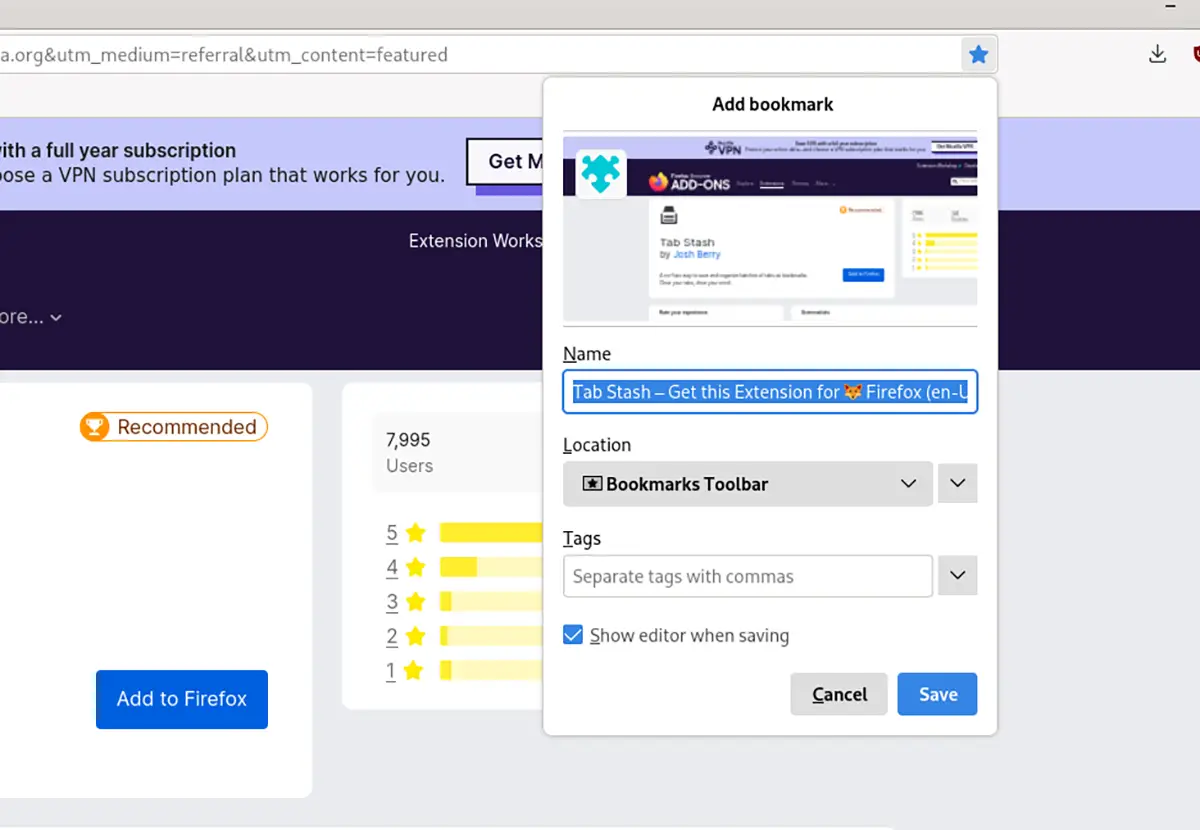
Once you’ve selected the star icon, you’ll add a bookmark. To view your bookmarks in LibreWolf, press Ctrl + B on the keyboard.
Accessories
LibreWolf is compatible with Mozilla Firefox add-ons. If you want to install a plugin, do the following. First, head over to the Firefox plugin website. Once on the website, use the search tool to locate a plug-in you want to install.
When you have found the add-on, click the “add to Firefox” button. Then click on the message to install the plugin on LibreFox. Repeat this process to install as many plugins as you need.














